(NLDO) - From a world 13 billion years ago, 6 "ghost" objects have broken the very things that were once considered "breaking cosmology".
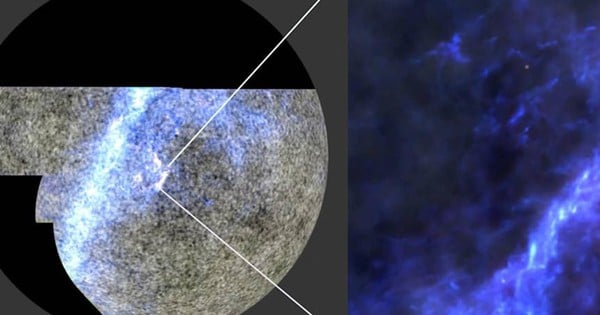
A study recently cited by NASA has decoded the nature of one of the most mysterious objects captured by the James Webb Space Telescope since its early days of operation: "Little Red Dots" (LRDs).
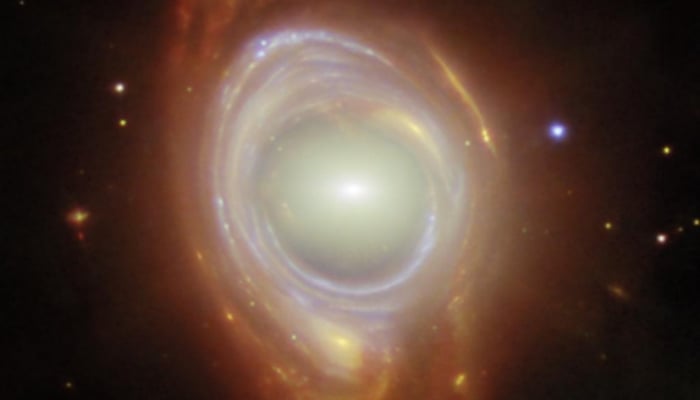
NASA images recently released show six such LRDs, existing in distant space, when the universe was only 600 million to 1.5 billion years old.
The above objects all appear bright red, meaning they have a high redshift.
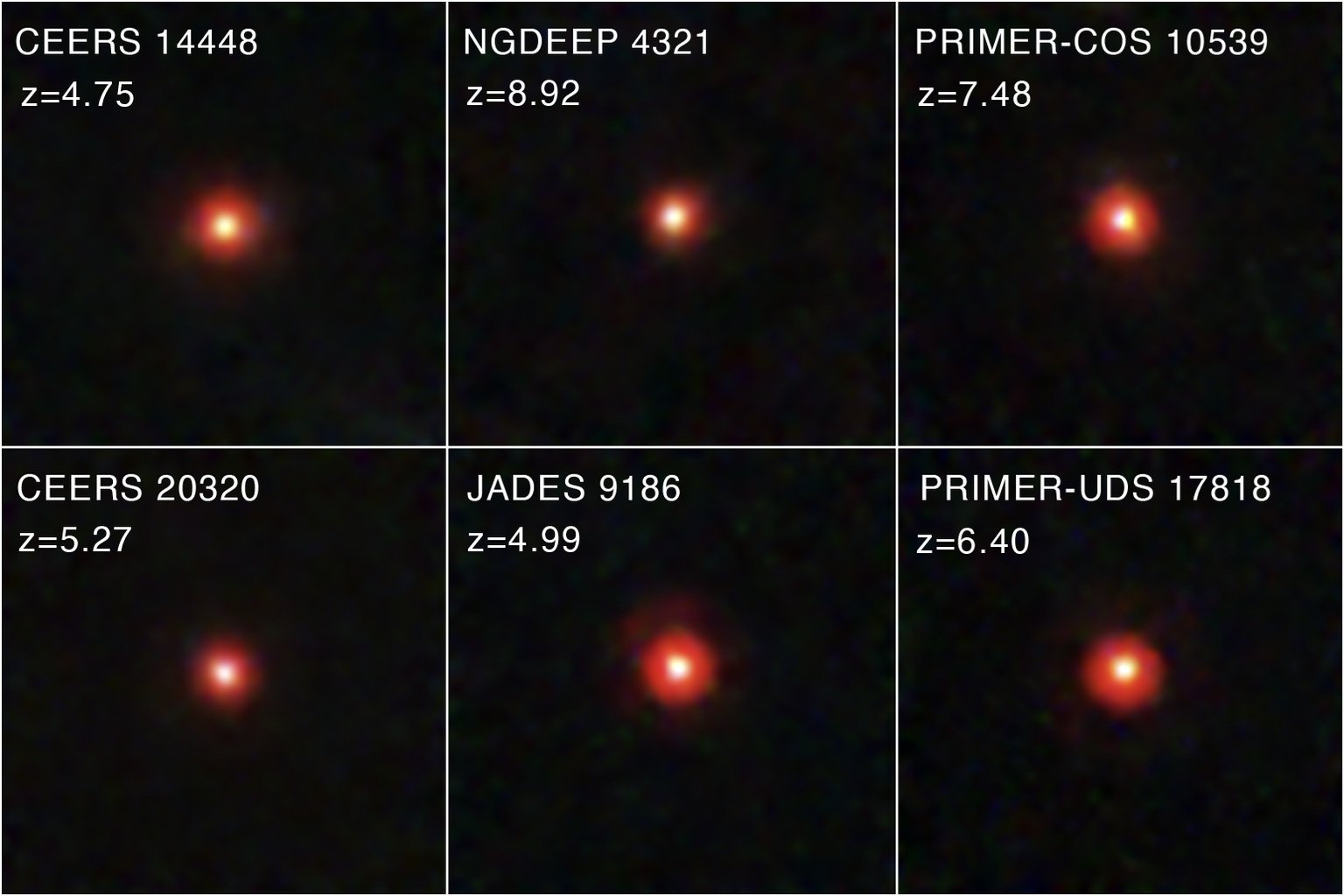

