During the changing seasons, children are susceptible to colds and flu. Many parents often assume that this is a common illness that can be treated at home.
Don't be subjective with seasonal flu
Recently, the Cardiovascular Center, National Children's Hospital has received and treated a number of cases of young children with symptoms of headache, cough and fever similar to the flu, but after performing tests, the results showed that the children had myocarditis.
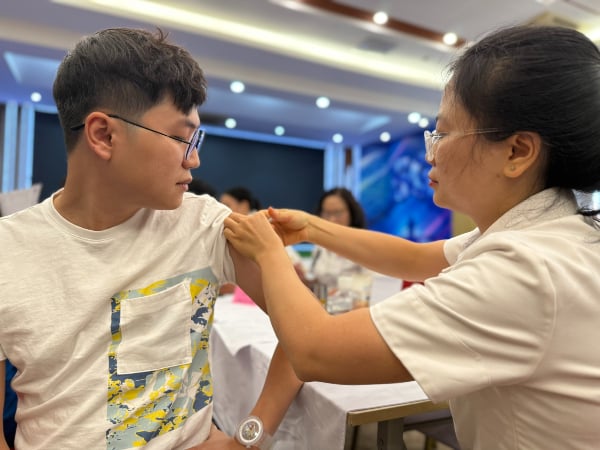 |
| Influenza vaccination is an important measure to reduce the incidence of influenza and its complications. |
Children may have symptoms similar to other common illnesses such as fatigue, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, fever, cough...
Because the initial symptoms of the disease are quite similar to fever and the common cold, many parents are subjective, and by the time the child is hospitalized, their life is already in danger.
Dr. Le Hong Quang, Head of the Department of Internal Medicine and Cardiology, Cardiovascular Center, National Children's Hospital, said that in some hospitalized cases, there was a child named P. (8 years old, Nghe An) who had the initial symptoms of the disease such as difficulty breathing and chest tightness.
The patient's family said that the child was healthy, active, and had no history of heart disease. After the chest pain caused difficulty breathing, the family was extremely worried and rushed the child to the provincial hospital and was transferred to the National Children's Hospital. Fortunately, the child only had mild myocarditis and received timely emergency care.
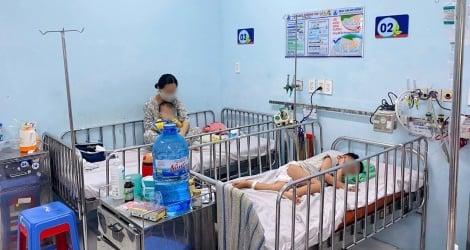
However, in some cases of critical myocarditis in children, the family mistook it for a common illness, so when the child was taken to the National Children's Hospital for examination, he was already tired and pale. The doctor ordered a monitor and an echocardiogram, which showed abnormal heart function.
Children must be treated with ECMO, combined with antiarrhythmic drugs, vasopressors, cardiac drugs... Symptoms of myocarditis in children are diverse and nonspecific, so misdiagnosis is very likely to occur.
Doctors recommend that, in addition to clinical manifestations of cough, fever, abdominal pain, vomiting... if the child has other symptoms such as rapid breathing, chest pain, difficulty breathing, rapid heart rate, pale lips and skin... the family should take the child to a medical facility for timely examination and treatment.
If in doubt, the child needs to undergo paraclinical tests such as chest X-ray, electrocardiogram, echocardiogram, cardiac enzyme test, cardiac MRI... to have a definitive diagnosis.
Flu is a respiratory infection caused by influenza viruses. The disease is easily spread into epidemics every time the seasons change, the weather turns cold or hot erratically.
Influenza is often spread quite quickly, because the patient inhales air containing the influenza virus. Children are very susceptible to this disease due to the influence of the weather. When infected with the flu, the patient has some basic symptoms such as headache, cough, fever, stuffy nose, sore throat... When children have signs of dry cough, sore throat, often cry, refuse to eat, and feel tired...
With common symptoms, the body will be tired for about 3-4 days and will go away on its own within 7-10 days. Because of this, many parents often subjectively think that this is a common disease, and the child can recover on its own without treatment.
In fact, the flu in children can be more severe and dangerous than in adults. In particular, for children under 12 weeks old, when the following unusual symptoms appear, they should be taken immediately to a reputable medical facility for examination and timely treatment: Body temperature exceeding 38oC, persistent fever that does not subside, continuous fever; wheezing, difficulty breathing, earache.
In case the flu persists and the flu symptoms become more severe, the patient should proactively visit a specialist for a proper diagnosis and treatment as prescribed.
Not only children, according to the recommendations of medical experts, when adults have flu with severe and prolonged symptoms, they need to take medicine and receive active treatment, otherwise it can lead to some dangerous complications such as causing myocarditis, pericarditis, acute bronchitis, chronic bronchitis, pneumonia, acute glomerulonephritis, otitis media, sinusitis...
