TPO - American billionaire Elon Musk wants his rocket to revolutionize space travel. The Starship rocket of billionaire Elon Musk's SpaceX company is currently the largest and most powerful rocket ever built.
Starship is a super heavy-lift rocket manufactured by SpaceX. The rocket is made up of a Super Heavy rocket stage and a Starship spacecraft, aiming to achieve high payload and low operating costs. Both rocket stages are capable of landing and delivering 100 tons to low Earth orbit. After refueling with liquid oxygen and liquid methane in orbit, the spacecraft will be able to fly to the Moon or Mars, as well as other locations in the Solar System.
How big and powerful is Starship?
Starship is a 50m tall spacecraft with a dry mass of less than 100 tonnes, the upper part of the Starship rocket of the same name. The Starship spacecraft can hold about 1,200 tonnes of liquid oxygen or liquid methane fuel, with each type of fuel being placed in a primary and secondary tank respectively.
In addition to the main fuel tank, the secondary fuel tank is used to fuel the spacecraft's landing gear. After being refueled by Starship spacecraft, the spacecraft's range is extended to the Moon, Mars, and many other locations in the Solar System. At the rear of the spacecraft are six Raptor engines, including three Raptor engines dedicated to running in the atmosphere and three Raptor Vacuum engines dedicated to running in space.
The Starship spacecraft has hexagonal tiles that prevent plasma generated when entering the atmosphere from damaging the spacecraft, allowing it to withstand temperatures of up to 1400°C. The payload volume of the Starship is around 1000m3, much larger than any other spacecraft.
The 33 engines at the bottom of the Super Heavy are capable of generating about 74 meganewtons of thrust, nearly 700 times more powerful than the thrust an Airbus A320neo passenger jet can generate.
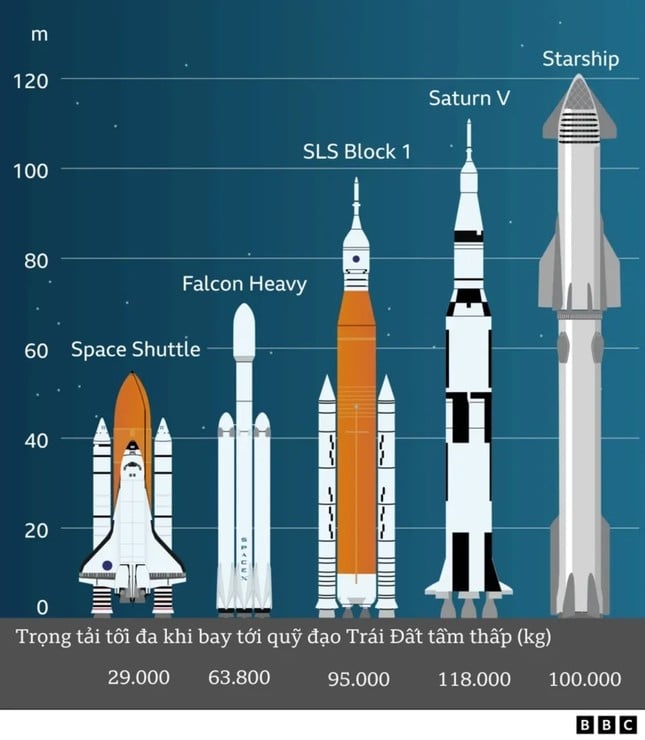
The Starship rocket is now 120m longer, an increase of 1m compared to its length during the second test launch in June 2023. The extra length is due to the Super Heavy being 1m longer.
The Starship rocket also has twice the thrust of the Saturn V rocket, which first took humans to the moon. According to SpaceX, this thrust can lift a payload of at least 150 tons from the launch pad to low Earth orbit.
Both the Starship and Super Heavy rockets are fueled by a mixture of ultra-cold liquid methane and liquid oxygen called methalox.
Currently, the Starship rocket is scheduled to launch from SpaceX Starbase, Kennedy Space Center, and the company’s two offshore launch pads. After firing its 33 Raptor engines, the Super Heavy stage separates from the Starship in mid-air. The rocket stage then flies through the atmosphere and lands on a pair of steel beams on the launch tower. Meanwhile, the Starship fires its three Raptor Vacuum engines and puts itself into orbit. At the end of the mission, the spacecraft enters the atmosphere and is protected by a heat shield. The spacecraft then glides back to the landing site using its two flaps, and fires its three Raptor engines for a vertical landing.
 |
Missile after many upgrades and adjustments. |
SpaceX first proposed a heavy-lift rocket in 2005. The rocket’s design and name changed frequently between then and 2019. In July 2019, Starhopper took off and landed at an altitude of 150 meters, becoming the first rocket to use the Raptor engine. In May 2021, Starship, codenamed SN15, flew to an altitude of 10 kilometers, entered freefall, and successfully landed after four failed attempts.
How does Starship land?
Those watching nearby will hear a thunderous boom as Super Heavy slows down from supersonic speed.
