Fat can accumulate in and around muscles, is difficult to detect, and poses more health risks than other forms of fat storage.
A new study published in the European Heart Journal found that increased intermuscular fat increases the risk of serious heart disease, as it affects the small blood vessels in the heart, according to the Telegraph .
Professor Viviany Taqueti, a cardiologist at Harvard Medical School who participated in the study, shared that their data showed for the first time that intramuscular fat tissue is potentially much more risky than other types of fat such as subcutaneous fat, epicardial fat around the heart, or fat in the liver.
Some people have a condition called thin on the outside, fat on the inside (TOFI), where they are not overweight but they still have fat stored in their muscles.
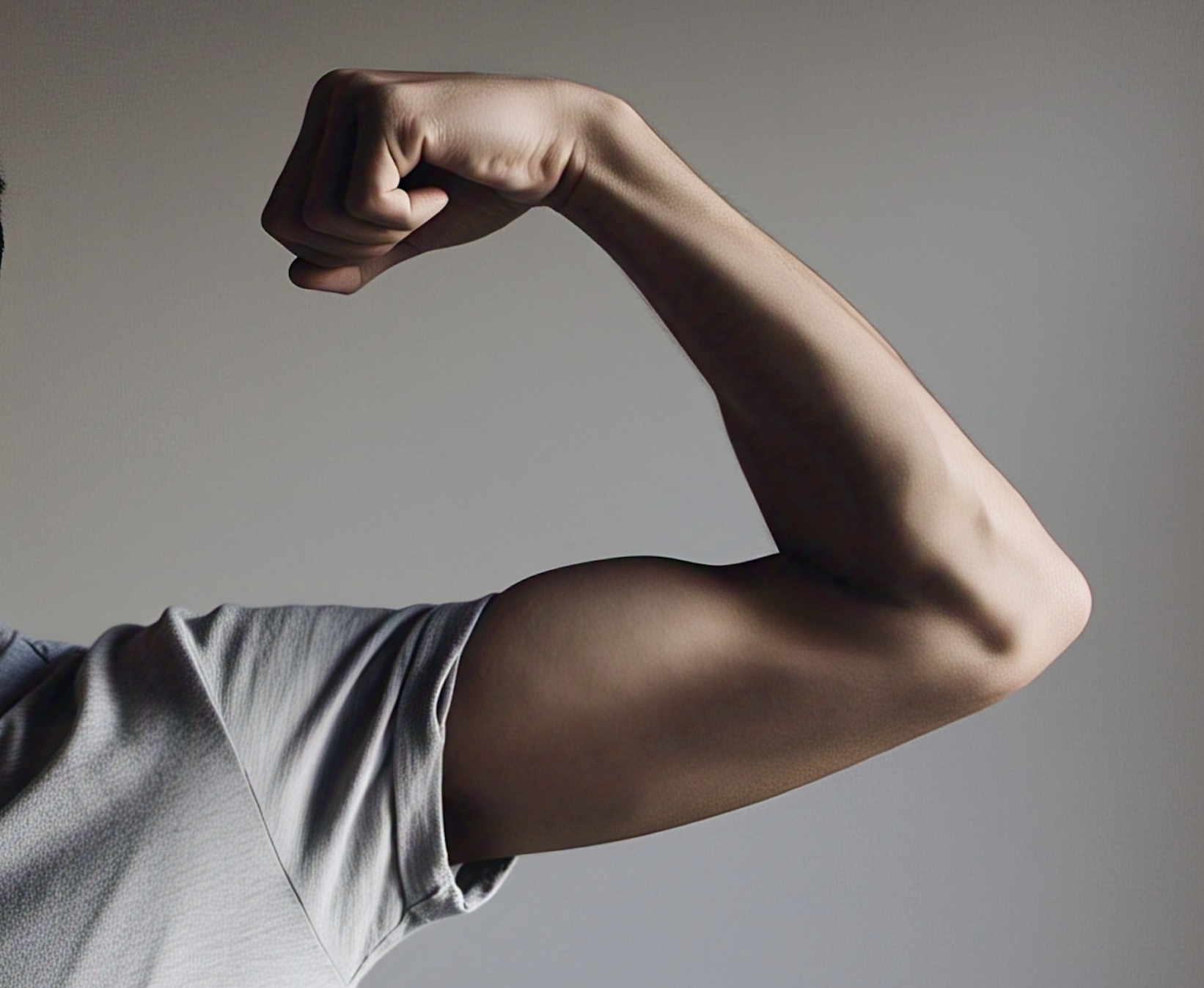

Avoid fat accumulation in and around the muscles to keep the body healthy.
As you age, you accumulate more fat, says Dr. Bret Goodpaster, chief scientific officer at Advent Health. So, older people with the same BMI as younger people are still likely to accumulate more muscle fat.
In other words, if you are at a healthy weight, don't smoke, and eat a healthy diet, but have fatty tissue wrapped around your muscles, it doesn't mean you're not at risk for heart disease.
“If you have more fat in your muscles, you're more insulin resistant and at higher risk for diabetes,” adds Dr. Bret Goodpaster.
Researchers also believe that fat in and around our muscles can accumulate due to excess calories and a sedentary lifestyle.
Your muscles are less likely to accumulate fat if you keep them in good shape with regular exercise. On the other hand, if they are not strong, you are more likely to accumulate fat, which can lead to coronary microvascular disease (CMD). This leads to chest pain and in some cases heart failure.
According to studies, every 1% increase in muscle fat increases a person's risk of CMD by 2% and the risk of major cardiovascular events by 7%.
Through the study, Professor Taqueti hopes that assessing muscle fat will contribute significantly to the assessment of obesity, because according to her, using "raw data such as body mass index (BMI) is not enough".
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/vi-sao-beo-co-so-hon-beo-bung-185250305200835932.htm





![[Photo] Visiting Cu Chi Tunnels - a heroic underground feat](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/8/06cb489403514b878768dd7262daba0b)













































































Comment (0)