The 'satellite constellation' is the European Union's (EU) third major initiative in space after the Galileo navigation system and the Copernicus Earth observation satellite constellation.
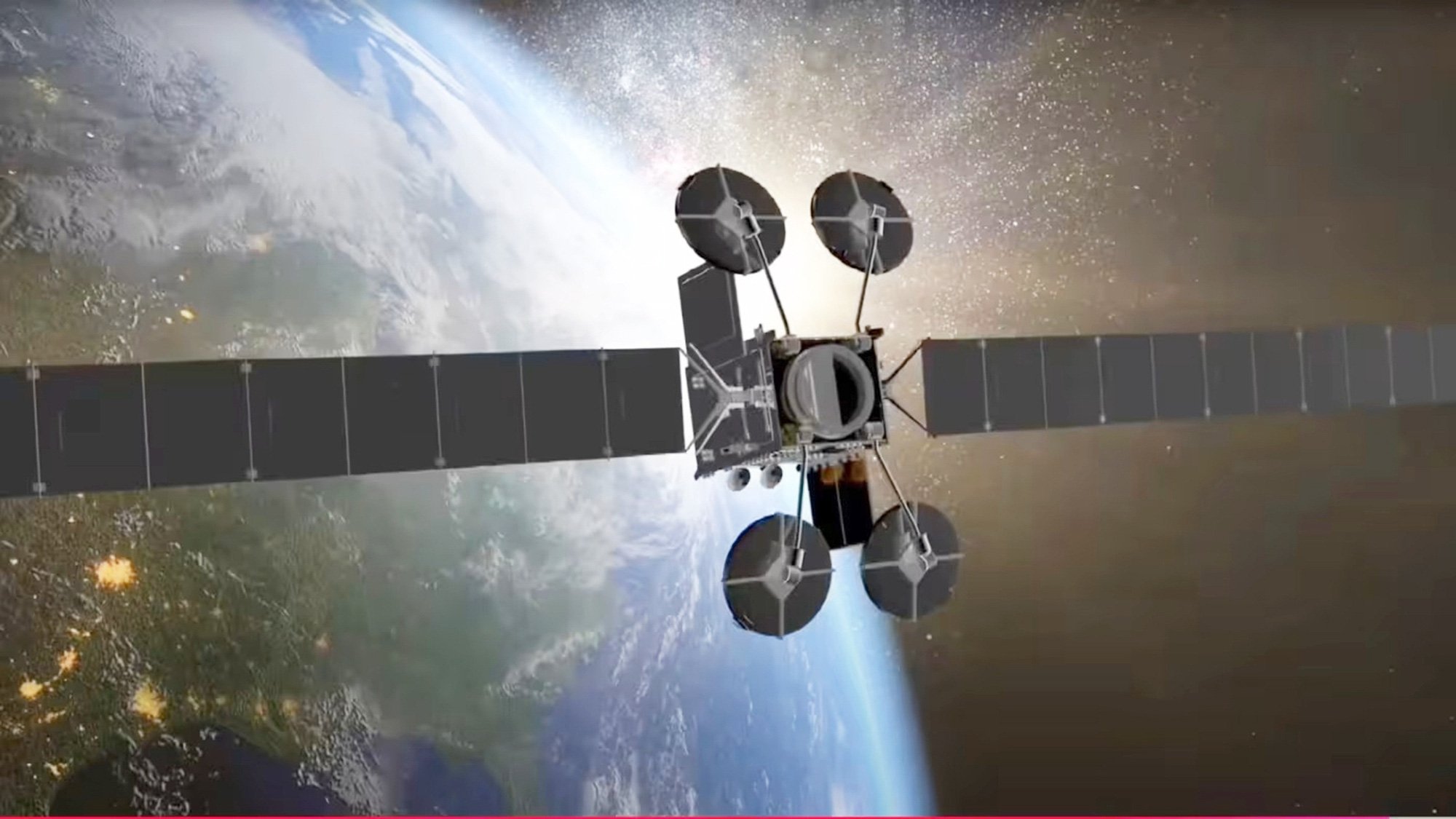

