 |
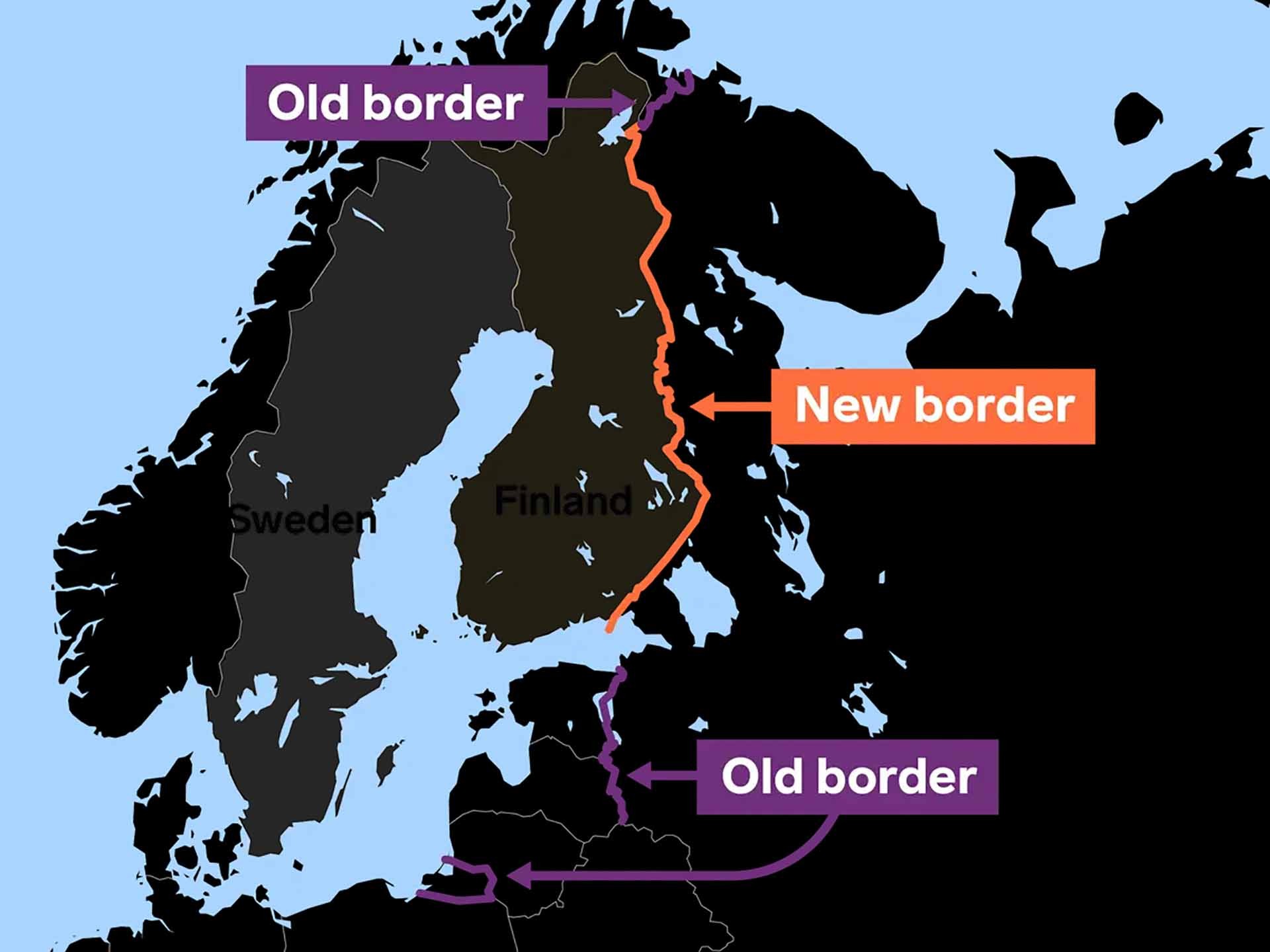
| The border between NATO and Russia doubled after Finland joined NATO (Source: Business Insider) |
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) was established on April 4, 1949 with 12 founding members, including the United States, Canada and 10 European countries: the United Kingdom, France, Belgium, Portugal, Denmark, the Netherlands, Iceland, Luxembourg, Norway and Italy. The purpose of NATO when it was established was to prevent the growth of Soviet influence.