To prevent and limit the risk of acute myocarditis in children, doctors recommend that parents should give their children a scientific diet, with enough nutrition and minerals to improve their resistance; fully vaccinate children, especially against diphtheria, flu, mumps, rubella...
Seasonal flu can be effectively prevented by vaccination.
According to doctors, anyone can get the flu, but it is most common in people with an incomplete immune system or weak resistance, such as infants: Infants under 6 months of age who have not been vaccinated against the flu are at very high risk of getting the flu.
For babies born prematurely (under 32 weeks old) with health risks are more likely to get the flu and have more severe symptoms.
Children, especially children under 2 years old with incomplete immune systems, are at high risk of infectious diseases, including seasonal flu.
For children with underlying medical conditions such as asthma, metabolic disorders, congenital heart disease, liver disease, kidney disease, etc., the risk of influenza and complications is especially high, so children are always recommended to be fully vaccinated against influenza and get a booster shot once a year.
Adults >65 years old; people with chronic underlying diseases such as diabetes, heart and lung disease, kidney or liver failure, immunodeficiency... are susceptible to serious complications when infected with the flu.
Pregnant or breastfeeding women also need to pay special attention to avoid catching the flu because it can greatly affect their health. Accordingly, when pregnant, a woman's body has many changes, hormones change, the immune system is weaker, causing their resistance to decrease.
This makes the pregnant woman's body more sensitive and vulnerable to pathogens. Similarly, after giving birth, a woman's physical health and resistance are reduced, making it easier for the flu virus to attack.
It is very dangerous for pregnant women to get the flu during the first 3 months of pregnancy. This is the stage when the fetus begins to form and develop many parts of the body, so if the mother gets the flu during this stage, there is a risk of fetal malformations, miscarriage or stillbirth.
The most dangerous complication of influenza is Reye's syndrome (which causes swelling of the liver and brain), most commonly found in children aged 2-16. Although this is a very rare syndrome, it has particularly serious consequences and a high mortality rate.
This complication can appear just a few days after having the flu. When flu symptoms show signs of decreasing, the child suddenly vomits, becomes delirious, has convulsions, goes into a deep coma and then dies.
In particular, influenza is a viral disease and can be effectively prevented by vaccination. Research by scientists in Canada has shown that influenza vaccination can reduce the risk of stroke, heart attack and death from cardiovascular diseases by up to 50%.
Every winter and spring, flu is at risk of breaking out into a major epidemic. When someone has the flu, it is necessary to isolate, clean the environment, and wear a mask to avoid infection. However, that is not a radical solution, but prevention with vaccines is the most effective and safest measure.
Dr. Nguyen Tuan Hai, Safpo/Potec vaccination system, said that seasonal flu is caused by influenza viruses (usually 4 strains from H1N1, H3N2 and 2 group B strains) and spreads in the community with the ability to continuously change antigens (we will often be exposed to new influenza viruses) but according to certain genetic rules. Each year, the circulating influenza virus strains are different, so we need to get a booster shot for seasonal flu every year (once a year).
WHO has long established seasonal influenza virus monitoring stations around the world (including in Vietnam) to isolate and identify seasonal influenza viruses circulating in regions (geographical, climatic, Northern and Southern Hemispheres). From there, it predicts and identifies influenza virus strains that will appear in the winter - spring in the Northern Hemisphere (from October to the end of April of the following year) and in the winter - spring in the Southern Hemisphere (from May to October every year).
From determining which influenza virus strains are likely to prevail where (Northern and Southern Hemispheres), WHO will provide guidelines on influenza virus strains for the production of seasonal influenza vaccines for vaccine manufacturers to follow and supply to the market at the best time (Northern Hemisphere is around August-September, and Southern Hemisphere is around April-May every year).
That is why we living in Vietnam need to get a seasonal flu vaccine once a year and before the flu season starts, as well as getting the recommended seasonal vaccine.
Because Vietnam is located in the tropical monsoon region, the flu season in the North and the South may differ slightly in time, but because our country is located entirely in the Northern Hemisphere and according to WHO recommendations, we should get the correct Northern Hemisphere seasonal vaccine, which covers from winter this year to the end of spring next year.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/canh-giac-voi-benh-cam-cum-giao-mua-d227897.html





![[Photo] Visiting Cu Chi Tunnels - a heroic underground feat](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/8/06cb489403514b878768dd7262daba0b)


















































































Comment (0)