 |
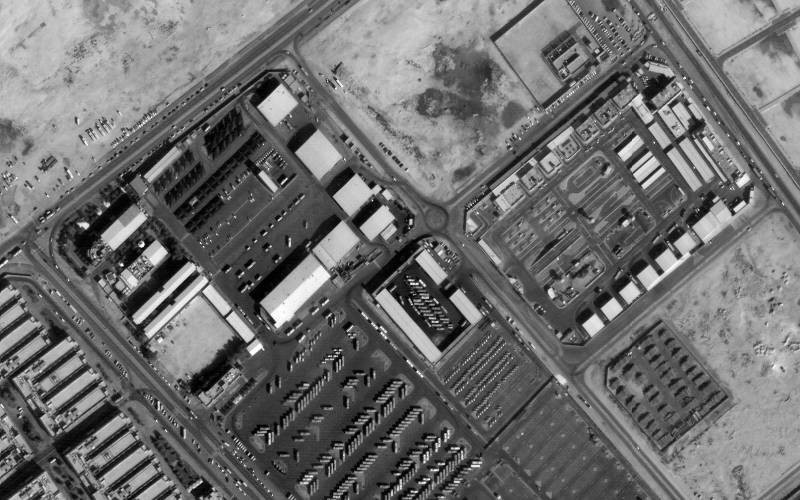
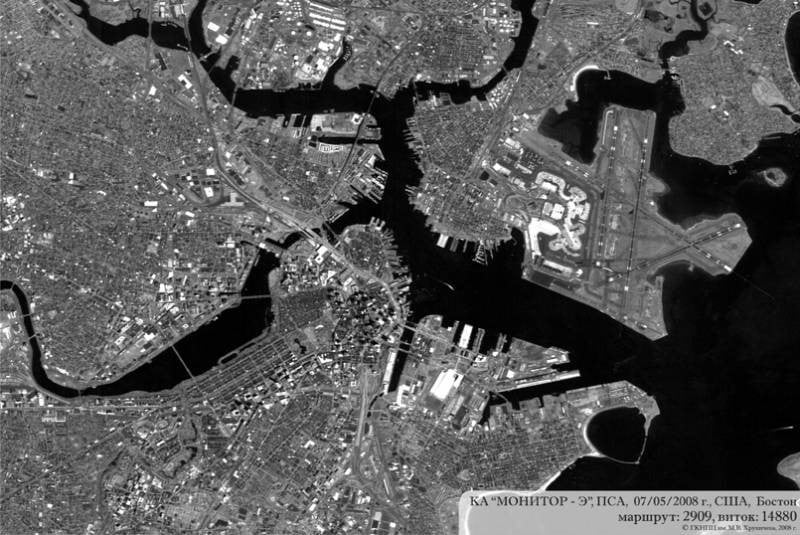
Satellite images are recorded very clearly. |
Unlimited space
The virtual absence of restrictive principles of international law has allowed NATO countries to significantly increase their technological advantage over Russia in low Earth orbit. The reality of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict has proven this. According to official data from the Russian Ministry of Defense, at least 500 satellites are in service with the Ukrainian military. The actual number accounts for about 50% of all space equipment of countries operating in low Earth space.
The problem is not limited to war zones, but the enemy's equipment is "looking" at the entire territory of Russia. Among the satellites supporting the Ukrainian forces are optical-electronic reconnaissance equipment, as well as communications systems, including civilian ones. Low Earth orbit turns out to be such a wonderful environment that any innocuous device can become an effective weapon. As in the case of billionaire Elon Musk's Starlink satellite internet service, which has greatly assisted Ukraine in the conflict.
Of the five hundred NATO satellites mentioned above, only 70 are purely military reconnaissance satellites, the rest are dual-purpose. It is no exaggeration to say that it was the enemy's reconnaissance equipment that completely changed the situation in Ukraine, both before the start, and during the current course of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict.
