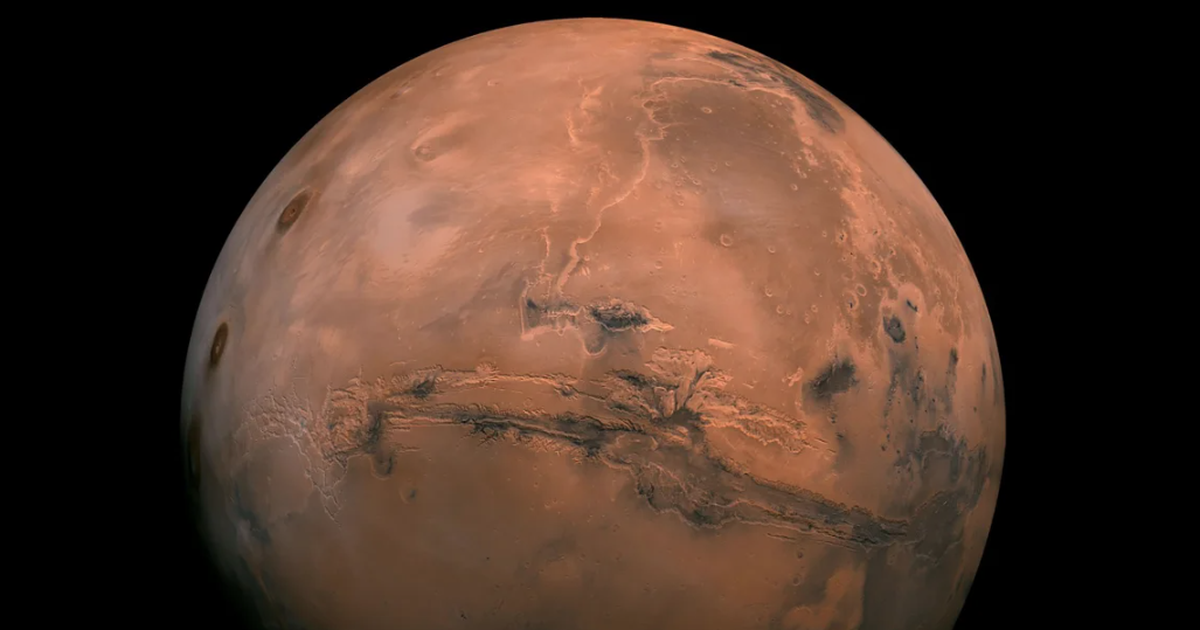
According to new research published in the scientific journal Nature Communications Earth & Environment, NASA experts say tiny creatures may be hiding beneath the ice of the red planet.
 |
| Although experts have yet to find any direct evidence of life on Mars , a new NASA study suggests that tiny creatures may be hiding beneath the red planet's ice. |
 |
| "If we're trying to find life anywhere in the universe today, the ice fields on Mars may be one of the most accessible places we should look," said lead author Aditya Khuller of NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) of the new study published in the journal Nature Communications Earth & Environment. |
 |
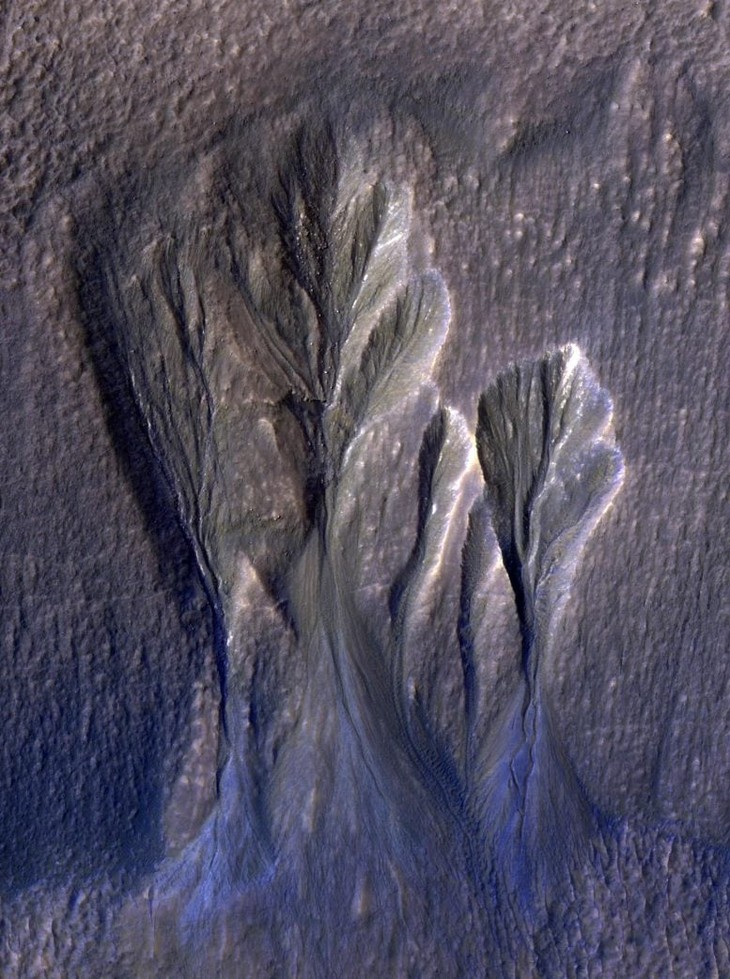
| Mars has two types of ice: water ice and carbon dioxide ice. The new study focused on the former. Khuller and his colleagues looked at water ice — large amounts of water ice that formed from snow mixed with dust that fell on the surface during the Red Planet ’s series of ice ages over millions of years. This process formed ice and scattered dust particles. |
 |
| Although dust particles can obscure light in deeper layers of ice, they play an important role in explaining how underground pools of water can form in ice exposed to the Sun. |
 |
| The black dust absorbs more sunlight than the surrounding ice, potentially causing the ice to warm and melt several dozen centimeters below the surface. |
 |
| On the Red Planet, atmospheric effects make melting difficult on the surface, but these obstacles would not exist below the surface of a dusty snow layer or glacier. |
 |
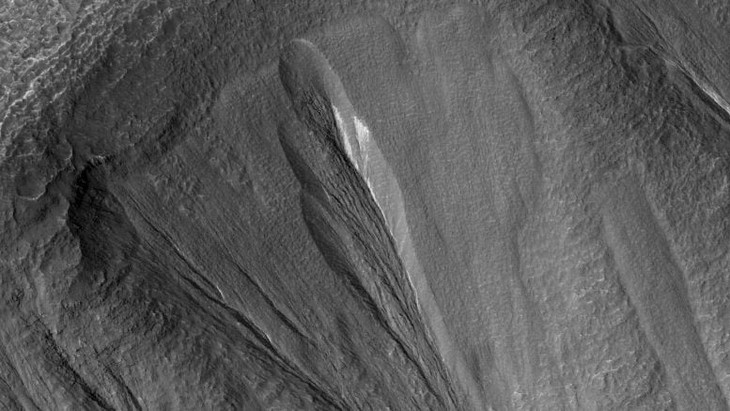
