The U.S. Air Force Rapid Capabilities Office is working with the Space Force to prepare for the launch of the seventh mission of the X-37B spacecraft. The orbital test vehicle will launch from Kennedy Space Center in Florida on December 7.
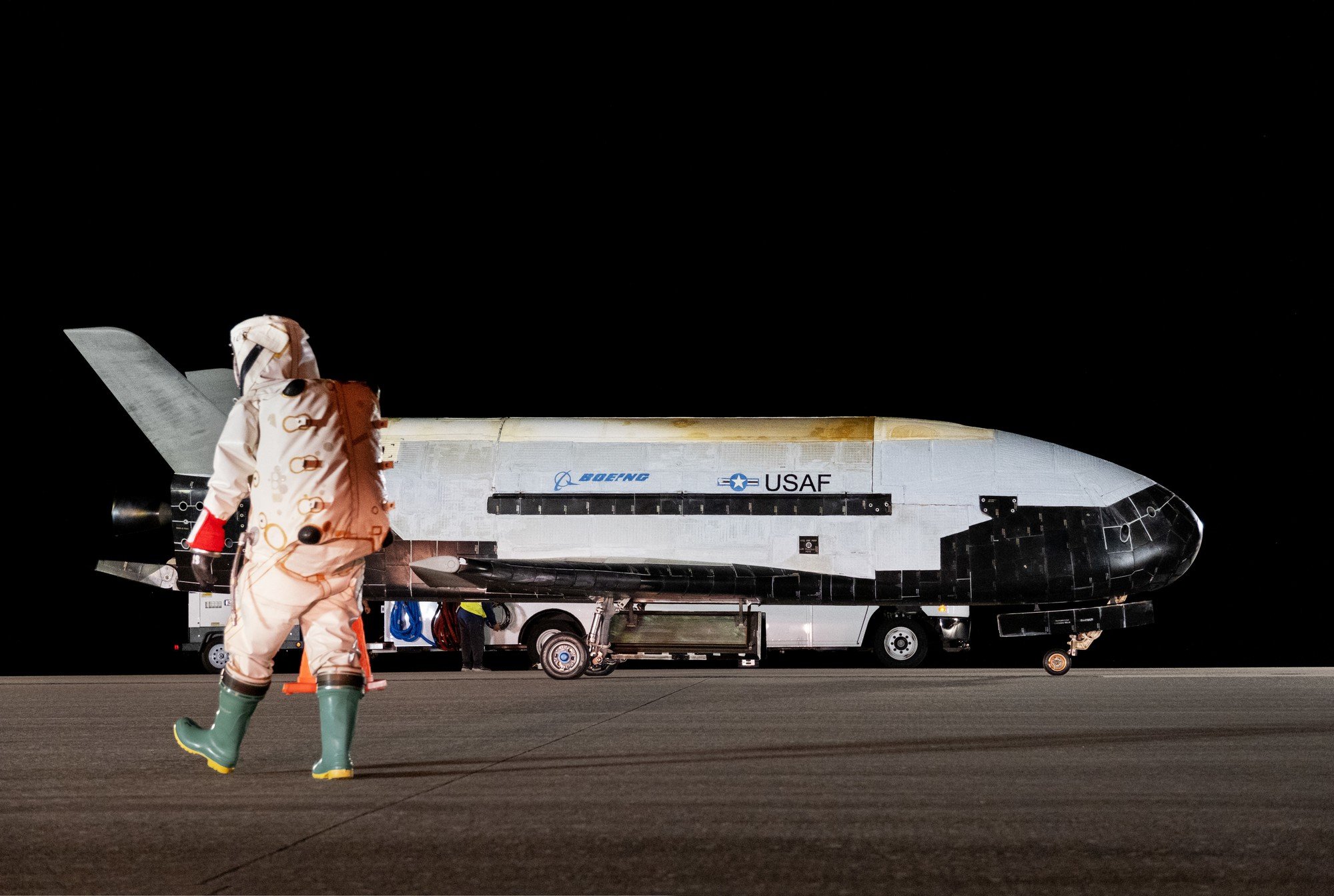

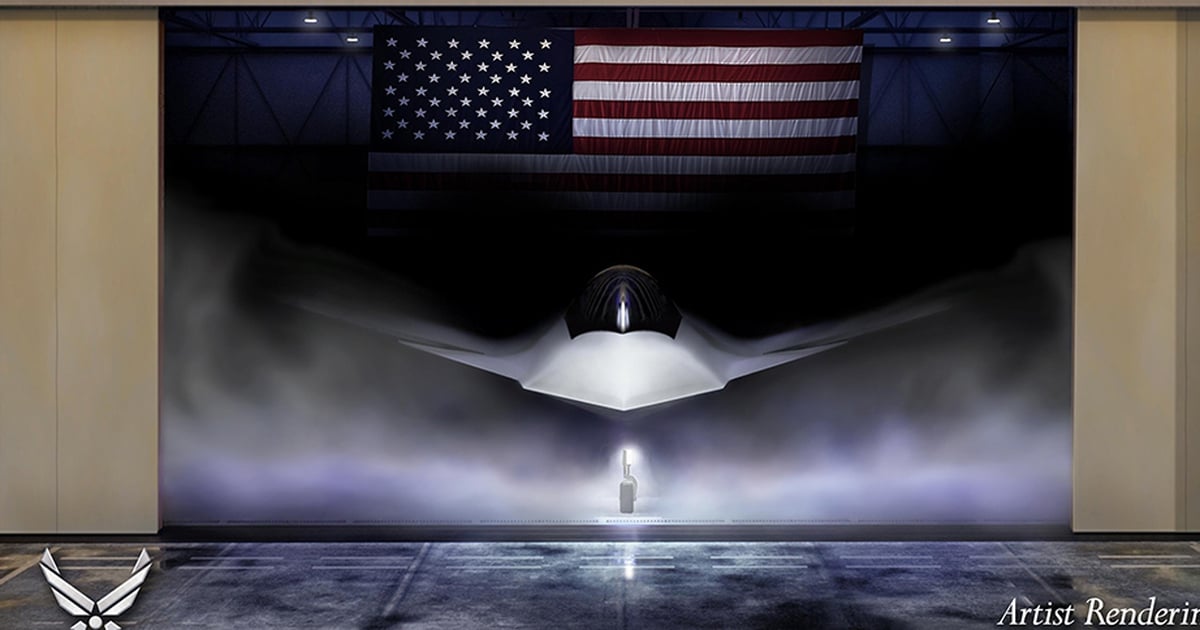
The X-37B spacecraft in the photo released in November 2022
US SPACE FORCE
What is X-37B?
The X-37B is an American reusable spacecraft that helps reduce the cost of space missions. According to SyFy, the X-37 program began at NASA in 1999, years before the final flight of the Space Shuttle program in 2011. In 2004, the X-37 and related activities were transferred to the control of the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency (DARPA) of the US Department of Defense. In 2006, the US Air Force announced its own program called the X-37B, also known as the Orbital Test Vehicle (OTV). By 2019, the management of the X-37B had changed and is now under the supervision of the US Space Force.
The X-37B spacecraft, built by Boeing, is similar in design to the space shuttle but smaller in size. It is 8.9 m long, 2.9 m high, has a wingspan of 4.5 m and has no crew on board. It is launched by a rocket, then separated and operates for many days in space thanks to solar panels. The spacecraft's engines help it return to Earth and land like a normal plane.
The first X-37B mission was carried out in 2010 and to date two have been built, completing six orbital missions for a total of 3,774 days.
