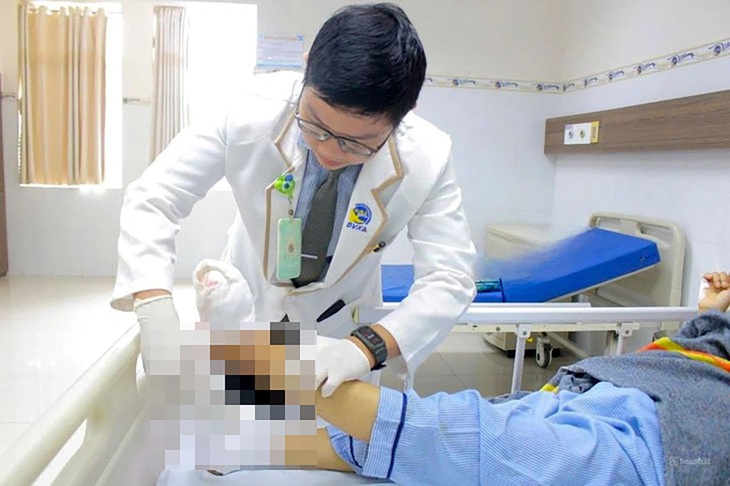
Patients with foot ulcers due to complications of diabetes are treated by doctors - Photo: Provided by the hospital
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, monitoring blood sugar and adhering to treatment will help reduce the risk of complications from type 2 diabetes, leading to a healthier life.
Why diabetes?
Some foods, when eaten, are converted into sugar by the body. Insulin is a substance secreted from pancreatic beta cells that transports sugar from the blood into the body's organs.
Type 2 diabetes occurs when pancreatic beta cells do not produce enough insulin or when insulin resistance in target organs such as muscles, fat tissue, and liver causes blood sugar levels to increase.
Typical symptoms of diabetes include: increased thirst, increased hunger, frequent urination, weight loss, itching or numbness in the hands or feet, susceptibility to infection, slow wound healing, blurred vision, dark skin, often in the armpits and neck.
Accordingly, risk factors leading to diabetes include: excess fat accumulation in the abdomen, family history of type 2 diabetes, lack of exercise, overweight or obesity, hypertriglyceridemia, over 35 years old, diagnosed with prediabetes.
Dangerous complications of type 2 diabetes
Cardiovascular disease: Patients with type 2 diabetes have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease than the general population, such as coronary heart disease, stroke, peripheral artery disease, and high blood pressure.
Diets high in sugar often have low HDL (good fat) and high LDL and Triglyceride (bad fat), increasing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Additionally, high blood sugar reduces the elasticity of blood vessels, leading to constriction and restriction of blood flow. This leads to reduced blood flow and oxygen, increasing the risk of damage to large and small blood vessels.
Diabetic kidney disease: As glucose is not absorbed, it accumulates in the blood and moves out of the body through the kidneys. High blood glucose levels damage the blood vessels of the kidneys, leading to kidney failure.
Diabetic neuropathy: High blood glucose levels also damage small blood vessels, reducing the amount of oxygen and nutrients reaching the nerves.
Furthermore, high blood glucose levels also affect nerve chemicals, reducing the ability to transmit nerve impulses, causing pain and numbness, especially in the fingers and toes.
Diabetic retinopathy: High blood glucose levels damage the blood vessels of the retina, causing blindness. Glucose also increases the risk of cataracts and glaucoma.
Skin problems: Diabetes increases your risk of skin problems, such as bacterial and fungal skin infections.
Alzheimer's disease: High blood sugar levels increase beta-amyloid protein, which increases the risk of Alzheimer's disease.
Sleep disorders: Diabetes affects central control of breathing and can also lead to obstructive sleep apnea.
Treatment of type 2 diabetes usually comes in two forms, including non-drug (diet and regular exercise: walking or jogging daily, or swimming at least 150 minutes/week... small, regular diet rich in fiber; weight loss), and drug (taking hypoglycemic drugs; insulin injections).
How to prevent diabetes
To prevent diabetes, it is necessary to maintain a normal weight index (BMI: 18.5 - 23).
Exercise regularly; eat lots of fiber and protein, reduce fat and saturated fat; reduce sugar and sweet fruits.
The author of the article, Dr. Tran Thi Kim Thanh, is currently the head of the Department of Cardiology IV, Department of Cardiology and Metabolism, Tam Duc Heart Hospital. She has many years of experience in the field of cardiovascular and endocrinology, specializing in echocardiography and cardiovascular rehabilitation.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/dai-thao-duong-type-2-am-tham-gioo-rac-7-bien-chung-nguy-hiem-20250320122637317.htm