Six objects belonging to the LRD group in the image just posted by NASA - Photo: NASA/ESA/CSA
Redshift is the phenomenon where light emitted by objects moving away from the observer appears redder. A more pronounced red color means the object is moving away from us faster, due to the expansion of the universe, and means it is very ancient.
Astronomers around the world are puzzled by these LRDs.
Researcher Dale Kocevski from Colby College (Maine - USA) explains that this is because they have never seen similar objects at lower redshifts.
Many studies have been conducted. Initially, some researchers thought that these red dots were breaking cosmology.
Because if all the light emitted by these objects comes from stars, it implies that some galaxies grew so large, so quickly, in the early universe that previous theories could not explain it.
The new study, which Dr Kocevski was involved in, argues that most of the light emitted by these objects comes from accreting black holes, not from stars.
Fewer stars means smaller, more massive galaxies that can be explained by existing theories. That means cosmology is not broken.
To arrive at the above argument, the authors applied a variety of approaches to understand the nature of LRD, including examining the mid-infrared properties of the sample and searching extensively for accreting black holes to see how many fit the LRD criteria.
They found that up to 70% of the targets showed evidence of gas spinning rapidly at 1,000 kilometers per second, a sign of an accretion disk around a supermassive black hole.
Another peculiarity is that LRDs appeared in large numbers about 600 million years after the Big Bang event and rapidly decreased in number at the 1.5 billion years post-Big Bang mark.
Thus, these really red, high-redshift sources essentially cease to exist at some point.
If LRDs originate from black holes, it would mean they represent a "hidden" era of black hole growth in the early universe, co-author Dr Steven Finkelstein from the University of Texas at Austin concluded.
So while cosmology is not broken, a particular phase still needs to be further studied and added to models.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/nasa-bat-duoc-6-vat-the-tu-vung-bi-che-khuat-cua-vu-tru-196250117112622278.htm




![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)

![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)



















































































Comment (0)