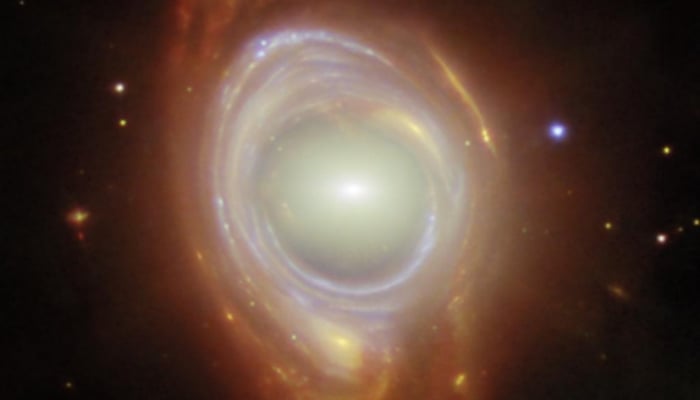
Using the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have completed the most comprehensive survey ever of the Andromeda Galaxy, the Milky Way's neighbor, creating a 417-megapixel image stitched together from more than 600 images taken over 10 years.
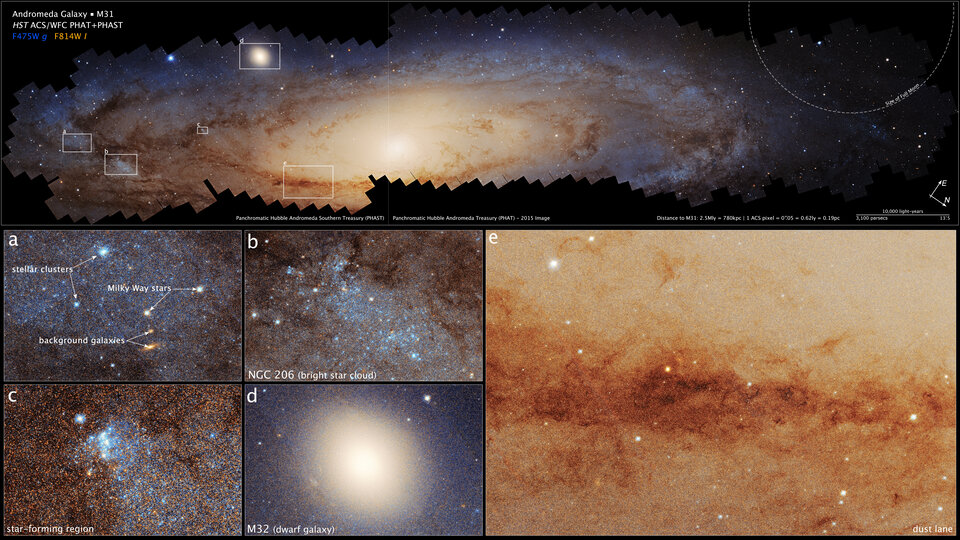
Composite image of the Andromeda Galaxy through Hubble's lens
The largest panoramic image of the Andromeda galaxy shows about 200 million stars and spans a resolution of 2.5 billion pixels, according to science.nasa.gov .
After the Hubble telescope was launched into low Earth orbit by NASA and the European Space Agency (ESA), astronomers counted more than 1 trillion galaxies in the universe.
However, only one galaxy stands out as the most important and prominent among them: the Milky Way's neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy (Messier 31).
Correct name for Andromeda galaxy
A century ago, American astronomer Edwin Hubble was the first to suggest that the so-called "spiral nebula", then identified as the Andromeda galaxy, was actually 2.5 million light-years away from the Milky Way.
Previously, astronomers had long believed that the Milky Way filled the entire universe. Therefore, overnight, Mr. Hubble's discovery completely overturned human understanding by revealing the fact that the universe is extremely large.
And Andromeda is officially identified as a galaxy, not a nebula, with over 1 trillion stars.
Astronomers can observe the Andromeda Galaxy with the naked eye on clear autumn nights, appearing as a cigar-shaped object in the night sky.
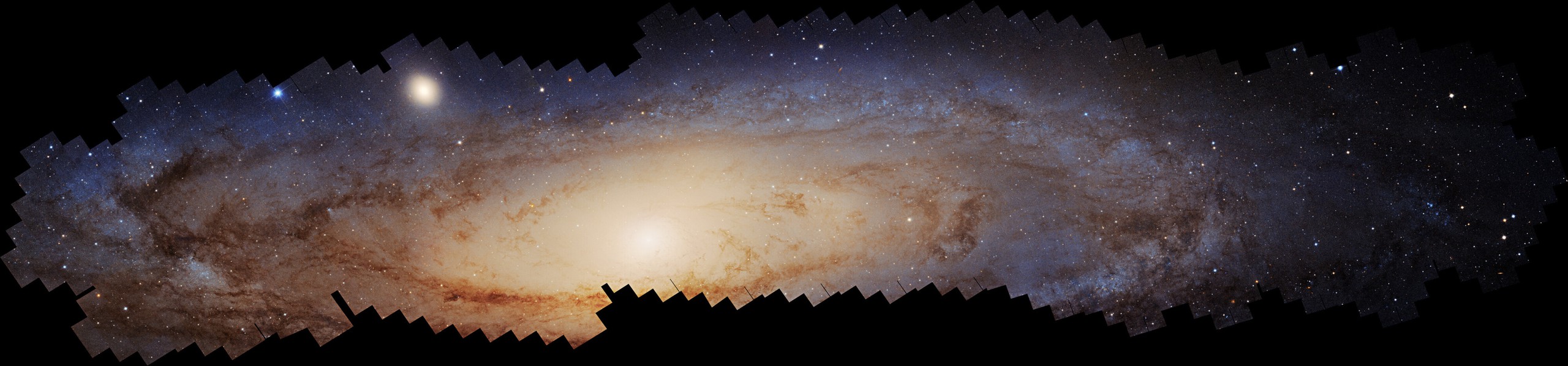

Image shows more than 200 million stars brighter than our sun in the Andromeda galaxy
The Importance of the Andromeda Galaxy
A century later, the telescope that bears his name has achieved an unprecedented feat by completing the most comprehensive survey of our neighboring galaxy. The new discovery provides clues to the Andromeda galaxy's evolutionary history, which is quite different from that of the Milky Way.
"Detailed observations of resolved stars will allow us to piece together past mergers and the history of galaxy interactions," said lead investigator Ben Williams of the University of Washington.
Without the Andromeda Galaxy as a reference for the universe's spiral galaxies, astronomers would have a much less understanding of the structure and evolution of the Milky Way. The reason is that humans are located inside our galaxy.
It is predicted that in about 4-5 billion years, the Milky Way and the Andromeda Galaxy will merge.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/kham-pha-lich-su-bi-an-cua-thien-ha-tien-nu-lang-gieng-185250117102146049.htm



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's special meeting on law-making in April](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/13/8b2071d47adc4c22ac3a9534d12ddc17)






























![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)


























































Comment (0)