A medical dye can help reduce the toxic effects of death cap mushrooms on mice, a Chinese research team said on May 16.
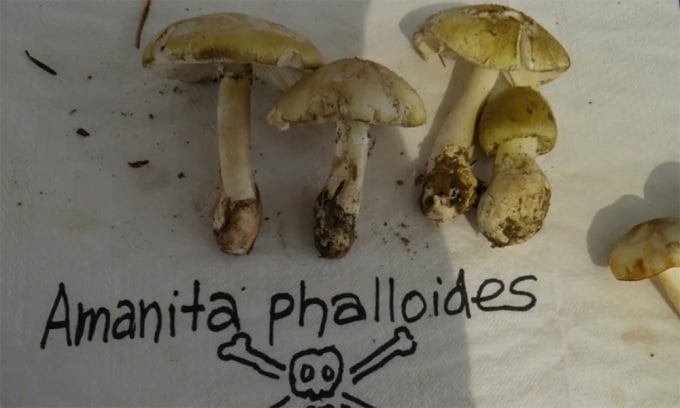

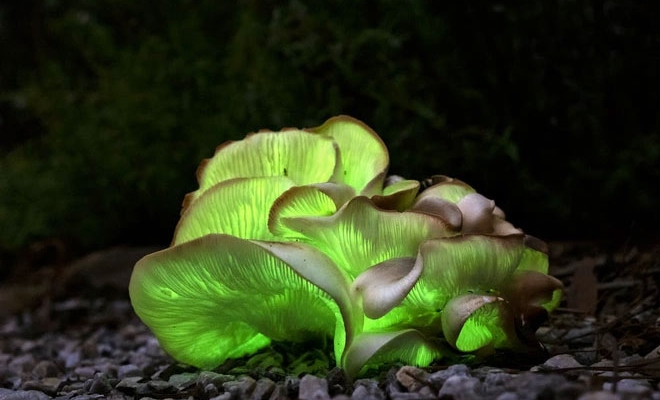
Amanita phalloides death cap mushroom. Photo: Bkaounas/iNaturalist
According to experts including Guohui Wan and Qiao-Ping Wang at Sun Yat-sen University, the fluorescent dye indocyanine green has the potential to save many lives in the future. Indocyanine green has not been tested for detoxification in humans, but has been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for other uses.
The death cap mushroom ( Amanita phalloides ) is estimated to cause more than 90% of mushroom poisoning deaths worldwide. It may look like other mushrooms that people like to pick in the wild, but eating just half of one can cause serious liver or kidney damage. Native to Europe, the death cap mushroom has spread around the world. It caused more than 38,000 illnesses and nearly 800 deaths in China alone between 2010 and 2020.
In a new study published in Nature Communications , scientists targeted alpha-amanitin, the main toxin produced by death cap mushrooms. They used CRISPR genomic screening, a relatively new technique that helps understand the role of specific genes in infection and poisoning.
CRISPR screening identified the protein STT3B as the main culprit behind the toxic effects of death cap mushrooms. The team looked at FDA-approved drugs and found that blue indocyanine had the potential to block this protein.
This is an intravenous fluorescent dye that has been widely used for decades in the United States, Europe and other regions for diagnostic imaging, helping doctors measure liver and heart function.
Wang said the team was surprised to find this unexpected connection. They tested the drug first on liver cells in a lab dish, then on mice. Both showed great potential in reducing the toxic effects of death cap mushrooms.
Next, the team plans to conduct human trials. "It could save many lives if it works as well in humans as it does in mice," Wang said.
Thu Thao (According to AFP )
Source link






























































































Comment (0)