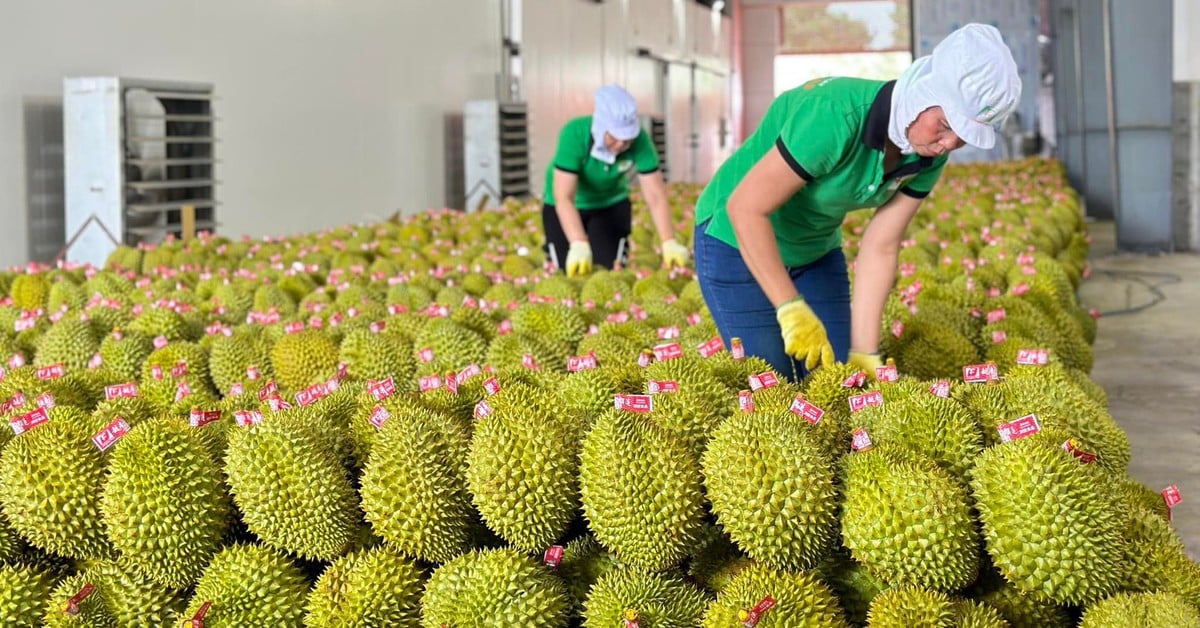
According to the Vietnam Association of Seafood Exporters and Producers (VASEP), many difficulties will continue to affect seafood production and exports in 2024. In addition, there will be other challenges that will slow down the recovery of exports next year.
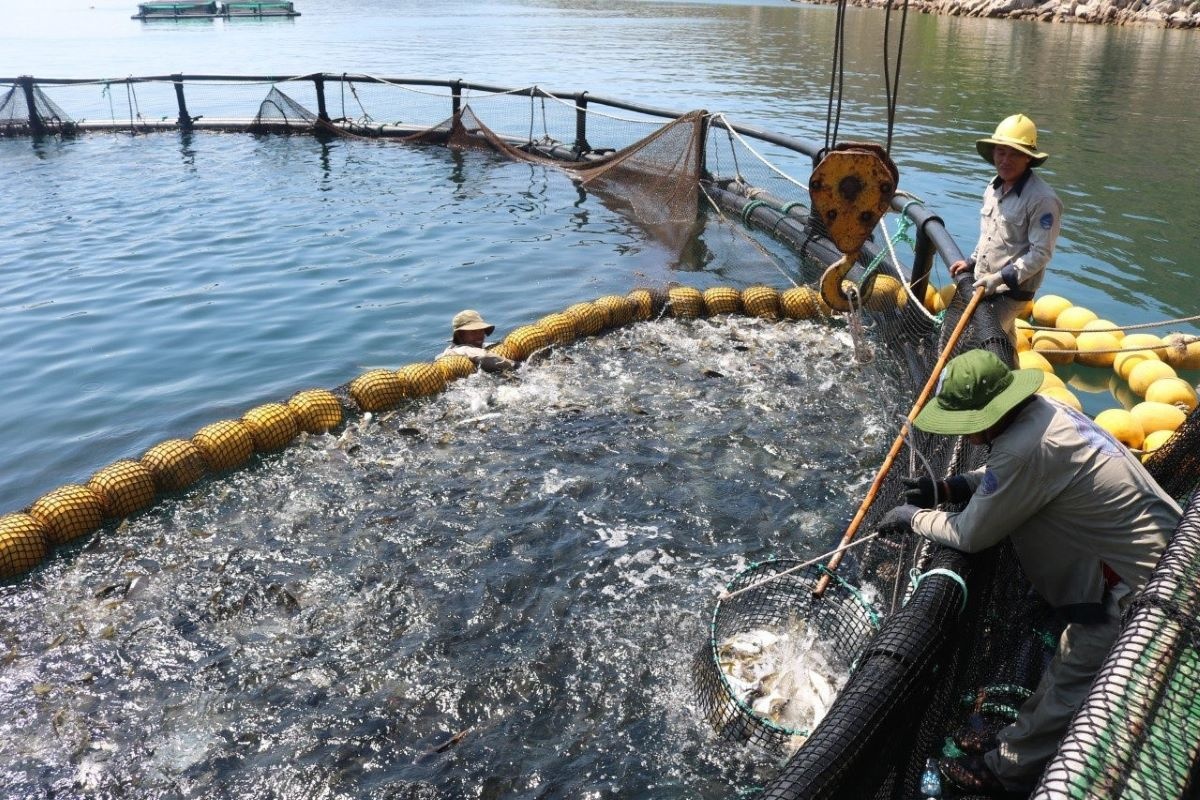 |
| Vietnam's seafood exports are forecast to gradually recover in 2024. |
VASEP has just released 10 comments on market trends and forecasts for seafood exports in 2024.
Firstly, inflation in major countries has been controlled, the world economy has bottomed out, but recovery is slow, affecting the demand for seafood consumption.
Second, the Russia-Ukraine conflict, fighting in the Middle East and other geopolitical issues around the world will certainly disrupt global trade, including seafood. The consequences will increase transportation costs and input prices for aquaculture and seafood processing. It may also cause a new inflationary storm that affects seafood consumption demand in 2024.
Third, Vietnamese shrimp will continue to compete with Ecuador and India in terms of price and supply, and the oversupply situation may continue until the first half of the year (world shrimp production in 2024 will increase by 4.8% to 5.9 million tons).
Ecuador and India are increasing their market shares in the US, China, EU and Japan, while also increasing their exports of processed shrimp, although their share is still modest.
Fourth, pangasius inventory in the US, China, and EU markets is no longer a problem. Export prices will increase again in these markets. In addition to frozen fillet products, the trend of importing value-added pangasius and by-products (fish bladders, pangasius cakes) continues to increase.
