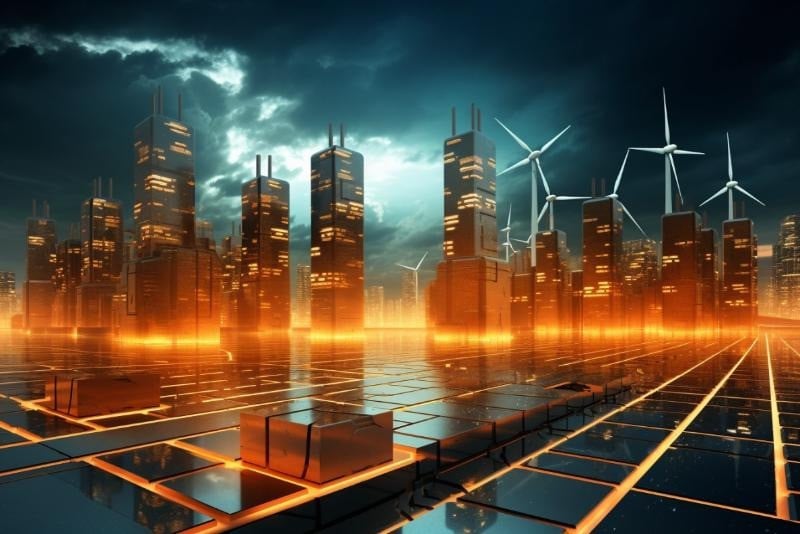

Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) have created an innovative supercapacitor using cement, carbon black and water. The device has the potential to provide an affordable alternative energy solution and can be used to store renewable energy.
Details of the technology are described in a paper in the journal PNAS by MIT professors Franz-Josef Ulm, Admir Masic, Yang-Shao Horn and others.
The basis for the new energy storage system is two common materials in life: Cement and carbon black. Researchers have discovered that combining them with water can create supercapacitors that store electrical energy.
One interesting application of this technology is incorporating a supercapacitor into the concrete foundation of a home, allowing energy storage without increasing the cost of building a foundation.
According to research data, a 45 m3 block of concrete can store about 10 kWh of electricity - the average daily consumption of a household. This type of concrete still retains its normal durability, allowing the integration of supercapacitors into different structural parts of the house.
Additionally, supercapacitors made from this material could be used to store energy captured from solar panels for wireless charging of electric vehicles.
MIT experts call this “a new perspective on the future of concrete in the energy transition.”
(according to Securitylab)
Source

























































































Comment (0)