Advantages of attracting investment
According to data from the General Statistics Office, as of May 20, 2023, there were 962 newly licensed foreign direct investment (FDI) projects with a registered capital of 5.26 billion USD, an increase of 66.4% over the same period last year in terms of the number of projects and an increase of 27.8% in terms of registered capital. With the extremely close relationship between industrial park (IP) real estate and FDI, the amount of capital flowing into Vietnam shows that the potential for development of this type is still very large.
In addition, many industrial parks in Vietnam are still attracting the attention of many foreign enterprises due to the trend of moving production factories out of China to spread risks. With political stability and a key location, Vietnam is an attractive destination for many large enterprises in the world.
A report from the Foreign Investment Agency - Ministry of Planning and Investment also shows that in the first 5 months of 2023, the total registered foreign investment capital in Vietnam reached more than 5.26 billion USD, an increase of 27.8% over the same period in 2022. There are 82 countries and territories investing in Vietnam. Singapore leads with a total investment capital of more than 2.53 billion USD, accounting for more than 23.3% of the total investment capital in Vietnam, followed by Japan, China and Taiwan, Hong Kong (China), South Korea... focusing on provinces and cities with many advantages in attracting investment.
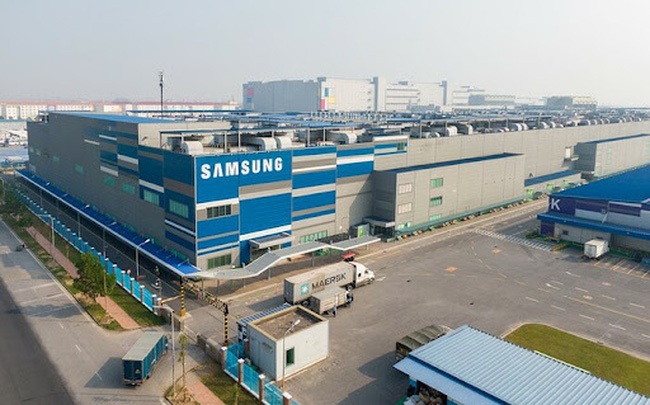

Vietnam still attracts many large enterprises thanks to its inherent advantages.
Vietnam’s strength also comes from its attractive rental prices compared to many countries in the region. According to some reports, Vietnam’s industrial park rental prices are currently 30-36% lower than those in Indonesia, Malaysia, Thailand and on par with the Philippines. Regarding the exchange rate, the fluctuations in the US dollar/VND are not much compared to other countries, thereby helping investors minimize losses when deciding to invest.
This type is also interested by the Government and is being developed in transport infrastructure, helping to solve outstanding problems in logistics, directly supporting the industrial park real estate industry. Logistics costs in Vietnam account for about 16.8% of the value of goods, while this cost in the world is only about 10.6%.
With the increasingly developed transport infrastructure, projects such as Ring Road 3 in Ho Chi Minh City, Ring Road 4 in Hanoi and especially the North-South Expressway are being promoted, which will be factors helping Vietnam's industrial park real estate increase its competitiveness, aiming for long-term development.
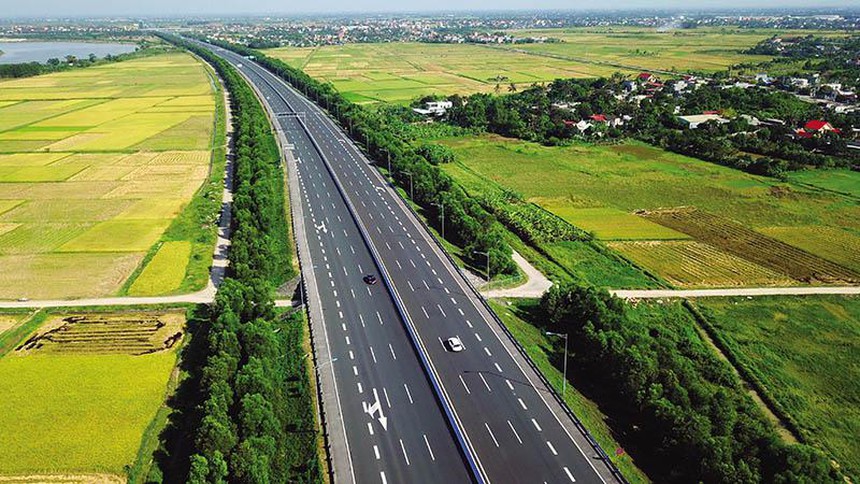