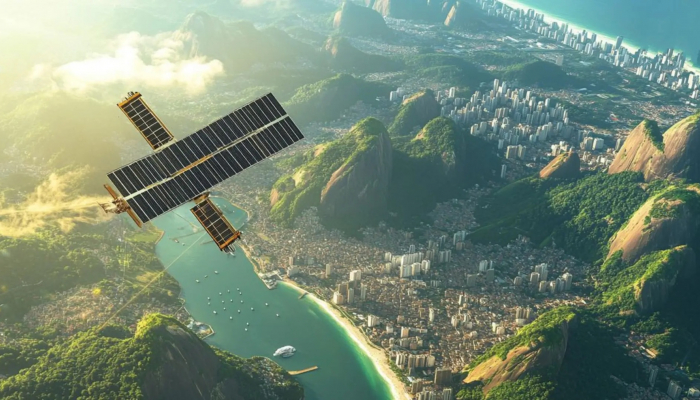
The IRIS² constellation will include hundreds of satellites in low Earth orbit and medium Earth orbit - Photo: Financial Times/OneWeb
Earlier this week the EU signed formal contracts to launch a project to build a "Satellite Constellation" infrastructure dedicated to high-speed Internet access.
With plans to build a multi-orbital network of nearly 300 satellites, the IRIS² project aims to compete with US satellite internet service providers such as billionaire Elon Musk's Starlink and Amazon's Kuiper project.
Historical milestone
The IRIS² constellation — short for Infrastructure for Resilience, Interconnectivity and Security by Satellite — will consist of hundreds of satellites in low Earth orbit and others in medium Earth orbit.
Placing interconnected satellites in different orbits like this will allow the constellation to operate safely, quickly, and maintain continuous connectivity without the need for thousands of satellites. An additional layer in low Earth orbit to provide additional services will also be developed.
With an estimated budget of 10.6 billion euros ($11.1 billion), IRIS² will enable secure communications for military, defense and diplomatic purposes. The system can also be used for surveillance, connectivity in disaster areas and providing commercial broadband access.
“In an increasingly complex geopolitical world, ensuring government communications are fast, secure and sustainable is essential,” commented European Space Agency (ESA) Director General Josef Aschbacher.
ESA is supporting the development of the IRIS² project through a contract with the SpaceRISE Industrial Group, selected by the European Commission. The European Commission has signed a 12-year concession agreement with the SpaceRISE Group. A second contract between ESA and the SpaceRISE Group has also been signed.
The satellite internet system is being developed as a public-private partnership and will serve both governments and private customers. Of the total cost of €10.6 billion, the EU will contribute €6 billion, ESA will provide €550 million and the private sector will provide more than €4 billion. ESA plays a key role in IRIS².
Under the 12-year concession, ESA will oversee the development activities carried out by the industrial consortium. “The signing of IRIS² is a historic milestone for the European space industry,” said Miguel Angel Panduro, CEO of Hispasat.
To not be too dependent on Starlink
The EU project was launched in the context of Starlink - a high-speed internet network using satellites of American billionaire Elon Musk's SpaceX Company - dominating the field of large satellite constellations.
Starlink currently operates a constellation of more than 7,000 satellites in low Earth orbit, while rivals like Amazon’s Project Kuiper and China’s low Earth orbit internet program are gaining momentum.
The main motivation for the EU to launch the project is the bloc's concern about over-reliance on Starlink and "an erratic Elon Musk." This danger was seen in the Russia-Ukraine conflict, when the Starlink satellite internet system was said to have blocked Ukraine's access during a major counterattack.
“We cannot afford to be too dependent,” said EU commissioner for defence and space Andrius Kubilius.
“It is absolutely vital for Europe to have sovereign capacity and Starlink will never have that,” said Eva Berneke, chief executive of Eutelsat.
However, Politico said the EU's move "is unlikely to keep Elon Musk up at night" as the project has faced delays and cost overruns in the past. The European Commission previously promised that IRIS² would start operating this year, but earlier this week EU officials said the target was... 2031.
Now that the contracts have been signed, the design phase will begin. The satellites are scheduled to launch in 2029 in 13 missions using Europe's Ariane 6 rockets.
China also competes with Starlink for satellite internet
On December 16, China launched the first satellites of the GuoWang (National Net) large-scale satellite constellation project from the Wenchang Spaceport. GuoWang first became known in 2020 when China submitted a dossier to the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) for a satellite constellation project consisting of nearly 13,000 satellites.
Considered a Chinese version to counter SpaceX's Starlink (USA), GuoWang has the mission of providing global broadband Internet services while meeting China's national security goals.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/khoc-liet-canh-tranh-internet-ve-tinh-20241217233432675.htm








































![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs Government Conference with localities on economic growth](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/2/21/f34583484f2643a2a2b72168a0d64baa)























































Comment (0)