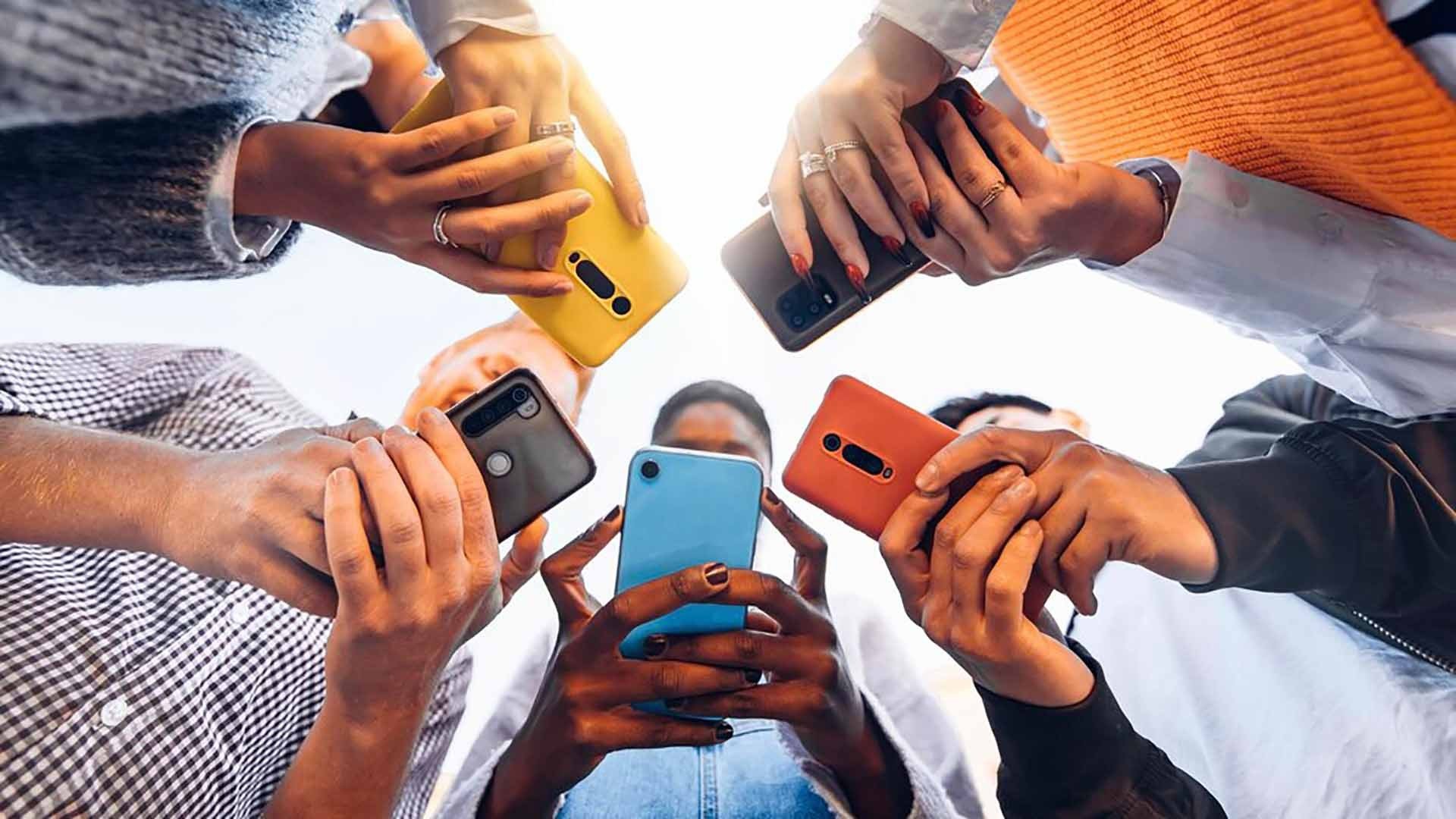
 |
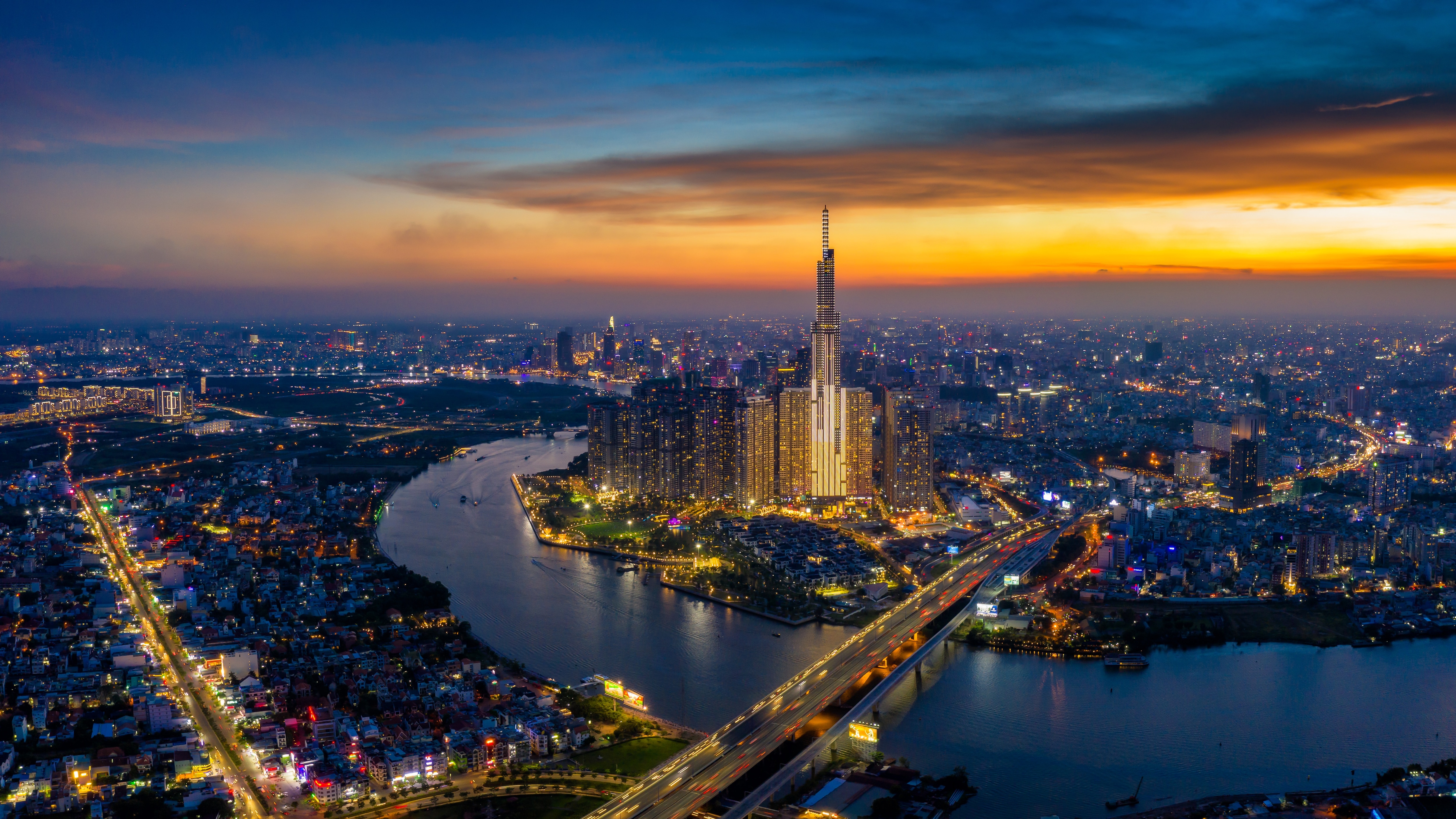
| Northeast Asian countries are rapidly developing information technology fields to serve people's lives. Illustration photo. (Source: engenhariae) |
China - "Internet Power"
China has begun operating what it claims is the most advanced Internet network in the world.
According to technology maker Huawei, the network can transmit at speeds of about 1.2 terabits (1,200 gigabits) per second, which is fast enough to stream 150 movies in a second.
At a press conference last week, Huawei and China Mobile announced the official launch of China’s next-generation “backbone network,” a collaboration with Tsinghua University (Beijing) and Cernet, a Chinese government-funded education and research network.
The “backbone” is the network infrastructure that helps move Internet traffic to different locations, and can carry data that belongs to 5G technology.
The new network will operate on nearly 2,900km of fiber optic cables connecting Beijing and southern China, and will be put into testing in the summer of 2023, according to a press release.
