Generative AI is transforming education
AI is having a profound impact on education by personalizing learning experiences, supporting teachers, expanding access to knowledge, and enhancing teaching methods.
Areas where AI "covers" include text generation (ChatGPT, Gemini, Claude), image generation (DALL·E, MidJourney, Stable Diffusion), video generation (Runway Gen-2, Sora), audio and voice generation (ElevenLabs, Murf.ai), programming code generation (GitHub Copilot, Code Llama), and 3D data generation (Nvidia GET3D, DreamFusion).
 |
AI applications have potential but also pose challenges regarding the risk of technology dependence. |
This technology with artificial intelligence is developing rapidly, bringing many applications in education, content creation, programming and design, helping to improve work efficiency and creativity in many fields.
However, the application of AI also poses the challenge of the risk of dependence on technology, "eroding" the thinking and, further, the thinking of learners.
Speaking with Associate Professor Agnis Stibe ( School of Business, RMIT University Vietnam), AI tools are often appreciated for providing personalized learning experiences and instant access to information.
However, AI also comes with a big challenge - easy access to everything can make learners over-rely on AI when it comes to problem solving or brainstorming, leading to stifling creativity and critical thinking.
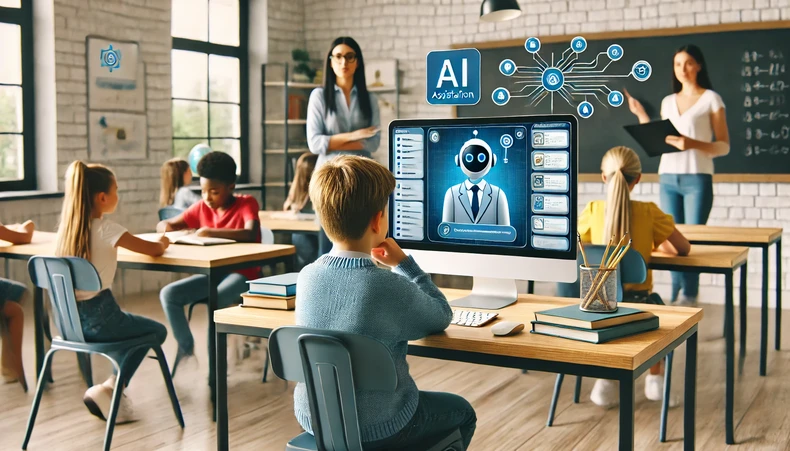 |
Image generated by AI. |
“Developing critical thinking skills is a fundamental goal of education. While enabling the exploitation of the benefits of generative AI, educators must ensure that the intellectual development of learners is not affected,” Associate Professor Agnis Stibe asserted.
Dr Anushka Siriwardana, a lecturer in Digital Marketing at RMIT University, also warned that overuse of AI could lead to a state of "understanding" in learners.
They are used to getting instant answers but lack the motivation to dig into complex issues or develop arguments based on their own thinking.
How can AI support, not "replace" critical thinking?
An important factor in regulating how learners interact with AI technology is age and education level.
Associate Professor Stibe said that older and more educated learners can use AI to enhance their understanding and conduct deeper analysis, but younger learners may rely solely on AI to get quick answers, which can hinder their own critical thinking.
 |
In Vietnam, highly educated learners can effectively integrate AI into their learning process because they have the ability to approach these tools with critical thinking. |
Therefore, educational environments, including Vietnam, need to consider these impacts and make adjustments in the process of using and integrating AI. It is also necessary to affirm that implementing educational strategies with the core of promoting critical thinking appropriate for different age groups and educational levels is essential.
“ By promoting a learning culture that values questioning and encourages learners to critically reflect on AI-generated information, educators can better equip learners to use technology consciously, thereby enhancing their critical thinking abilities in AI-supported learning environments, ” said Dr Siriwardana.
One way to foster critical thinking in learners is to design exercises that require them to develop effective questioning skills using the GenAI tool.
One practical way to foster critical thinking in students, Associate Professor Stibe suggests, is to design exercises that require them to develop effective questioning skills (also known as “prompts”) using the GenAI tool. The ultimate goal is to help students ask fewer prompts per problem while still receiving relevant and creative information.
For example, in a Digital Marketing course, students might be tasked with researching the latest AI-based marketing innovations. They might start by asking the AI a general question like, “What are the latest trends in AI-based marketing?”
 |
Critical thinking is a characteristic of the human brain, so cultivating it in parallel with using supporting applications is something that needs to be taken into consideration. |
Then, instead of constantly asking generic questions, students can refine their inquiry to be more specific, such as: “How are AI tools being used to personalize customer experiences in a digital marketing environment?”.
Through these forms of thinking, students not only learn how to interact more effectively with AI, but also develop the ability to analyze and prioritize information, thereby improving critical thinking skills.
In short, although AI can provide answers, in order to not get "lost" in that information, users need to go from general to specific, keeping the level of thinking at a deep level - demonstrated by asking specific, multi-faceted questions. At the same time, continuously check and criticize the authenticity of the information.


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attends conference on ensuring security and order in the Northwest and surrounding areas](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/933ce5c8b72e4663bd6c6cd8be908f23)
![[Photo] Editor-in-Chief of Nhan Dan Newspaper Le Quoc Minh receives the delegation of Nhan Dan Daily](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/a9ac668e1a3744bca692bde02494f808)
![[Photo] The flavors of Southern Vietnamese traditional cakes](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/b220c9f405b945d798738ea0a94b29b8)
![[Photo] Overcoming the sun to remove temporary and dilapidated houses for poor households](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/824ba71165cc4f8fb6a3903ca0323e5d)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh dialogues with Vietnamese youth](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/7fd8b4735134417cbaf5be67ee9f88b1)
![[Photo] Vietnam team's strength guaranteed for match against Laos](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/24/1e739f7af040492a9ffcb09c35a0810b)




































































Comment (0)