Hip joint damage is a common disease in orthopedic trauma, affecting the patient's ability to walk, live and work.
Hip joint damage is a common disease in orthopedic trauma, affecting the patient's ability to walk, live and work.
Hip joint damage has many different causes: femoral head atrophy, hip osteoarthritis, femoral neck fracture, hip tuberculosis, lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, etc.
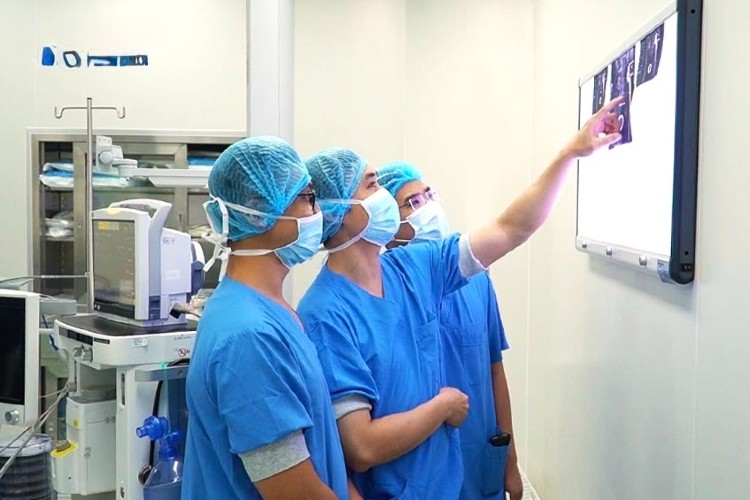 |
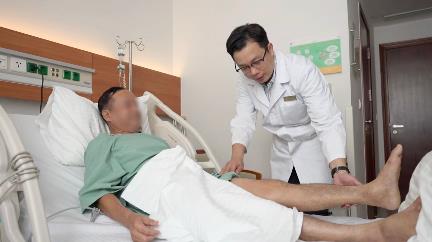
| The doctor reads the preoperative film for the patient. |
Mr. Duong, 68 years old, had a hip replacement 14 years ago, had multiple re-infections causing pain and fluid leakage, and had to have another artificial joint replacement.
Over the past 14 years, Mr. Duong has undergone three surgeries to remove the infected lesions, keeping the artificial joint, but the treatment was not complete. The pain, fever, and fluid leakage persisted, and his physical condition deteriorated. Recently, the infection spread and became severe, so he went to the hospital for treatment.
X-ray, blood test, and joint aspiration results showed bone perforation, high white blood cell count, and hemolytic staphylococcus aureus bacteria in the damaged joint area.
According to the patient's doctor, the patient had a recurrence of infection after hip replacement. If the inflammation is only localized in the external area, the patient may only need intravenous or oral antibiotics. In more severe cases, only flushing is needed, without removing the prosthesis.
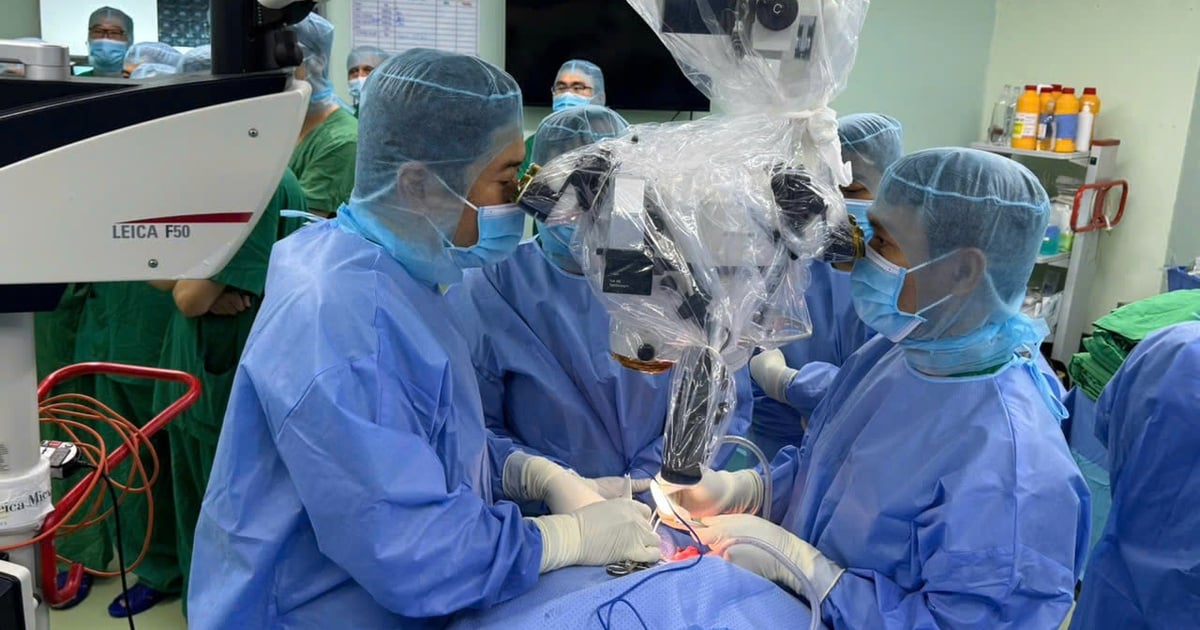
The patient had repeated infections, widespread infection, oozing wound, bone loss around the acetabulum, upper femur, even spreading into the pelvis and iliopsoas muscles, the only way left was to remove the joint. If not intervened immediately, the patient is at risk of further bone loss and loss of mobility.
In addition, the patient also had kidney failure, compensated cirrhosis, and the infection had grown high, creating a large abscess in the back. Surgery to treat the infection was quite complicated, with a lot of blood loss and the patient's weak physical condition slowing down the recovery process, with a high risk of complications, most commonly myocardial infarction.
To rule out the cause of the patient's poor health due to tuberculosis, the doctor ordered a tuberculosis culture to monitor the patient's recovery. The tuberculosis test was negative. After a month of intensive care, the patient recovered enough to undergo surgery.
MSc. Nguyen Quang Ton Quyen, Deputy Head of the Department of Orthopedics and Traumatology, Tam Anh General Hospital, Hanoi, hip replacement is an advanced surgical treatment method, helping to restore range of motion to the joint in cases of degenerative joint deformity and femoral head necrosis.
However, there are still some postoperative complications, about less than 2% of patients experience serious complications, typically hip joint infection.
There are many causes of infection after hip replacement, one of which is an unsanitary surgical environment. The artificial materials used for joint replacement provide a place for bacteria to adhere and develop biological barriers, helping them hide and avoid the body's immune system.
Bacterial infections can occur in the skin, soft tissues around the joint, or spread deep into the artificial joint. Infections can occur during a hospital stay, after discharge, or many years after surgery.
Treatment of infection after joint replacement is more complicated and expensive than joint replacement. Doctors recommend that patients who have sudden sharp pain in the joint after 2-3 weeks of artificial joint replacement, redness of the skin around the surgical wound, high fever, night sweats, fatigue, etc., should see a doctor.
Source: https://baodautu.vn/nhiem-trung-sau-nhieu-lan-thay-khop-hang-d228994.html





![[Photo] Capital's youth enthusiastically practice firefighting and water rescue skills](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3f8481675271488abc7b9422a9357ada)
![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City speeds up sidewalk repair work before April 30 holiday](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/17f78833a36f4ba5a9bae215703da710)




















































































Comment (0)