In the latest test launch, SpaceX caught the Super Heavy rocket on its launch turret. Since there are no launch turrets on Mars or the Moon to do this, the Starship rocket must be able to land on its own using its landing gear. To do this, Starship will gradually rotate to a horizontal position as it descends, in what Musk calls a “belly flip.”
This increases Starship’s drag surface and helps it slow down. Once close enough to the surface, Starship will slow down enough to fire its engines to return to vertical. Starship will then use its own rockets to right itself and land on a hard surface using its landing gear.
Starship has done all of the above in previous test launches—except landing on a hard surface. So far, it has only landed in the ocean.
SpaceX tried something it had never done before. After separating, the lower part of the booster slowed down and slowly descended toward the launch pad while two giant mechanical arms grabbed it—a move known as “grabbing.”
After several simulated landings at sea, on the fifth test launch, the landing of the lower part of Starship, the Super Heavy booster, was successful.
One of the purposes of a test launch is to clarify any remaining problems. Even a single mistake could cause the entire internal structure of the rocket to melt due to the amount of gas released by the engine.
Starship has ambitions to fly to the Moon and Mars
Starship has never had a crew, but billionaire Elon Musk and his company have ambitious designs, with the aim of sending humans to Mars one day.
In the short term, the Starship will launch satellites, then serve space tourists and land astronauts on the Moon as part of the Artemis program. In the more distant future, the rocket is expected to make the company’s Mars settlement ambitions a reality and conduct intercontinental flights.
There have been four previous test launches of the Starship rocket. The first time the rocket exploded prematurely, before the booster had time to separate. SpaceX accelerated the development process by testing the rocket even though it knew the system was not perfect, so it could learn from the mistakes.
Indeed, SpaceX has made progress with each test launch — first with a failure-free launch, then with a successful reentry, where both the Starship and Super Heavy rockets descended in a controlled manner and hovered, respectively, over the Indian Ocean and the Gulf of Mexico, before splashing down in the ocean.
What else is Starship used for?
In the near future, the Starship rocket could be used for a few different purposes.
So far, billionaire Elon Musk has used his rockets, like the Falcon 9 series, to launch Starlink commercial satellites.
These satellites have a short lifespan of about five years, and SpaceX needs to continuously launch satellites just to keep the same number in space.
NASA wants to use Starship as part of its Artemis program, which aims to sustain a human presence on the Moon over the long term. NASA plans to use Starship for a lunar mission in 2026.
In the more distant future, Elon Musk wants the Starship rocket to be capable of making long flights to Mars and back – each way taking about nine months.
The idea is to launch the Starship rocket into low Earth orbit and leave it there. It would then be fueled by a SpaceX “refueling ship” and continue on its journey to Mars.
One could also imagine using the Starship rocket to launch a space telescope. To quickly launch thousands of satellites into space, or a larger space telescope, would require a large rocket.
Starship is also designed to carry the heavy payloads needed to build space stations, and eventually, possibly, infrastructure to support human habitation on the Moon.
The Starship spacecraft could carry passengers to the Moon, Mars, and other destinations in the Solar System. It could also conduct intercontinental flights. A single ship could carry up to 100 passengers, with “private sleeping quarters, common areas, storage, radiation shelters, and glass rooms.” The life support systems on board would be “sealed,” meaning the materials inside would be reused and recycled continuously.
The Starship fuel tanker spacecraft will be used to extend the range of other spacecraft. According to Elon Musk, to send a Starship to the Moon, we need to launch up to seven fuel tankers. This idea was presented by Elon Musk in September 2019, by attaching the tails of two spacecraft to each other. Then, both spacecraft accelerate slightly towards the fuel tanker with auxiliary engines, pushing fuel into each other. In October 2020, NASA awarded SpaceX $ 53.2 million to test transferring 10 tons of fuel between two Starships in space.
Starship HLS is a variant of the Starship spacecraft intended to land on the Moon as part of the Artemis program, the successor to the Apollo program. At the top of the Starship HLS are windows and airlocks, along with elevators and a steering propulsion system for landing on the Moon. The most important feature of the spacecraft is its huge payload when flying round-trip between Earth and the Moon. During an Artemis program flight, the Starship HLS spacecraft will fly ahead of the crew for up to a hundred days, and then the spacecraft will transfer fuel to the Starship HLS.
The 122-meter-tall Starship rocket was successfully launched by SpaceX in its fifth test from Starbase, Texas on October 13 (around 8:25 p.m. Hanoi time). In this test flight, the Starship/Super Heavy rocket combination system created a miracle when it successfully performed the "grab" mechanism on its first try. After successfully taking off from the Mechazilla launch tower, the Starship landed in the Indian Ocean while the Super Heavy rocket returned, landed exactly near the launch tower and was held tightly by the tower's "chopstick" robotic arm.
According to BBC, Space.com
Source: https://tienphong.vn/ten-lua-sieu-khung-cua-ty-phu-my-co-the-thay-doi-ca-nganh-vu-tru-post1682682.tpo

































































































Comment (0)