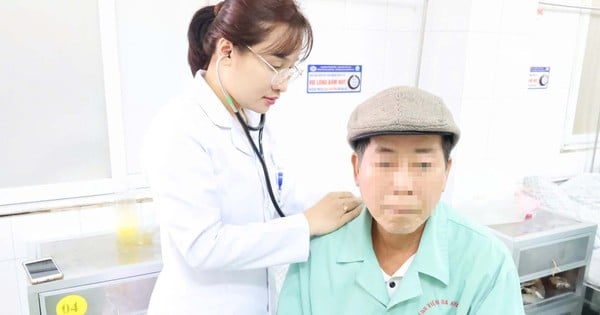
According to the Central Hospital for Tropical Diseases, blood biochemistry test is a common medical test that measures the concentration of certain chemicals in the blood, thereby helping to assess the function of certain parts and organs in the body such as the liver and kidneys.
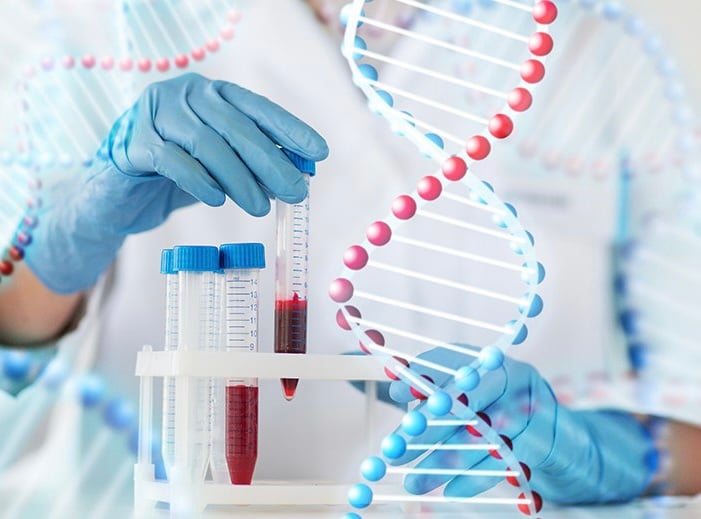

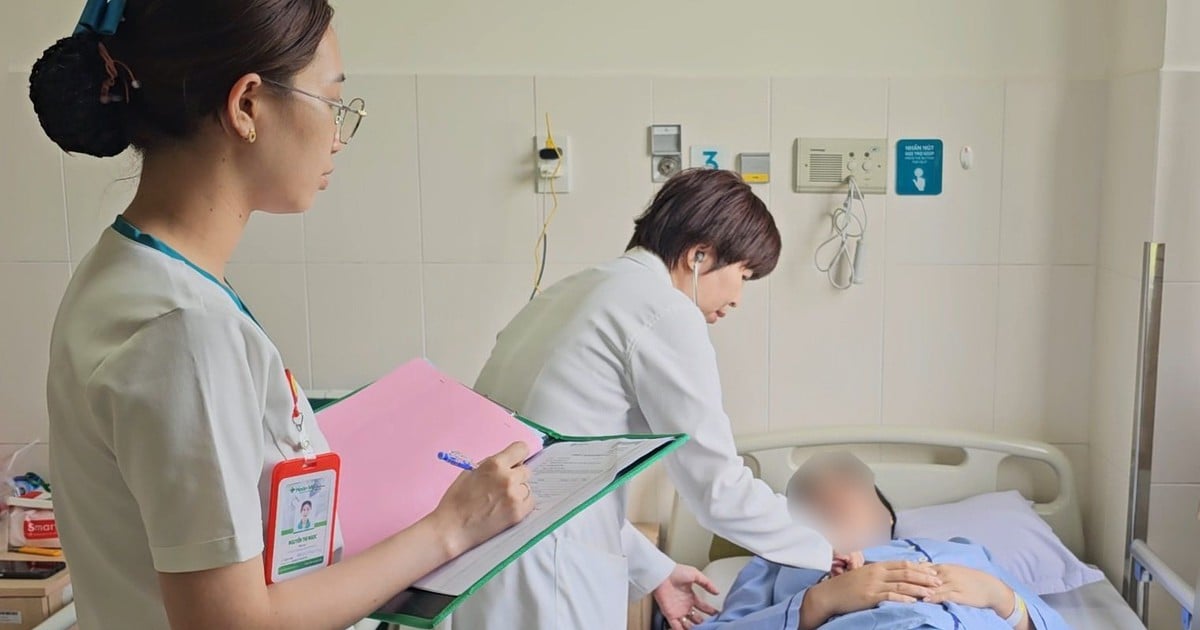
Blood biochemistry tests help assess health status
Basic blood biochemistry test indicators include: liver function assessment group: AST, ALT, GGT, ALP. In addition, there are Albumin, Bilirubin, NH3, LDH; kidney function assessment: urea, creatinine, eGFR; diabetes: glucose, HbA1c; blood lipids: cholesterol, triglyceride, HDL-C, LDL-C; gout: uric acid; nutritional status: protein, albumin.
In specific cases, doctors may order tests for other indicators (such as inflammation, minerals, pancreas, cardiovascular...): CRP, ASO, RF, calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, Lipase, Amylase, CK, CK-MB, LDH...
Or hormone tests, cancer screening such as: FT3, FT4, TSH, CA153, CA125, CEA, AFP, PIVKA II, TG, ViTD...
Cases requiring blood biochemistry tests
Regarding the time to do a blood biochemistry test, Master Ha Van Dai (Department of Biochemistry, Central Hospital for Tropical Diseases) said that the examining doctor will advise the patient in detail about the appropriate time to do a blood biochemistry test after discussing the patient's personal and family medical history.
However, in general, blood biochemistry tests are often performed in the following main cases: periodic health check-ups or when the body shows abnormal signs related to liver, kidney, cardiovascular diseases... such as: fatigue, frequent or little urination, nausea, vomiting...
Blood biochemistry tests are also indicated when the body shows abnormal symptoms that are not related to the disease mechanism, such as signs of fatigue due to chronic blood loss from a gastric or duodenal ulcer...
Meaning of blood biochemistry test results
On the text showing the results, in addition to the patient's test results, reference indicators of the normal population are also displayed to support the doctor in concluding whether the indicators and health status of the tested person are "normal" or possibly "abnormal".
"However, the conclusion of the test results depends on a number of factors, including gender, age, previous medical history as well as current medical condition. From there, the doctor will have a way to monitor the progression of the disease and evaluate the appropriate treatment method," added Dr. Dai.
In case the doctor receives abnormal results, it may be necessary to re-examine. If the results are determined to be abnormal, the patient should be referred to the appropriate specialist to find out the suspected diseases and treat them early. Conversely, if the results are normal, these parameters should also be stored as reference values for future examinations.
Source link


![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)



























![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)
























































Comment (0)