The development of transport infrastructure is promoted to greatly support the development of industrial park real estate.
Commenting on the investment prospects in Vietnam, Mr. Morgan Ulaganathan, Director of Property Services & Tourism - Hotel Advisory, Colliers Vietnam, Executive Board Member, Singapore Chamber of Commerce Vietnam, said that Vietnam has a strategic position to become a logistics hub thanks to its potential to help businesses save significantly on transportation costs. Vietnam's labor productivity is relatively competitive compared to other countries in the region. In addition, Vietnam also has a relatively stable political system, good domestic consumption and economic openness.
According to this expert, land rental prices in Vietnam are quite competitive compared to other emerging markets, which are big pluses for industrial real estate. Although some recent developments such as global minimum taxes and geo-economic fragmentation will certainly impact FDI flows into emerging markets, including Vietnam.
There are still many challenges ahead.
With great potential and advantages, like other types of real estate, industrial park real estate is facing supply problems due to legal procedure problems.
In the Southern market, there has been no new supply of industrial real estate since the last 6 months of 2022 since the sharp increase in supply at the beginning of the year. This market will face difficulties in implementing new projects in 2023. In the North, due to later development, the industrial land fund of the Northern market is still abundant and at reasonable prices.
The reason for the shortage of supply is pointed out in a recent report by VNDirect, which is due to the dispersion of industrial park development planning and decisions made by localities. In particular, the change of senior leaders in many localities in recent times has also slowed down the project approval process. This has led to impacts on slow site clearance and overlapping planning. Although more projects have been approved recently to improve this situation, the shortage of supply will last at least until the end of 2023.
In addition, a new challenge for the industrial park real estate industry has also emerged, which is the “global minimum tax”. This is one of the two main pillars of the Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (BEPS) Program initiated by the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) and has been agreed upon by more than 140 countries.
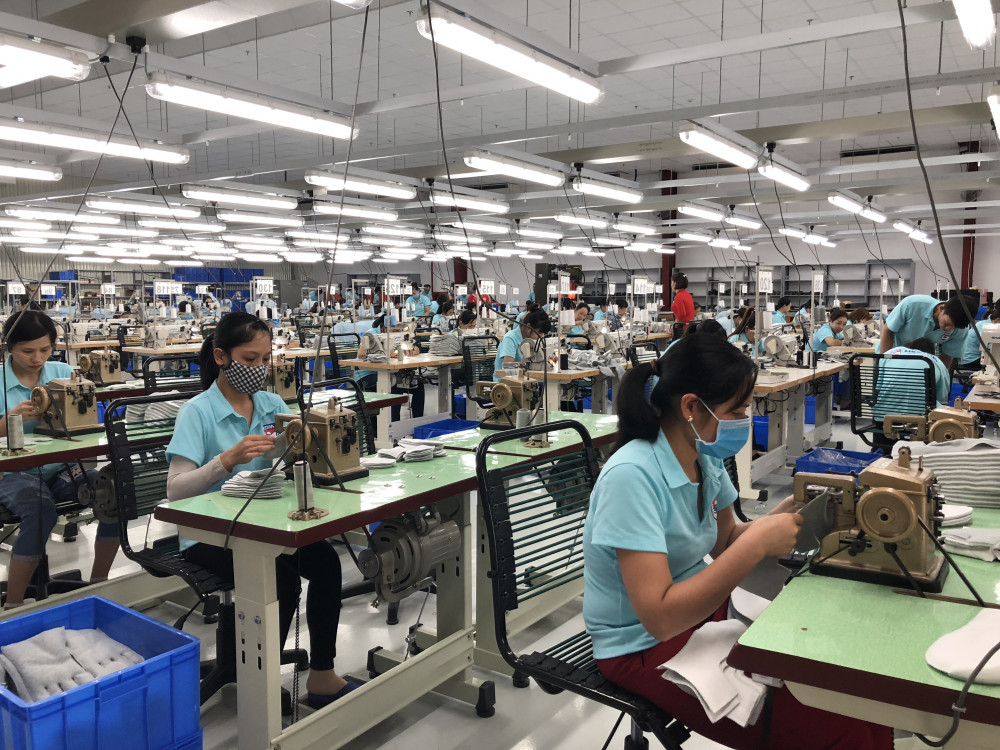

This type still has many challenges in the future such as labor costs, supply or the new issue of "Global Minimum Tax".
Accordingly, the global minimum tax rate is 15%, applied to multinational companies with total revenue of 750 million EUR (or 800 million USD) or more in 2 of the 4 most recent consecutive years. OECD estimates that with the application of pillar 2, total global tax revenue from multinational companies will increase to 220 billion USD.
The global minimum tax policy is required to be applied from January 1, 2024. According to experts, the global minimum corporate tax rate of 15% will cause many concerns about the trend of strategic disruption in investment locations, the way multinational companies operate as well as FDI attraction strategies if the response is slow.
Currently, Vietnam is using tax incentives as a financial leverage tool to attract foreign investors by applying tax rates of 10%, 15% and 17% depending on the sector, industry, scale and location of investment. In some special cases, preferential tax rates can be at 5%, 7% and 9%. However, these incentives will no longer be effective when the global minimum tax policy is applied, thereby somewhat affecting Vietnam's prospects of attracting FDI in the coming years.
In addition, Vietnam's advantage in low labor costs has decreased significantly. In 2013-2014, the average worker's salary in Vietnam was 162 USD/month, equal to 75% of India; 69% of Indonesia and 44% of Thailand. Meanwhile, in 2022, the average worker's salary in Vietnam increased to 277 USD/month, equal to 84% of India; 74% of Indonesia and 72% of Thailand. Vietnam's expected wage increase rate in 2023 is 5.9%, leading Southeast Asia, and only behind India (8.7%), while the labor productivity of Vietnamese workers has not increased as expected by businesses.
The country currently has about 563 industrial parks in planning in 61/63 provinces and cities; 397 industrial parks have been established; 292 industrial parks have been put into operation with a total natural land area of about 87.1 thousand hectares, industrial land area of about 58.7 thousand hectares. In addition, there are 106 industrial parks under construction with an industrial land area of about 23.8 thousand hectares.
By the end of the first quarter of 2023, the occupancy rate of level 1 industrial parks nationwide continued to increase, reaching over 80%, of which the Southern region averaged 85% (leading the country).
In key markets in the North and South, industrial park occupancy rates will remain above 90% in 2022. Some industrial parks in Hanoi, Ho Chi Minh City, Dong Nai, Bac Ninh, Bac Giang, and Binh Duong are almost fully occupied. Binh Duong has the highest occupancy rate, reaching over 95%.
Source




























































































Comment (0)