After the Warsaw Pact was established in 1955, the rivalry and arms race between these two opposing military blocs was one of the main reasons that pushed the Cold War to a new level. When the Berlin Wall fell in 1989, the Warsaw Pact disintegrated, NATO no longer had a counterweight but did not disband but continued to expand and participate in wars, such as in Yugoslavia...
After the events of September 11, 2001, NATO shifted its focus to the fight against terrorism, typically through military interventions in Afghanistan, Iraq and Libya.
Expansion process
NATO's “open door policy” stipulates that any European country capable of promoting the principles of the Treaty and contributing to the security of the North Atlantic region can join.
Since its inception, NATO has expanded nine times in 1952, 1955, 1982, 1999, 2004, 2009, 2017, 2020 and 2023. During the Cold War, NATO added Greece and Türkiye (1952), West Germany (1955) and Spain (1982).
After the Cold War, the Czech Republic, Hungary and Poland joined NATO in 1999. In 2004, NATO added Bulgaria, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Romania, Slovakia and Slovenia. In April 2009, NATO admitted Albania and Croatia. Montenegro joined NATO in June 2017, the Republic of North Macedonia in March 2020 and most recently Finland (April 4, 2023).
In addition to the 31 full members, 22 other countries participate in NATO as relationship partners in the Peace Program and 15 other countries participate in institutionalized dialogue programs.
Georgia, Ukraine, Bosnia-Herzegovina and Sweden are currently pursuing NATO membership. Sweden has applied alongside Finland but has not yet been approved by Türkiye and Hungary. Ankara believes that Stockholm has not acted strongly enough against the Kurdish group it considers terrorists, while Hungary has used its veto to demand concessions from the EU on other issues. Ukraine formally applied to join NATO in September 2022, but since 2008, NATO members, especially the US, have said they could admit Ukraine “at some point”. However, Kiev’s NATO membership process has stalled because countries such as France and Germany believe that the move would provoke Russia.
After the end of the Cold War, NATO carried out three “Eastward Expansion” phases. In the first expansion, NATO’s borders were opened 900 km to the East, its military strength increased by 13 divisions, and it received all the weapons and equipment of the new members and East Germany. This caused a serious imbalance in the Russia-NATO balance.
 |
A flagpole outside NATO headquarters in Brussels remains unfurled pending Finland's formal accession ceremony. (Source: The Hill) |
New member, old worries
Finland’s official accession to NATO marks the end of Helsinki’s decades-long policy of “Finlandization.” After World War II, Helsinki declared that it would not join NATO to avoid being attacked by the Soviet Union. However, after the conflict in Ukraine broke out in early 2022, Helsinki changed its mind and accelerated the process of joining, a goal that has strong domestic public support.
Speaking at the admission ceremony on April 4, the President of Finland joyfully declared: “Today, Finland has become a member of the NATO military alliance, ending the era of military non-alignment in Finland's history and a new era has begun. Every country must ensure its own security to the maximum extent possible, and Finland is no exception. Becoming a member of NATO strengthens Finland's international position and creates opportunities for action. As a partner, Finland has long been actively participating in NATO activities. In the future, Finland will contribute to NATO's collective defense and deterrence capabilities.”
NATO believes that with the addition of Finland, “collective defense against Russia will be easier thanks to access to Finnish territory and Helsinki’s ability to provide military support.” For many years, NATO’s main concern in the region has been the Suwalki Corridor, a 65-km strip of land connecting Kaliningrad, a Russian exclave nestled between the Baltic states of Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, and Belarus. If Moscow were to control the Suwalki Corridor, it would cut off the connection between these three countries and Poland and other NATO members. However, the addition of Finland also poses major defense challenges for NATO because previously, only Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Norway, and Poland had a direct border with Russia of about 1,300 km. Now, with Finland’s 1,340-km border with Russia stretching from the Barents Sea in the north to the Gulf of Finland in the south, NATO’s border with Russia would double.