Fifth, the IUU yellow card continues to be a challenge. If it is not resolved in 2024, exports to the EU will stagnate because the procedures for confirming and certifying exploited seafood are still inadequate due to inadequate resources, human resources and infrastructure. Industries such as tuna, squid, octopus and marine fish are most affected.
Sixth, in terms of consumption, market demand focuses on cheaper segments such as canned fish, raw fish for processing canned fish, dried fish, and dried shrimp.
Seventh, the downward cycle in prices for many seafood species is likely to continue through the first half of 2024.
Eighth, feed costs continue to be a major challenge for both shrimp and pangasius farming industries.
Ninth, due to slow recovery in demand and increasing trend of cheap shrimp imports from Ecuador, shrimp exports to the US will be more difficult if anti-subsidy duties (CVD) are imposed.
Finally, Chinese market demand recovered more strongly, but paid low prices, difficult to compete.
According to VASEP, there will be a trend of increased processing prices in the Chinese seafood processing industry and China's move to ban the import of Japanese seafood will cause Japanese factories to flock to Vietnam to find processing partners. In addition, businesses may increase the import of raw materials for production and business and increase processing for the Japanese and US markets.
Vietnam's seafood exports are forecast to gradually recover in 2024 and become more positive in the second half of the year. With adaptation and adjustment to the market context, seafood businesses are predicted to help the industry's export turnover recover to 9.5 billion USD - 10 billion USD in 2024.
Of which, the shrimp industry aims for 4 billion USD, tra fish reaches about 1.9 billion USD, the rest are seafood products forecast to earn about 3.6 - 3.8 billion USD.
