(NLDO) - Three telescopes have together recorded a terrifying stream of black hole energy, erupting from the "heart" of a giant replica of the Milky Way.
According to the description of astronomer Patrick Ogle from the Space Telescope Science Institute (USA) and colleagues, nearly 1 billion light years away from Earth, a magnified copy of the Milky Way is "screaming" because it is being torn apart by the energy jet erupting from the central black hole.
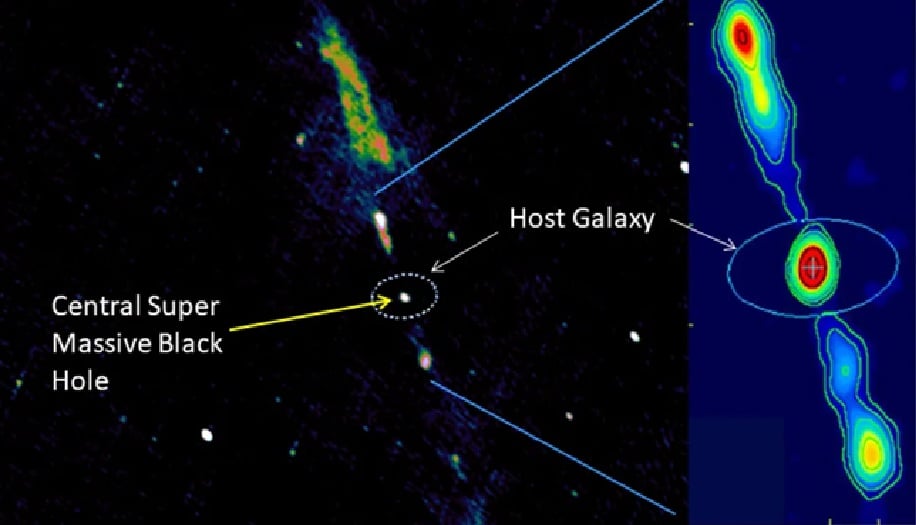

Observational data shows a giant replica of the Milky Way being torn apart by a jet many times larger than itself - Photo: Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope
The Milky Way, the galaxy that contains Earth, is a spiral galaxy.
The galaxy being torn apart in the captured image - J2345-0449 - is also a spiral galaxy of the same shape, but three times larger than the Milky Way.
The only difference between the two galaxies is that the Milky Way has a dormant central black hole, while the "heart" of J2345-0449 is a violently active monster, according to Live Science.
The black hole is emitting powerful radio jets, streams of fast-moving charged particles that emit radio waves, that stretch more than 5 million light-years.
Writing in the scientific journal Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, the authors say radio jets of this type are rare for spiral galaxies.
Galaxies like the Milky Way can also emit radio jets from black holes, but they are weak jets.
Powerful jets like the one just observed typically only appear in giant elliptical galaxies, because the black holes of these galaxies are much larger than the central black holes of spiral galaxies.
But the black hole inside J2345-0449 may be unusually large compared to the galaxy, leading to strange phenomena.
Not only does it appear to be tearing J2345-0449 apart in observational images, these monstrous radio jets are literally wreaking havoc on the galaxy.
Combined data from the Hubble Space Telescope, the Giant Metrewave Radio Telescope and the ALMA radio telescope array together confirm that radio jets from J2345-0449's black hole are preventing stars from forming near the galactic center.
These jets heat nearby gases so much that they cannot collapse into new stars, or even push this material out of the galaxy entirely.
This exciting observation provides a rare piece of the puzzle, helping scientists refine cosmological models regarding the evolution of galaxies.
Source: https://nld.com.vn/mot-dai-ngan-ha-khac-dang-bi-xe-toac-196250327100611156.htm





![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs conference on anti-smuggling, trade fraud, and counterfeit goods](https://vphoto.vietnam.vn/thumb/1200x675/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/5/14/6cd67667e99e4248b7d4f587fd21e37c)





























































































Comment (0)