Ho Chi Minh City: A 12-year-old boy with liver and kidney damage due to poisoning after eating mushrooms growing on cicada pupae is showing good health and has been discharged from the hospital.
On the evening of June 21, a representative of Children's Hospital 2 said that after nearly 10 days of intensive treatment, the child's liver, kidney function and perception had recovered.
Before that, she and her mother ate mushrooms grown from tick carcasses, picked from a field in Dong Nai. About an hour later, both mother and child suffered from stomach cramps, dizziness, and vomiting, and were taken to the emergency room. The mother's condition was stable, while the child was in a coma and was transferred to Children's Hospital 2. Test results determined that the child was poisoned by Gyrommitrin, a substance found in mushrooms grown from tick carcasses, causing liver and kidney damage.
This is the first recorded case of poisoning from eating mushrooms growing on tick carcasses.
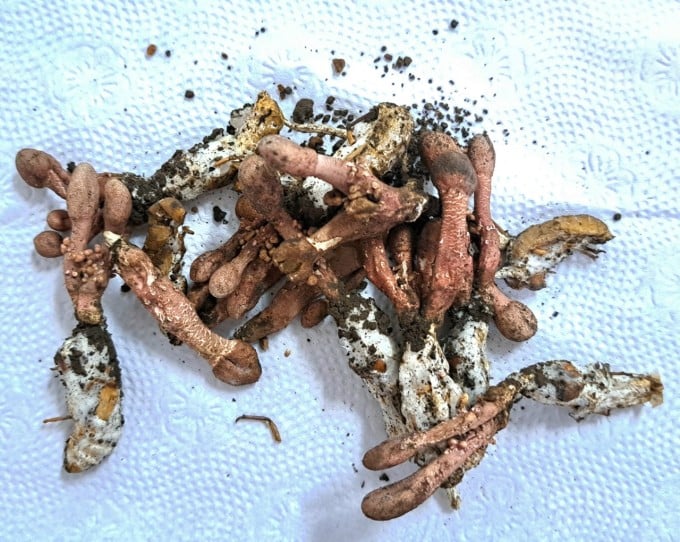

The poisonous fungus Gyrommitrin parasitizes cicadas. Photo: Provided by the hospital
Gyrommitrin mushroom has a shape similar to deer antlers, dark red color, spherical mushroom head, very beautiful. This is a poisonous mushroom. Symptoms of poisoning include vomiting, vomiting, convulsions, loss of consciousness, deep coma, using a lot can be life-threatening. Gyrommitrin poison is not lost when cooking with heat.
This fungus parasitizes adult cicadas. They live in the abdomen of cicadas and are highly contagious during mating season. When cicadas die or cannot molt and die underground, the Gyrommitrin fungus will develop when the rainy season comes. At this time, the entire body of the cicada turns white and soft like foam, and on the head of the cicada pupa there are 1-5 stems (mushroom stems) and a slightly swollen end (mushroom fruit) - it looks like cordyceps (a medicine) so it is confusing.
Summer is the time when cicadas are active, combined with the rainy season, which is the condition for the poisonous fungus Gyrommitrin to sprout and grow on the body of cicadas. Many people mistake it for common mushrooms or "cordyceps", so they pick it to process into food, leading to poisoning and even death.
There is currently no specific treatment for Gyrommitrin poisoning, treatment is mainly symptomatic. Doctors recommend avoiding the use of strangely shaped mushrooms, wild mushrooms, and mushrooms that are not commonly available on the market to ensure safety.
American Italy
Source link























































































Comment (0)