Chinese President Xi Jinping has said that developing a “backbone network” will turn China into a “cyber power” and “accelerate the promotion of core Internet technologies.”
The system, including both software and hardware, is entirely made in China, said Wu Jianping, a professor at Tsinghua University's department of computer science and technology who is overseeing the project. He called it the most advanced network in the world.
Society 5.0 in Japan
While China is busy operating the “world’s most advanced Internet,” neighboring Japan is pushing for digital transformation to build a digital society. The country sees digital transformation as an inevitable trend and a matter of national survival.
Internet development has long been a top priority for the Japanese government, with high-speed fiber optic networks in many areas. The country's average Internet speed is currently 42.2 Mbps.
The proposal to build a super smart society, also known as Society 5.0, was announced by the Japanese government in the “5th Basic Plan for Science and Technology 2016-2020” to promote the development of science and technology, since January 2016.
The goal of Society 5.0 is to solve social problems by connecting systems using digital technology as a platform to merge physical and digital spaces. This is a society that provides goods and services according to individual needs.
Japan's Society 5.0 initiative aims to create an economic model that harnesses technological innovations to promote digitalization in government agencies, as well as in service industries.
According to a forecast by GlobalData (UK) data analysis and consulting company, the Society 5.0 initiative will boost Japan's Internet of Things (IoT)-based information technology market from 42.1 billion USD in 2021 to 60 billion USD in 2026, with an annual growth rate of 7.4%.
The Digital Japan Agency is encouraging local governments to switch entirely to government cloud computing services by fiscal 2025. An official said a full shift to cloud computing could cut the annual IT budget, currently at $7 billion, by about 30 percent.
Prime Minister Kishida Fumio announced in 2022 that the government will promote the development of services based on the latest Internet technology (third-generation Internet or Web 3.0), including new services such as blockchain-based digital assets (NFTs) and metaverses.
As one of the first countries to launch commercial 5G services, Japan aims to cover 98% of its population with 5G by the end of the first quarter of 2024.
5G is identified as a key enabler for digital transformation, and Japan has been promoting the development of 5G in industrial environments and other use cases to positively impact its economy.
In addition to promoting the development of 5G technology, the Japanese government funds research and development of future 6G mobile technology.
Lifestyle in Korea
With bright market prospects, many countries are actively engaging in efforts to promote the Internet of Things (IoT) as a core industry.
Not out of this trend, in the Northeast Asia region, the Korean government identifies IoT as a core industry, and sets out clear strategies to promote IoT development.
In Korea, “ubiquitous connectivity” is not inspirational, but it is a word that describes the lifestyle in the land of kimchi.
With direct high-speed mobile Internet connections across a wide range of digital devices, South Koreans boast some of the most connectivity on the planet.
The Korean government believes that IoT not only helps increase productivity and production efficiency by promoting innovation, creating new industries and growth opportunities.
The Korean government encourages the development of promising IoT services based on the needs of the government, private sector and citizens such as healthcare, smart homes, smart cities, transportation, logistics, energy, safety, etc.
Korea's smart cities include sub-sectors such as smart transportation, smart resource management, smart healthcare, etc. In these sub-sectors, the Korean government builds cross-cutting cooperation between the government, large technology corporations, and small and medium-sized enterprises. Local governments coordinate with corporations to provide the necessary platforms and networks, while small and medium-sized enterprises undertake the development of related hardware and software.
The Korean government encourages joint ventures and partnerships between small and medium-sized enterprises and universities to support the development of business services.
According to Mr. Bui Dong Hung, a researcher at the Institute of Northeast Asian Studies (Vietnam Academy of Social Sciences), the Korean government still has a lot to do to promote the development of IoT. Korea will face much greater challenges when compared to the challenges related to technology and engineering in the IoT deployment phase.
These challenges are related to human, economic-political, and social, where IoT will create far-reaching impacts. These will be useful experiences that Vietnam can refer to in the process of implementing the current and future IoT development strategy.
Source



![[Photo] Visiting Cu Chi Tunnels - a heroic underground feat](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/8/06cb489403514b878768dd7262daba0b)


























































































Comment (0)