Gut health plays an important role in the entire body, not just limited to the digestive system.
The intestines are home to trillions of microorganisms, including both beneficial and harmful bacteria, according to the health site Health .
A healthy gut microbiome not only helps digest food, but also plays an important role in synthesizing vitamins, metabolizing energy, and protecting the body from pathogens. However, when this balance is disrupted due to an unhealthy diet, stressful lifestyle, or environmental factors, health problems can arise.
Ms. Mallory Christopherson, a medical expert in the US, shared necessary information about intestinal health.
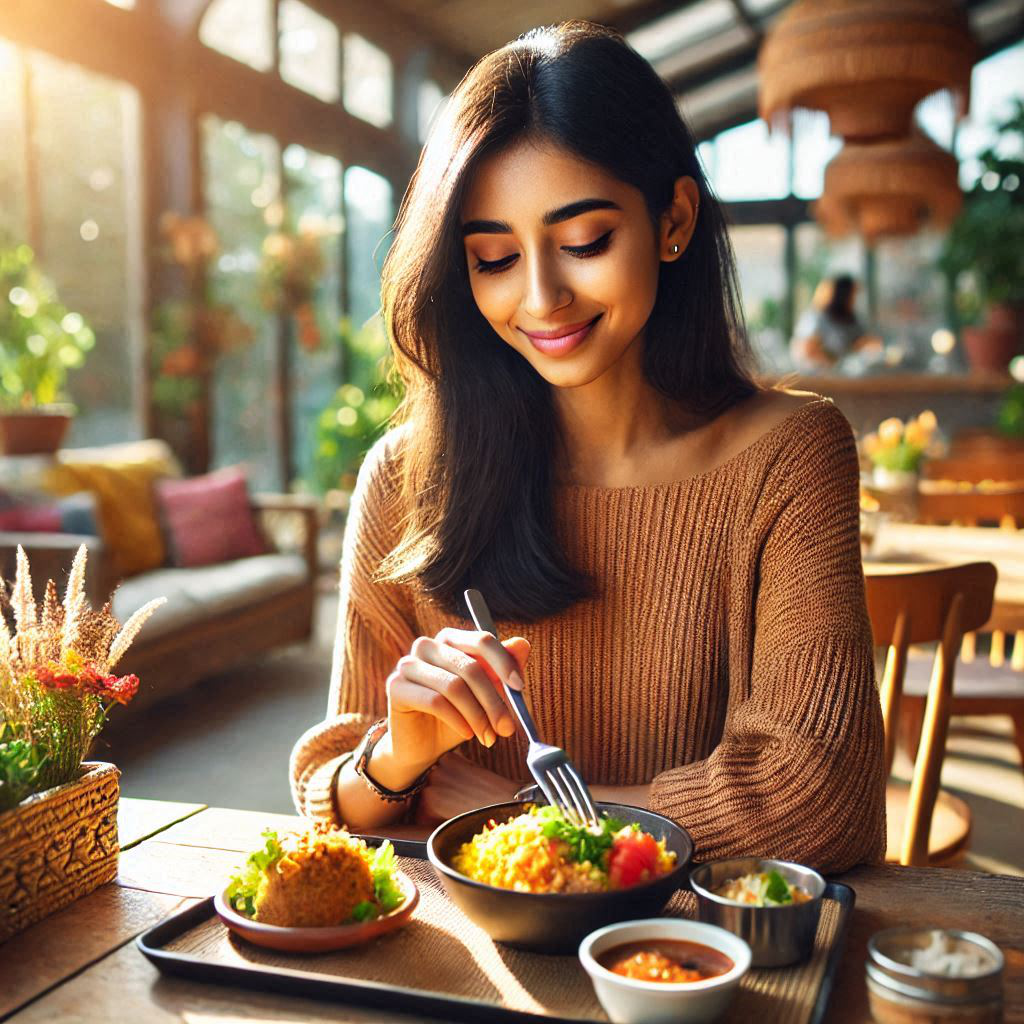

