Specialists are highly qualified and work in specific medical fields. They must undergo intensive training after completing a medical university degree, and have important roles and responsibilities in the medical examination and treatment system of hospitals.
In the specialist doctor is divided into two different levels, specialist 1 and specialist 2. To know what specialist 1 and specialist 2 are and how they are different, let's find out in the content of the article below.
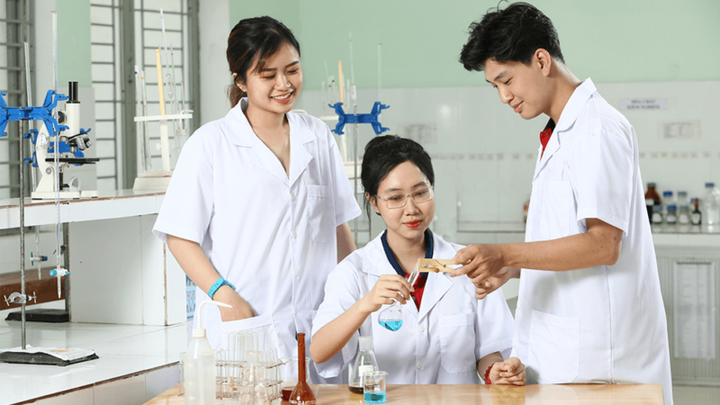

Is there a difference between studying for a specialist 1 and specialist 2?
What is a specialist?
A specialist is a doctor with high qualifications and expertise in a specific medical field. For example: neurologists, orthopedists, dentists, pediatricians, obstetricians.
In addition to the responsibility of taking care of patients' health, specialists must also have in-depth knowledge of the specific diseases they are trained in, and update the latest information to be ready to respond to different clinical situations and diagnose and treat diseases.
Depending on the level, concept, level, and duties of a specialist doctor are also different. In the system of hospitals and medical facilities, specialists play a very important role.
Distinguish between specialist 1 and specialist 2
| STT | Compare | Specialist 1 | Specialist 2 |
| 1 | Concept | - A person with high expertise in a specific field of medicine. - Normally, after graduating from university, students need to study for 1 more year to become a specialist and 2 more years to become a specialist 1. | - A doctor with high expertise in a specific field of medicine. A specialist 2 has a higher position than a specialist 1. - Specialist 2 applies to those who have completed a specialist training program and have been confirmed to have a postgraduate degree (master's degree). |
| 2 | Level | - Bachelor's or master's degree in medicine (doctor, pharmacist). - Level I specialized diploma. | - Master's degree in medicine (doctor, pharmacist). - Level II specialized diploma. |
| 3 | Mission | - Diagnosis and treatment of specific specialties and diseases such as: cardiology, neurology, pediatrics, dermatology. - Usually work in clinics, public hospitals or private hospitals. | - Diagnosis and treatment of specific specialties and diseases such as: cardiology, neurology, pediatrics, dermatology. - Usually work in medical facilities (clinics, public hospitals, private hospitals) and clinical practice facilities. |
Above are comparisons of studying and working as a specialist 1 and specialist 2, are they different or not, everyone can refer to.
Anh Anh (Synthesis)
Source






















































































Comment (0)