On March 20, Dr. Nguyen Hoai Nam, Deputy Director of the Digestive - Hepatobiliary Center, Bach Mai Hospital (Hanoi) said that new technology in gastrointestinal endoscopy has brought about progress in the early diagnosis of gastrointestinal cancer.
Currently, doctors at the center are performing 800-1,000 gastrointestinal endoscopy cases every day. Among these, many patients are found to have stomach, colorectal, and esophageal cancer (accounting for 1-2%), mainly in people over 50 years old.
According to Dr. Nam, gastrointestinal endoscopy is one of the important techniques in detecting and treating digestive diseases such as ulcers, polyps and especially cancer. However, even experienced doctors may have difficulty identifying small or hidden lesions.
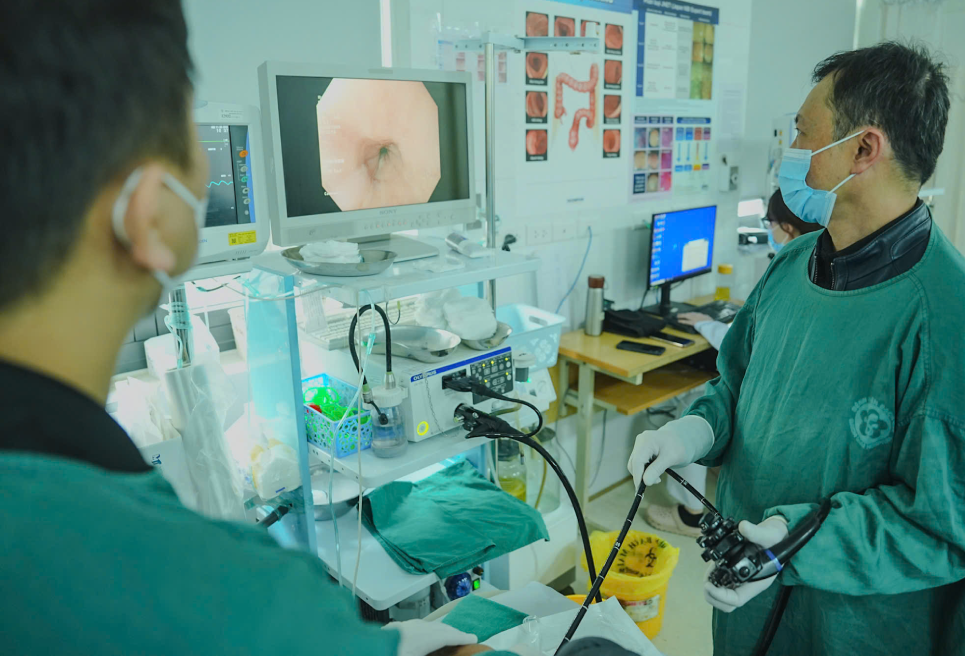
Recently, with the development of endoscopic technology and artificial intelligence (AI), many patients have had cancer detected at an early stage.
At Bach Mai Hospital, AI technology applied in digestive endoscopy helps to identify lesions that are invisible to the naked eye; supports doctors in assessing abnormal signals, improving the rate of early cancer detection and reducing the risk of missing.
This technology can display and delimit the lesion with warning boxes, the system predicts the percentage of cancer in this case and the correct rate is up to 99%. Thanks to that, patients can detect cancer from the "egg" and intervene early when malignant cells have not invaded or metastasized elsewhere.
AI is bringing about major changes in the detection and management of gastrointestinal diseases. AI systems not only improve the rate of early detection of polyps and cancers, but also reduce human errors and improve the quality of medical services.
In addition to AI, magnifying endoscopy technology uses very short wavelengths to highlight vascular structures and characteristics of inflammatory lesions of tumors, vascular proliferation, and abnormal lesion markers...
Doctors can rely on it to clearly see suspicious cancerous lesions very early.
For suspected malignant lesions, doctors only need to cut and separate the mucosa through endoscopic methods, preventing the lesions from progressing and invading surrounding tissues. Therefore, patients are completely healthy after 45-60 minutes of endoscopy, without having to undergo major surgery or large tumors as before.
Doctors recommend that groups with high risk factors need regular screening such as:
- History of stomach disease, especially people with severe atrophic gastritis.
- Family has someone with digestive tract cancer (parents, siblings).
- People over 40 years old, smoke, drink a lot of alcohol, prolonged stress.
- People at high risk of gastrointestinal bleeding when using anticoagulants or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory pain relievers.
- In case of vomiting blood, black stools, unexplained weight loss, difficulty swallowing.
Depending on each specific case, periodic gastrointestinal endoscopy will be recommended to be repeated every one to three years.





![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attend the first Congress of the National Data Association](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/22/5d9be594d4824ccba3ddff5886db2a9e)


















![[Photo] Overview of the Workshop "Removing policy shortcomings to promote the role of the private economy in the Vietnamese economy"](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/21/d1c58c1df227467b8b33d9230d4a7342)






















































Comment (0)