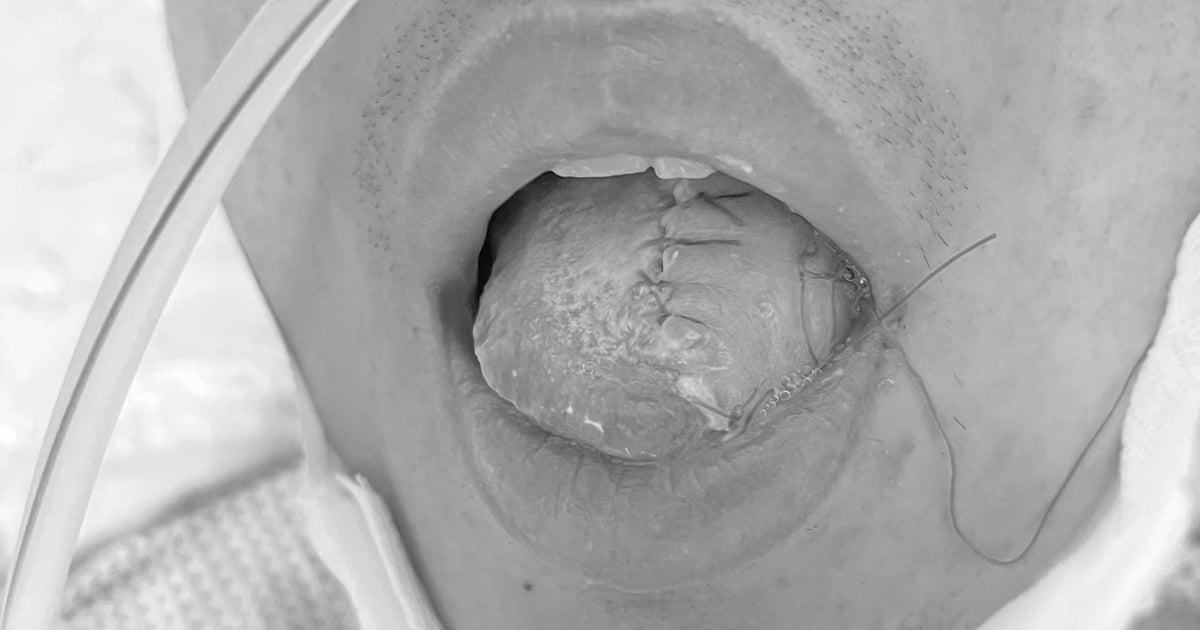
Tongue cancer usually occurs in the 50-60 age group. This is a malignant disease, because the tongue has many blood vessels, it easily metastasizes to the neck lymph nodes and other internal organs.
The risk group for tongue cancer is people with worn, chipped, or crooked teeth... causing the teeth to rub against the edge of the tongue, causing damage and chronic inflammation of the edge of the tongue. If chronic inflammation is not controlled, it can produce strange cells and turn into cancer. People with cavities, chronic damage to the gums, alcohol abuse, smoking, or HPV infection (type 11, 16)... are also at risk of the disease.
Early stage tongue cancer can be treated with surgery. In the late stage, patients must combine surgery, radiotherapy and chemotherapy.
The disease can be detected early because the tongue is an external organ that is easy to observe and feel. Most cases of tongue cancer have a feeling of numbness, discomfort, tongue bumps, pain when eating and drinking, abnormal taste changes... These symptoms do not appear in succession so patients can ignore them.
Other signs include mouth ulcers that last more than two weeks and do not improve, causing ulcers on the lips, gums, and tongue. Pain in the mouth, difficulty chewing and swallowing, bleeding, poor tongue movement, swollen lymph nodes in the neck, and abnormalities in teeth and gums.
Doctors recommend that people should treat oral lesions early and have regular health check-ups. In case of chronic glossitis, check-ups should be done every 6 months.
Source link







![[Photo] Visiting Cu Chi Tunnels - a heroic underground feat](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/8/06cb489403514b878768dd7262daba0b)















































































Comment (0)