![[Photo] Editor-in-Chief of Nhan Dan Newspaper Le Quoc Minh receives Iranian Ambassador Ali Akbar Nazari](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/26/269ebdab536444818728656f8e3ba653)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong attends the 90th Anniversary of Vietnam Militia and Self-Defense Forces](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/26/678c7652b6324b29ba069915c5f0fdaf)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam receives Singaporean Prime Minister Lawrence Wong](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/26/4bc6a8b08fcc4cb78cf30928f6bd979e)
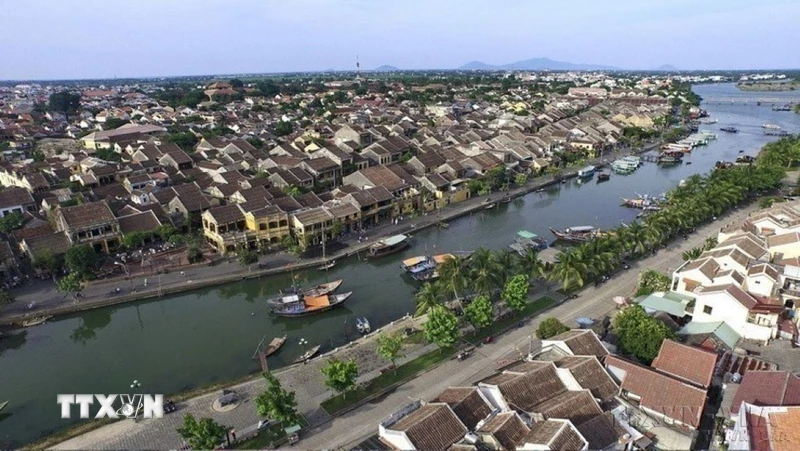
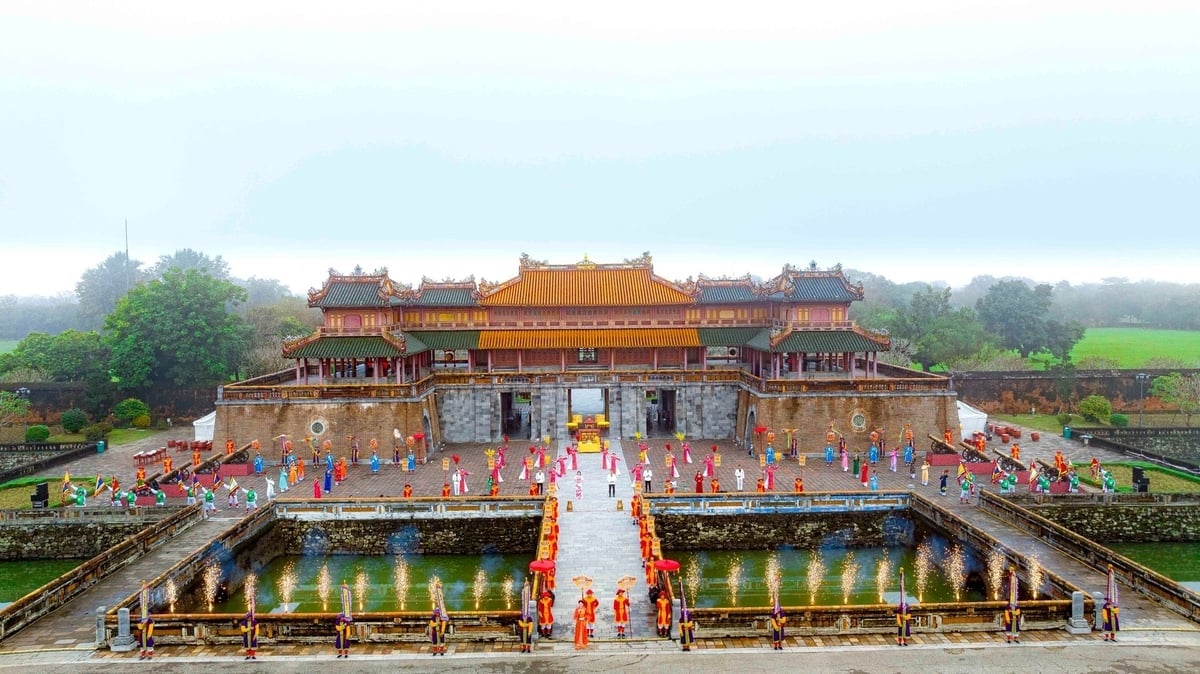


























































![[6pm News] Proposal to keep 11 provinces unchanged, including Thanh Hoa](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/3/26/2ffa21acb3844cd78a9433fec227511d)














Comment (0)