Many experiments were performed
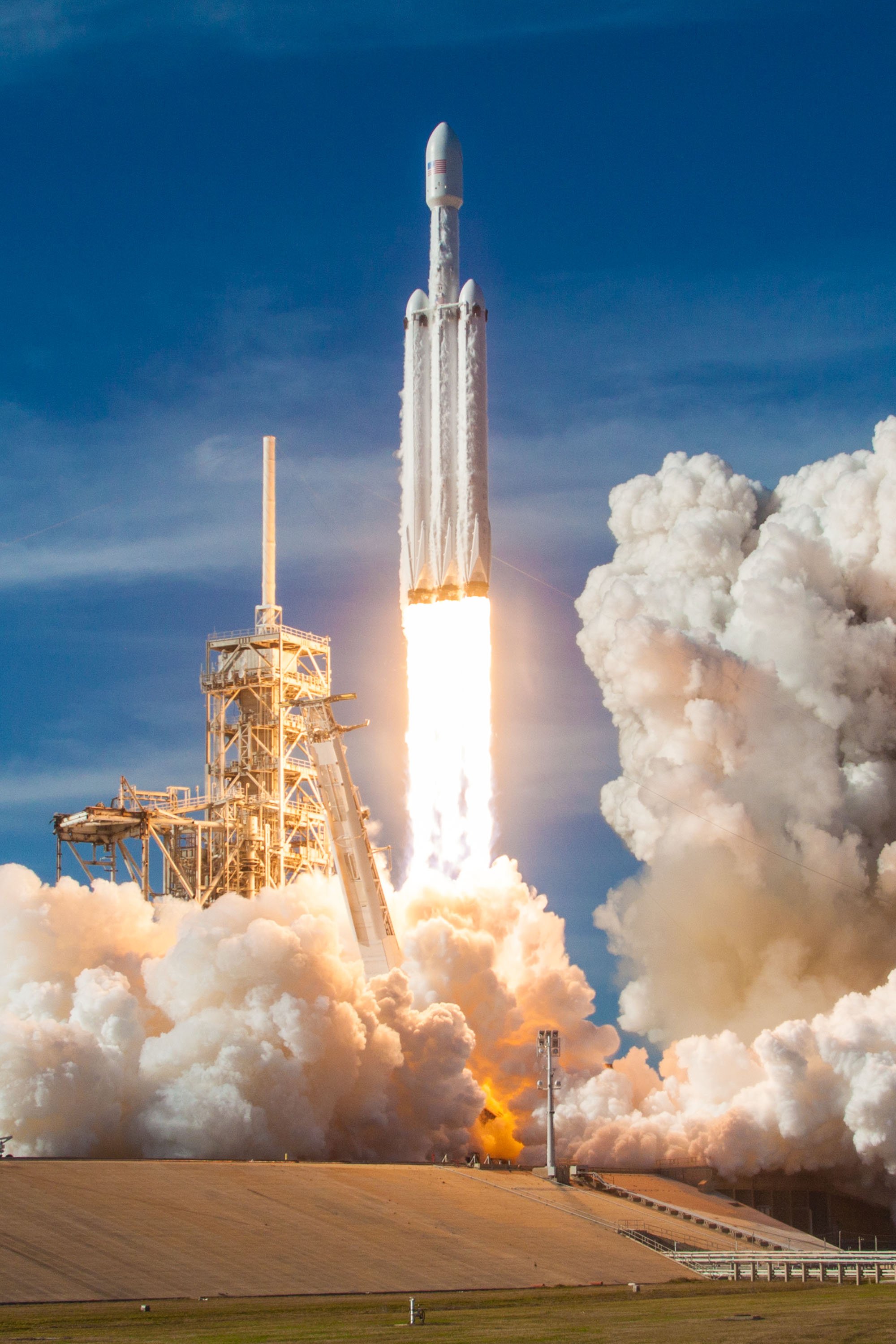

Falcon Heavy rocket test launch in 2018
In previous missions, the X-37B has been launched on SpaceX's Falcon 9 rocket and the Atlas V of United Launch Alliance (ULA), a joint venture between Lockheed Martin and Boeing. However, on the December mission, the spacecraft will be launched for the first time on SpaceX's Falcon Heavy rocket.
According to Space News , billionaire Elon Musk's space company was awarded a $130 million contract in June 2018 to launch the X-37B on this mission, designated USSF-52. The launch was originally scheduled for 2021 but was delayed due to payload issues.
The Space Force has not released much information about the upcoming mission, saying only that part of it will be to operate the reusable spacecraft “in new orbital regimes.” That’s why the X-37B will be launched on a Falcon Heavy rocket, as it needs to be boosted to a higher orbit than usual.
The spacecraft will also conduct tests on “space-based cognitive technologies” and study the effects of radiation on materials provided by NASA.
