
Essential online activities like video conferencing and high-definition television today require download speeds of 25 Mbps or more. In 2019, an average of 4.4% of Americans did not have access to such speeds.
The problem is four to five times worse in rural and remote areas of America, at 17 percent and 21 percent, respectively, exacerbating the digital divide within communities.
In a world where business, life, and communication are increasingly conducted via mobile devices, high-speed Internet is becoming a necessity. Yet large areas of the United States still lack high-speed broadband or cellular service.
A possible solution could be provided by sixth-generation (6G) mobile networks. According to experts, 6G networks will fill the gaps in ground-based systems with space-based networks.
In mid-2023, the U.S. government took steps to improve connectivity by expanding existing broadband infrastructure. In late June 2023, the U.S. government allocated $42.4 billion to the Broadband Equity, Access, and Deployment (BEAD) program, which aims to provide Americans with reliable high-speed Internet access.
In 2022, software products are being developed in Russia to accelerate the development of 5G and 6G networks. However, despite ambitious plans, the full deployment of 5G networks in Russia faces a number of difficulties, including sanctions and a lack of consensus on the issue of 5G deployment.
So, unlike many other countries, Russia is considering skipping the full rollout of 5G and moving straight to developing 6G networks.
Russian experts are actively developing 6G technology, including using satellites and drones, in an effort to improve connection speeds, reduce network latency and enable wide-area coverage, even in remote and sparsely populated areas of the country.
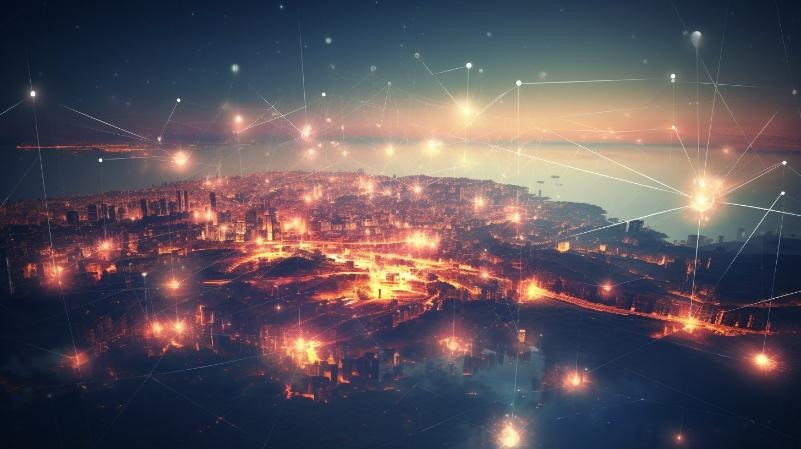

Many parts of the world are still struggling to deploy 5G widely. Total 5G coverage is estimated to only cover about 10% of the Earth's surface. With the advent of 6G, some of which will be launched into space, this could change dramatically.
6G networks are still in the early stages of development and even the key parameters have not been determined. However, 6G technology is expected to be much faster, even thousands of times faster than current 5G networks due to the use of higher frequency radio waves. This technology will provide faster connections, with lower network latency.
Current 6G research and development efforts focus on creating “off-Earth” networks through the support of low-Earth orbit (LEO) satellites and unmanned aerial vehicles, which would reduce costs compared to 5G networks, which currently rely mainly on terrestrial fiber optic cables and mobile base stations.
Experts say 6G technology will open the door to future technologies. In particular, 6G networks will provide services that exceed the capabilities of today's home routers, especially in terms of latency, thanks to the support of increasingly remote base stations.
The application of artificial intelligence (AI) technology in 6G will help improve real-time data usage analysis and increase data processing speed.
While 6G technology promises revolutionary changes, deployment is still a long way off: 6G is not expected to be commercially available before 2030.
(according to Securitylab)
Source























































































Comment (0)