| On Earth, dust in ice can create cryoconite holes. These are small cavities that form in ice as windblown dust particles fall into it, absorbing sunlight and melting deeper into the ice each summer. Eventually, as the dust particles move farther away from the Sun, they stop sinking but still get hot enough to create a pocket of meltwater around them. |
 |
| Co-author Phil Christensen of Arizona State University in Tempe, USA, said this is a common phenomenon on Earth. Thick snow and ice can melt from the inside out, letting sunlight in to warm it like a greenhouse, rather than melting from the top down. |
 |
| In a new study, scientists found that dusty ice on Mars allows enough light for photosynthesis to occur about 3 meters below the surface. In this case, the upper layers of ice prevent shallow pools of water below the surface from evaporating and also provide protection from harmful radiation. |
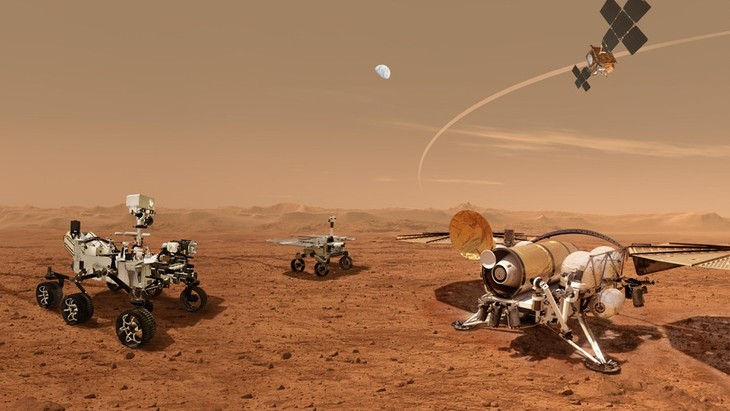 |
| Experts say frozen water with the highest potential to form underground pools would exist between Mars' latitudes of 30 and 40 degrees, in both the northern and southern hemispheres. |
Readers are invited to watch the video: Elon Musk shows off rockets that can go to the moon and Mars. Source: VTV24.
Source: https://khoahocdoisong.vn/nong-nasa-he-lo-noi-su-song-co-the-ton-tai-tren-sao-hoa-post251334.html


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's special meeting on law-making in April](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/13/8b2071d47adc4c22ac3a9534d12ddc17)





























![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)




























































Comment (0)