Sports injuries such as torn ligaments and sprained ankles are common causes of cartilage damage, increasing the risk of osteoarthritis later on, even after treatment.
Master, Doctor, Doctor Dao Duy An Duy, Orthopedic Trauma Center, Tam Anh General Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City, shared the above information, further explaining that cartilage is located between the two ends of the bones of the joint, with the function of protecting and reducing friction in the joint. If the cartilage is damaged and worn, the ends of the bones rub against each other when the patient moves, causing osteoarthritis.
A torn or ruptured anterior cruciate ligament is one of the most common sports injuries, according to Dr. Duy. If not treated promptly, this condition can cause cartilage damage, leading to osteoarthritis. Patients suffer from long-term pain, reduced mobility, and face the risk of disability and needing joint replacement later.
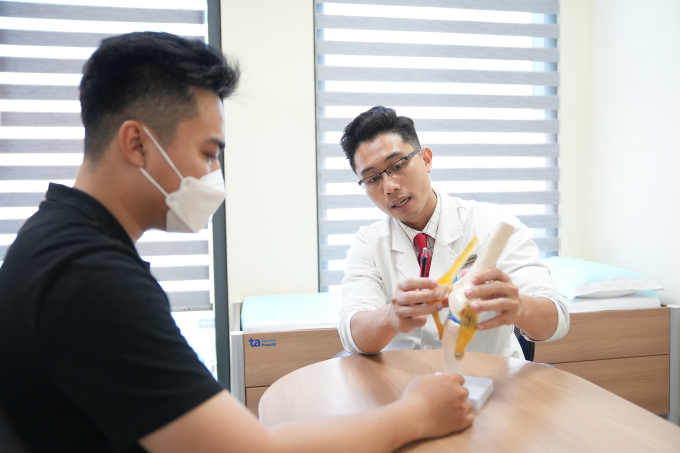

Doctor Duy consults on joint health for a patient at Tam Anh General Hospital. Illustration photo: Provided by the hospital
Dr. Duy cited several studies showing that about 50% of people with complete ACL ruptures develop osteoarthritis within 12-14 years after surgery, three times higher than those without the injury. Even mild ligament injuries that do not cause discomfort at the time of occurrence can damage the articular cartilage. In addition, other injuries that have recovered but recur frequently still increase the risk of osteoarthritis in the future.
All sports have the effect of improving overall health, maintaining a healthy weight, thereby slowing down the process of joint degeneration. Dr. Duy notes how to reduce the risk of injury when playing sports below.
Choose the right sport : Soccer, basketball... with the characteristics of high speed movement and frequent sudden changes in direction can easily lead to injury, especially in the ligaments. Practicing yoga, swimming... properly helps significantly reduce the risk of injury.
Yoga or tai chi are forms of exercise that focus on improving neuromuscular coordination; enhancing balance and coordination of body movements. Swimming or cycling, on the other hand, help develop strength, flexibility, balance and endurance.
Exercise at a moderate intensity : Overtraining increases the risk of injury and accelerates joint degeneration. Avoid sudden increases in activity intensity, only increasing by 10% every one to two workouts. Do not overexert yourself, especially if you are tired, in pain, or experiencing other unusual symptoms.
The body needs adequate rest and recovery time by training one day, resting one day, or alternating between heavy and light training sessions.
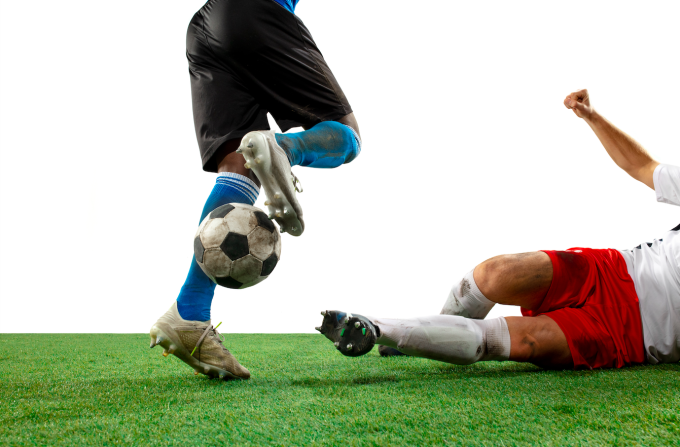

Highly competitive sports like football are prone to injury. Illustration: Freepik
Full stretching : Warming up before exercise and cooling down after exercise effectively reduces injuries. Stretching, twisting, running in place at low intensity... helps the body transition from a resting state to a state of exercise. Heart rate, breathing rate and body temperature gradually increase to prepare for higher intensity physical activity.
At the end of the workout, you should stretch again. At this time, stretching movements create an opportunity for muscles to recover quickly, reduce fatigue after exercise, and help eliminate toxins and waste accumulated in the muscles during physical exercise.
Phi Hong
| Readers send questions about musculoskeletal diseases here for doctors to answer |
Source link


![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)


![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)























![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)




























































Comment (0)