Diet has a big impact on gut health
Signs of an unhealthy gut
An imbalance of gut microflora can cause many health problems.
When harmful bacteria overgrow, it creates an inflammatory environment in the gut, affecting digestion and causing symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, diarrhea, constipation, nausea and a feeling of fullness after eating.
Not only that, harmful bacteria and inflammatory substances can penetrate the intestinal wall into the bloodstream, causing widespread inflammation in the body, increasing the risk of chronic diseases such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, irritable bowel syndrome, asthma, depression and anxiety.
In addition to digestive symptoms, an imbalance in gut microbiota can also cause non-digestive problems such as headaches, mood swings, chronic fatigue, and skin problems.
Factors affecting intestinal health
Many factors influence gut health, including genetics, diet, lifestyle habits and environment.
Among them, diet is an important factor determining the balance of intestinal microflora.
A diet rich in fiber from vegetables, fruits, whole grains, nuts and beans helps feed beneficial bacteria, while processed foods, high in sugar and saturated fat can upset the microbiome balance and cause inflammation in the gut.
Within just 24 hours of changing your diet, your gut microbiome can be significantly affected.
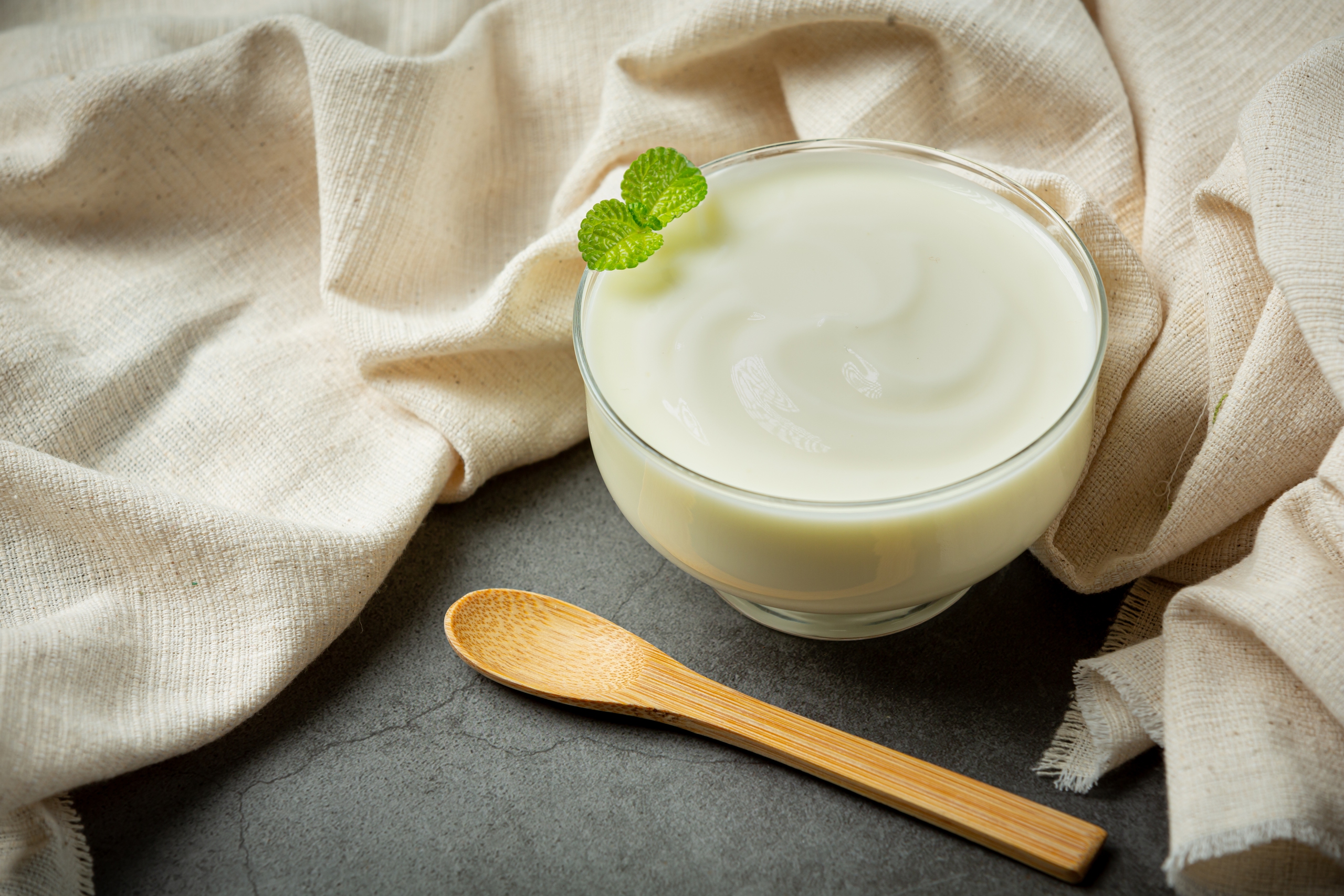

Fermented foods like yogurt contain probiotics that help improve the diversity of the microbiome.
How to change your diet
Fermented foods like yogurt, kimchi, and sauerkraut contain many beneficial bacteria that help improve the diversity of the microbiome.
Prebiotic-rich fruits and vegetables like bananas, garlic, and onions help feed beneficial bacteria. Beans like black beans, green beans, and chickpeas also provide the fiber needed to support the intestinal lining.
Whole grains like oats help boost beneficial bacteria and improve digestion.
Meanwhile, certain foods can negatively affect the gut and should be limited, including artificial sweeteners, saturated fats, cold cuts, sugary cereals and candy.
How to adjust your lifestyle
Regular exercise can help improve gut microbiota diversity and reduce inflammation.
Getting enough sleep and maintaining a reasonable sleep schedule helps the digestive system work more effectively.
Chronic stress can deplete beneficial bacteria, so relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, massage, and walking can help reduce stress and improve gut health.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/cach-phuc-hoi-suc-khoe-duong-ruot-185250206234517718.htm



![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)
![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)




















































































Comment (0)