According to the Firepower Index, Finland's military strength is currently ranked 51st in the world. Its annual defense budget is about $6 billion, with a standing armed force of about 23,000 and 900,000 reservists who are regularly trained. If necessary, Finland can expand its military force to about 280,000 soldiers.
The Finnish army is considered to have combat experience, having served with the Western coalition in Afghanistan. Finland has 239 main battle tanks, of which 179 are combat-ready. These include 100 German-made Leopard 2A4s and Leopard 2A6s. Among Finland's thousands of armored vehicles, there are more than 100 CV-90 infantry fighting vehicles (IVFs), considered one of the most powerful IFVs in the world, produced by Sweden. Finland has more than 100 self-propelled artillery pieces, of which 39 are K9 Thunders made by South Korea, which are among the most sought-after guns on the market.
Finland also has 29 M270 towed multiple rocket launchers, along with the more mobile and wheeled HIMARS system. The Finnish military has a fleet of 55 US-made F/A-18 Hornets, equipped with advanced US weapons such as the AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missile and the AGM-158 JASSM air-to-ground cruise missile. Finland's F/A-18s will begin to be replaced by 64 US F-35 fifth-generation fighters from 2026, with a projected completion date of 2030.
Finland has the 12th largest navy in the world, with bases along a 4,441 km (2,700 mi) coastline on the Baltic Sea. Latvian Foreign Minister Edgars Rinkevics said that when Finland becomes a NATO member, the Baltic Sea will be considered “NATO waters”.
Stakeholder Response
NATO Secretary General Stoltenberg affirmed that Finland's admission is beneficial to NATO's security because of its large and well-equipped military. US President Biden welcomed Finland's official accession to NATO, saying it has made NATO stronger than ever. The Turkish president affirmed that Helsinki has "made real progress" in dealing with groups that Ankara considers "terrorists" and changing defense exports.
Meanwhile, Russian Presidential Press Secretary Dmitry Peskov stated: “Finland’s accession to NATO will aggravate the situation and will also be an infringement on Russia’s interests, forcing Russia to take countermeasures to ensure its security, both tactically and strategically.” He explained that Finland’s accession to NATO is different from Ukraine’s, however, “it cannot but affect the nature of bilateral relations. NATO remains an unfriendly and hostile structure towards the Russian Federation.”
Russian Defense Minister Sergei Shoigu announced the re-establishment of the Moscow and Leningrad military districts. He also ordered the creation of a new army corps in the Republic of Karelia as part of the Ground Forces and two airborne assault divisions of the Airborne Forces. The Levashovo airfield near St. Petersburg, after reconstruction, will become a base for the naval aviation of the Russian Navy Fleet. From Levashovo, Russian naval aircraft will be able to control the entire Baltic region, and if necessary, will be transferred to the Kola Peninsula.
According to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute (SIPRI), Russia could respond to NATO expansion at the expense of Finland in an asymmetric way – deploying tactical nuclear weapons near its borders. These are Iskander missiles. In the event of NATO aggression against Russia, Helsinki and major Finnish ports would become potential targets for Russian strategic nuclear missile strikes. However, experts also believe that this is not Moscow’s choice, but only a forced solution.
 | NATO Secretary General Visits Japan: Europe Cannot Ignore What Happens in East Asia During his visit to Japan, Secretary General of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) Jens Stoltenberg had a meeting ... |
 | Sweden 'green lights' a request from Türkiye Sweden said on April 6 it would extradite a Turkish citizen wanted by Ankara but rejected a request ... |
 | Looking back at the world in the first quarter of 2023 The first quarter of 2023 has passed with many events and trends of 2022, while revealing many events and current ... |
 | Finland joins NATO: 'Fuel' for tensions with Russia? Finland's accession to the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) is considered a historic turning point in the structure of ... |
 | NATO suffered a serious cyber attack, 40% of its infrastructure was paralyzed. On April 10, the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) suffered a large-scale cyber attack, causing 40% of its infrastructure to be... |
Source































































































Comment (0)