Experts from Viet Duc Friendship Hospital said that kidney cancer is a malignant lesion of the kidney, accounting for about 3% of cancers in adults.
The disease is more common in men than women at a rate of twice as much. Of kidney cancers, renal cell cancer accounts for 90%.
The incidence of kidney cancer varies by region, with the US incidence rate being about 10.9%, Japan 5.4% and Vietnam 1.2%.
According to experts, kidney cancer can affect the whole body when there are paracancerous syndromes, weight loss, hematuria, and ruptured kidney tumors causing bleeding (photo source: Viet Duc Friendship Hospital).
The cause of kidney cancer is not really clear. Some risk factors that have been pointed out include: smoking, exposure to asbestos and tanning chemicals, polycystic kidney disease, etc.
According to experts, renal cell cancer has a very rich and diverse clinical picture.
The disease can develop latently and when typical symptoms appear, it is often in a late stage.
Common functional symptoms of kidney cancer include hematuria. This is a common symptom, accounting for 80% of cases. Gross hematuria can resolve spontaneously and then recur, without fever.
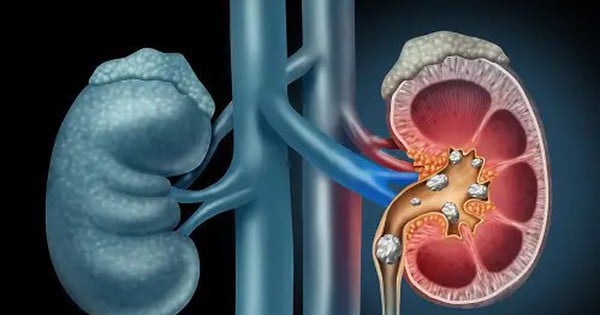
Lumbar pain when the patient feels a dull pain in the lumbar region due to the tumor stretching the renal capsule. Lumbar mass is often found to have signs of touching the lumbar region when the renal tumor is large.
In addition, patients may have symptoms of paraneoplastic syndromes such as prolonged fever, weight loss, polycythemia, hypertension, hypercalcemia, etc.
When a patient comes to the clinic with suspicious symptoms, the doctor will conduct a systematic examination combined with diagnostic imaging for early diagnosis.
Exploiting personal and family history, risk factors need to clinically examine the urinary system, diagnostic imaging. Currently, in clinical practice, ultrasound and computed tomography of the urinary system are the two most commonly used methods.
Ultrasound is an easy-to-use, safe method and has the ability to detect kidney tumors well, even with small tumors that have not yet shown clinical symptoms. Ultrasound can indicate metastatic lesions and lymph node status. Vascular ultrasound also allows assessment of renal vein and vena cava thrombosis.
Computed tomography is a method that provides a lot of information about the nature of the tumor, size, level of invasion, metastasis to other organs, and the status of renal vein and vena cava thrombosis, which is important in definitive diagnosis and staging.
According to experts, kidney cancer can affect the whole body when there are paracancerous syndromes, weight loss, hematuria, and ruptured kidney tumor causing acute bleeding.
The patient's prognosis depends largely on the stage of the disease when it is detected. In the early stages, the 5-year survival rate is about 60-80%, in the late stages this rate drops to 15-20%, and when there is metastasis, this rate is even lower.
In treatment, the choice of kidney cancer treatment method depends on the stage of the disease, in which surgery plays a major role.
Early stage when cancer is still localized: total nephrectomy is considered a radical and effective treatment method. Partial nephrectomy is indicated in some cases. Currently, nephrectomy can be performed through traditional open surgery or through laparoscopy or retroperitoneum. Ipsilateral adrenalectomy is indicated when there are signs of invasion.
Late stage cancer with metastasis: often progresses rapidly with a 5-year survival rate of less than 10%. Surgical treatment at this time is not a radical treatment but has a limited role.
The main purpose is to stop bleeding, reduce pain for the patient, and limit some paraneoplastic syndromes. In cases where kidney cancer has only one metastatic site, surgery is very effective when combined with other treatment methods.
Currently, in addition to the main treatment method of surgery, some combined treatment methods are also applied to kidney cancer: Radiation therapy for metastases in the brain, bones, and lungs. Treatment with vinblastine and fluoripyrimidine chemicals often has a low response rate.
Immunotherapy is currently a new research direction, initially showing effectiveness when using Interferon α, Interleukin-2.
To prevent the disease, according to experts, because the cause is not clear, the main prevention is to control risk factors. Do not smoke; Avoid exposure to chemicals; Control systemic diseases such as obesity, diabetes; Correct and timely treatment of urinary system diseases such as urinary tract infections, urinary stones, kidney failure, etc. Regular health check-ups to detect damage early.
After treatment, patients will be monitored by clinical examination and paraclinical testing, usually every 3 months in the first year. During the re-examination, patients will receive: Clinical examination; Paraclinical: general urinalysis, urinary ultrasound, blood biochemistry test, etc.
Source
























































































Comment (0)