Source link

























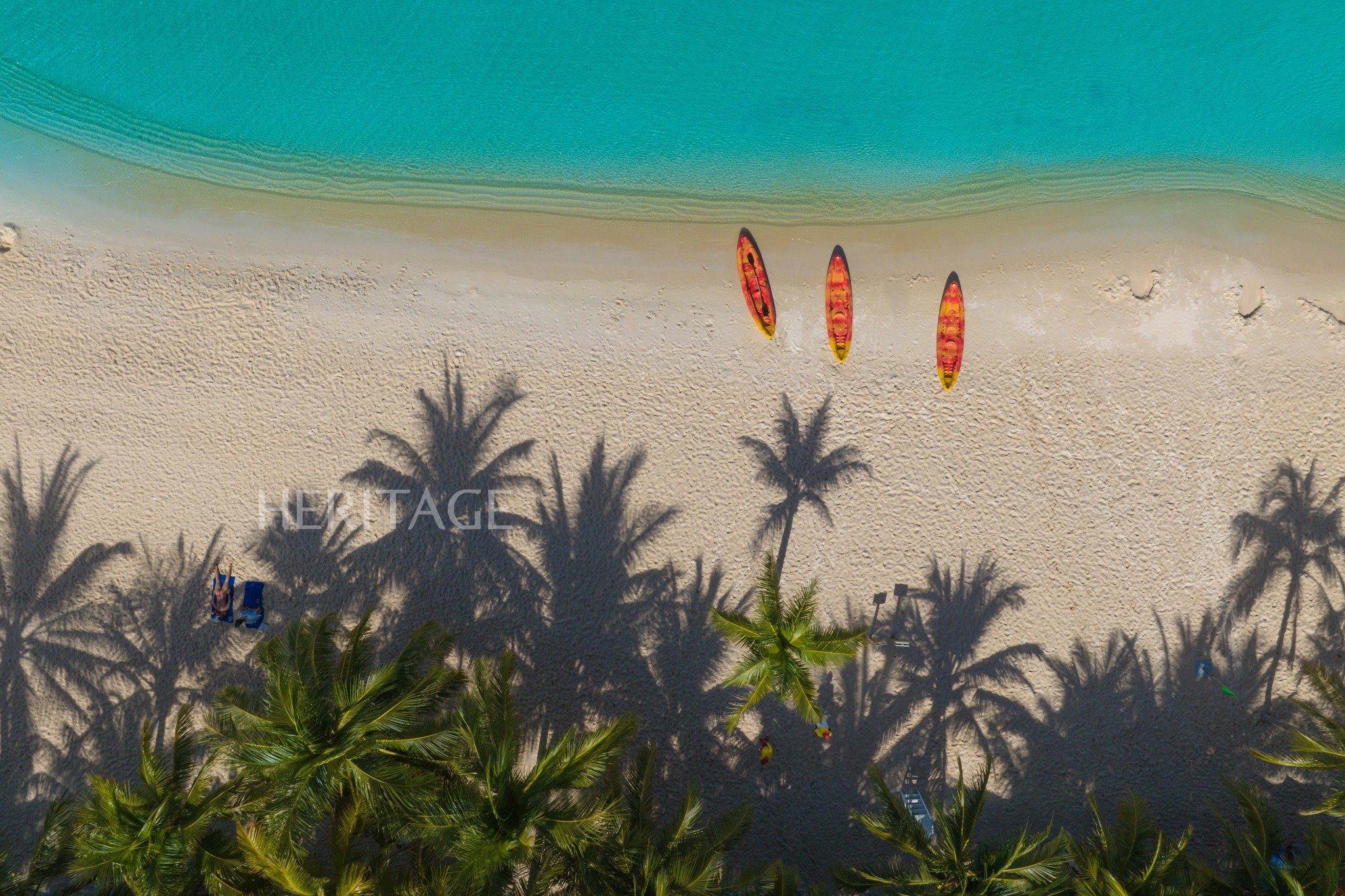
































































Comment (0)