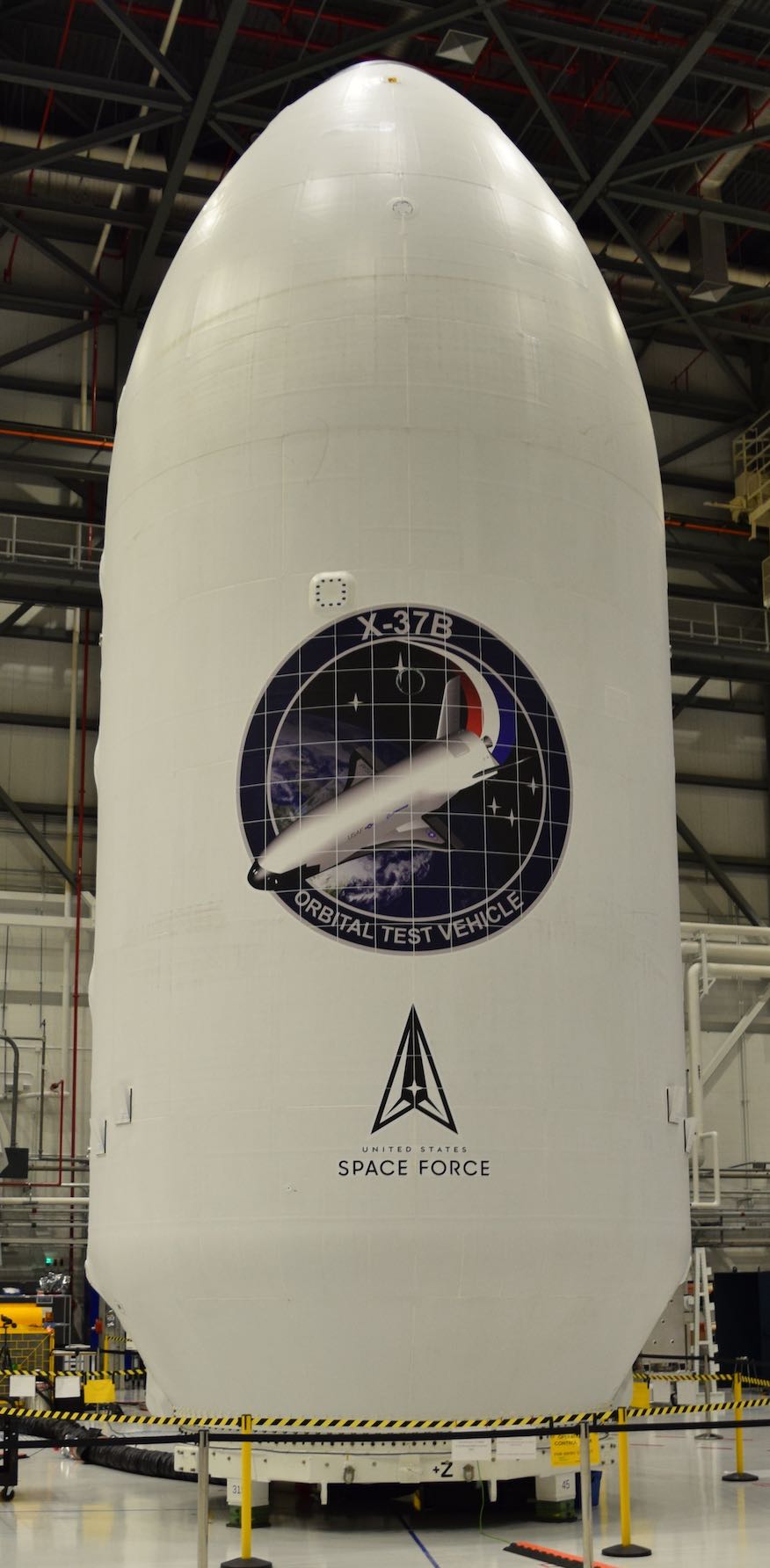

The X-37B spacecraft is encased in its shell, preparing for mission USSF-52.
Most of the cargo and experiments on the X-37B are classified, but one is NASA’s Seed-2 experiment, which will send seeds into space to test the effects of radiation on them during long flights. Knowledge of how space affects plants could have implications for the future of long-term human space missions.
The sixth X-37B mission, launched in May 2020, was the first to include a special service module that allowed it to carry out more experiments than previous missions. The mission also included a solar-to-microwave energy test module, two NASA experiments to study the effects of radiation and space effects on materials and food seeds. The sixth X-37B also deployed a small satellite called FalconSat-8, developed by the US Air Force Academy with support from the Air Force Research Laboratory.
Mission 6 ends in November 2022 after the X-37B spacecraft sets a record 908 days in orbit and returns to Earth.
Source link







![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam and Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh attend the first Congress of the National Data Association](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/22/5d9be594d4824ccba3ddff5886db2a9e)














































































Comment (0)