People with upper respiratory tract infections such as pharyngitis, tonsillitis, colds, etc. often have runny nose, sore throat, fatigue, and fever.
Most upper respiratory infections are caused by viruses that affect the nose, sinuses, throat, and voice box. Viruses spread when an infected person talks, coughs, or sneezes. When a healthy person comes into contact with respiratory droplets from an infected person, the virus can enter the mucous membranes in the mouth, nose, or eyes. A person can also become infected if they touch a surface contaminated with the virus and then touch their mouth, nose, or eyes.
Symptoms of an upper respiratory infection usually begin 1-5 days after exposure to the pathogen. Most people experience mild to moderate discomfort for 1-2 weeks, but symptoms can last up to 3 weeks. Common symptoms of an upper respiratory infection include: runny nose, nasal congestion, sneezing, sore throat, cough, fatigue, mild body aches, headache, watery eyes, and low-grade fever.
Symptoms may go away on their own, but patients should see a doctor if: the illness lasts more than 10 days without improvement, shortness of breath, high fever, chest pain, worsening cough, change in color of mucus when coughing.
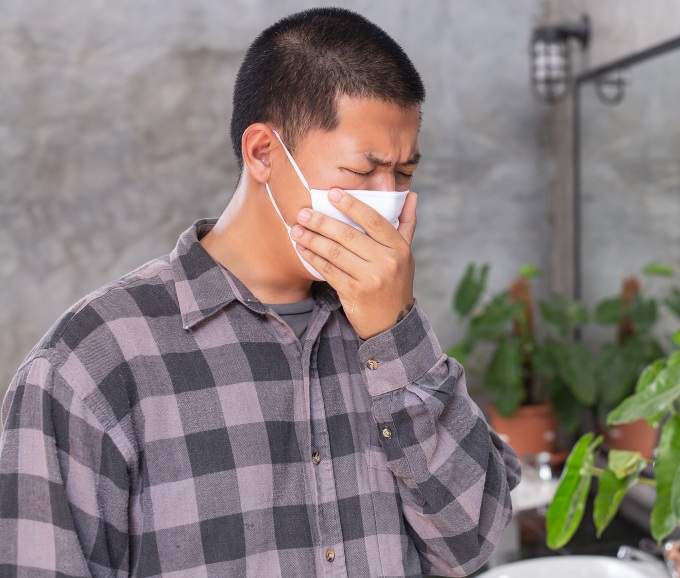

Sore throat, fatigue, and discomfort are common symptoms of respiratory infections. Photo: Freepik
Types of infections and risk factors
Common types of upper respiratory tract infections include:
Common Cold: More than 200 viruses can cause the common cold. Symptoms appear a few days after exposure and last 1-2 weeks.
Flu: This disease is caused by the influenza virus and has many different strains, which change every year.
Sinusitis: A sinus infection occurs when fluid builds up in the sinuses — air-filled cavities in the forehead, nasal cavity, cheeks, and around the eyes. Sinusitis can be acute (less than 4 weeks), subacute (4-12 weeks), or chronic (more than 12 weeks).
Laryngitis: Laryngitis can occur due to infection and cause hoarseness or loss of voice.
Pharyngitis: Pharyngitis or a sore throat is caused by a viral infection, like the common cold.
Tonsillitis: Tonsillitis is more common in children and is usually caused by a viral infection or a bacterial infection such as strep throat.
Factors that increase the risk of the disease include: close contact with sick people, smoking or exposure to secondhand smoke, weakened immune system, living in an environment with air pollution, abnormalities in the upper respiratory tract due to facial trauma, upper respiratory tract trauma or nasal polyps...
In addition to taking medication as prescribed by your doctor, home remedies for upper respiratory tract infections include: resting, drinking plenty of water, gargling with salt water, and steaming. Getting plenty of rest helps your body recover faster. Drinking plenty of water can reduce congestion and prevent dehydration. Gargling with salt water helps eliminate some of the pathogens and relieve sore throat. Steaming and hot baths also help reduce nasal congestion and cough.
To prevent disease, people should wash their hands frequently with soap and water, especially after being in public places; avoid close, prolonged contact with sick people; and do not touch their face, nose or mouth with their hands, especially when in public places. In addition, a healthy diet and regular exercise also help strengthen the immune system and prevent disease.
People can prevent the spread of germs and viruses by covering their nose and mouth with a tissue when sneezing and coughing; staying home when sick; cleaning countertops, doorknobs, and children's toys when someone is sick; and wearing a mask when in contact with others.
Kim Uyen (According to Health )
Source link




![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City speeds up sidewalk repair work before April 30 holiday](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/17f78833a36f4ba5a9bae215703da710)

![[Photo] Capital's youth enthusiastically practice firefighting and water rescue skills](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3f8481675271488abc7b9422a9357ada)





















































































Comment (0)