In an effort to uncover the mysteries of dark matter, NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Telescope project, scheduled to launch in May 2027, is poised to provide important insights into this elusive material.
The telescope's mission involves exploring voids between star clusters, specifically those located between globular clusters orbiting the Andromeda Galaxy, with the aim of expanding modern astronomers' current understanding of dark matter, by further studying the disturbances and voids present in these interstellar streams.
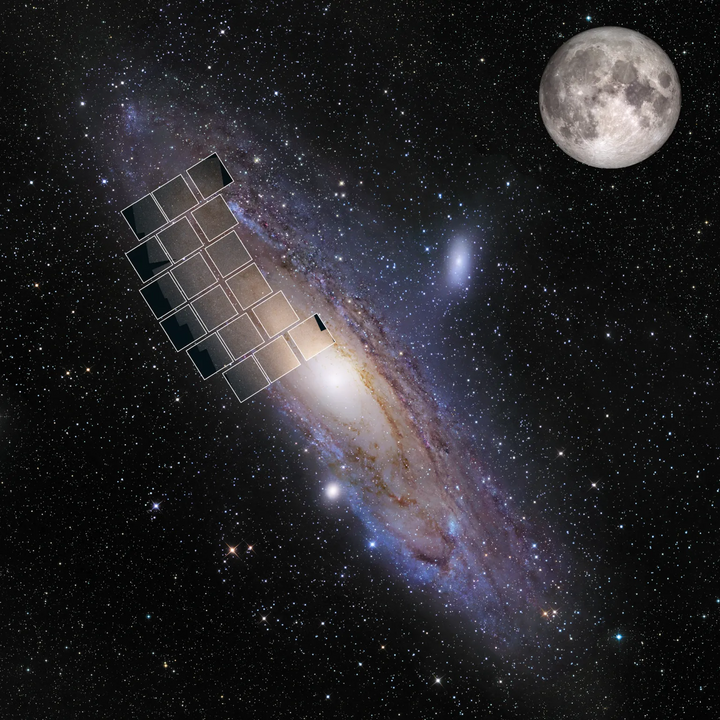
NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Telescope, launching in 2027, aims to unravel the mysteries of dark matter by studying the voids between globular clusters around the Andromeda galaxy. (Image: NASA, STScI, Benjamin F. Williams (UWashington)
Technically, NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Telescope will feature 18 ultra-deep-field detectors that are expected to revolutionize observational capabilities. With the ability to observe 200 times deeper than the Hubble Space Telescope’s near-infrared camera, and with slightly better resolution, the new telescope is expected to produce the most exquisitely detailed snapshots of our neighboring galaxy, Andromeda.
According to Christian Aganze of Stanford University, who is also leading the project, the Nancy Grace Roman Telescope will be able to take a huge panoramic picture of the Andromeda Galaxy that no other telescope has been able to fully capture. The telescope’s enhanced resolution will allow it to detect individual stars in globular clusters with unprecedented clarity compared to previous astronomical observations.
Meanwhile, dark matter, which makes up about 27% of the universe, remains undetectable by direct observation, since it does not interact with light. However, its influence on galaxies is reflected in their rotation patterns, making it an important indirect indicator of the presence of dark matter. “We see the effect of dark matter on galaxies,” says Tjitske Starkenburg of Northwestern University. “So observing the rotation patterns of galaxies could be an important precursor to explaining the existence of dark matter.”
Meanwhile, globular clusters, described as cosmic ribbons, offer a unique vantage point for studying dark matter. Recent studies have shown that clumps of dark matter can penetrate these clusters, creating distinct voids.
Unlike previous observations limited to the Milky Way, NASA's Nancy Grace Roman Telescope will allow researchers to explore nearby galaxies like the Andromeda Galaxy for the first time, greatly expanding the data set of globular clusters to study the properties, and mass, of dark matter halos.
HUYNH DUNG (Source: Interestingengineering)
Source


























































































Comment (0)