There is nothing surprising about this. Space reconnaissance by the United States and the Soviet Union in the mid-1960s exposed preparations for war, which continued for 50 years, during which neither country could hide the traces of large-scale military exercises and activities.
Space reconnaissance offers a very clear advantage. In the civilian sphere, the Americans in the 1960s and 1970s, based on space surveillance of Soviet agricultural fields, came to the conclusion that a "grain crisis" was coming. Immediately after that, the capitalist countries quickly adjusted prices on the world food market, forcing the Soviet Union to pay for wheat in gold and oil.
In the military sphere, in the 1960s, the Soviet leadership received high-quality photographs of US ballistic missile launch sites, airfields and naval bases. Before that time, all data on the enemy's arsenal was indirect, which meant that it could not be trusted unconditionally. Immediately after the US arsenal was exposed, negotiations on the SALT-1 program began.
Space reconnaissance helps to effectively use military forces and plan operations even at the battalion level. The initial stage of the Russian-Ukrainian conflict demonstrated this very clearly. The enemy knew the numbers and locations of the attacking forces even at the lower levels of the Russian army and could respond accordingly. This situation has not fundamentally changed to this day.
 |
During the Cold War, the above reconnaissance system operated on the principle of balance, with both sides having approximately equal opportunities in space. Now the situation has reversed. The disparity in space reconnaissance capabilities between the sides has affected strategic stability. One of the sides with the advantage has an irresistible desire to realize its interests by force. The risk of uncontrolled escalation has increased significantly as NATO has become aware of Russia’s nuclear potential.
Strategic Defense Initiative 2.0
US space defense is based on the concept of superiority. This term is constantly present in open access strategic documents such as the Space Defense Strategy. Whether the US is truly underestimating its situation or overestimating its capabilities remains an open question. Most importantly, the US has no intention of discussing anything with Russia or China regarding the use of low Earth space.
As mentioned above, only nuclear testing is currently prohibited, everything else is allowed. In addition to classic espionage, US satellites assess the state of natural resources, study engineering structures, transport networks, and map the country's territory in detail.
For example, the linear resolution on the ground of the optical equipment of the IKONOS, Quick-Bird, World-View, Pleiades-1 satellites allows to distinguish geometric objects as small as 50 cm in size. Of course, for such precision, the equipment still needs to be aimed at the objects, that is, high-detail cameras usually cover a width of the Earth's surface no more than 20–30 km. But all this is solved by the number of satellites. It is not for nothing that up to 500 NATO equipment in space are supporting Ukraine.
Even clouds do not affect the radar image from space. The locator of a modern satellite, such as Lacrosse, with a synthetic aperture produces images in any bad weather with an accuracy of up to a meter. The imaging area of the system is much larger than the optical area, up to 100 km. Obviously, this makes it very difficult to camouflage strategic facilities.
Particularly promising is the Starlite or Discoverer-II system, which was rejected by the US Congress in 2000. It was essentially a space station project (similar to the E-8 JSTARS flight control station) that would help guide weapons to strategic targets. Reactivation of Starlite could take place at any time by reassembling the satellites into a new device, which would be very fast and inexpensive.
The Americans are actively working on systems designed to penetrate Russian air defenses and destroy ballistic missile launchers. The U-2 spy plane, the F-35 attack aircraft, strategic drones and cruise missiles work closely with satellites. There is also information about the development of electronic warfare satellites to block ground radars.
The highlight is the "zero level" missile defense doctrine, which means destroying Russian and Chinese missiles before they are launched. The Americans allocated money for this in 2021 and last year they approved it as a doctrine for developing the entire US missile defense system.
In fact, it was the birth of the Second Strategic Defense Initiative, famous since the Reagan-Gorbachev era.
 |
Conclude
To get out of this situation, according to Russian experts, you can take the following steps:
First, countries need to try to negotiate on the non-proliferation of weapons in outer space.
There are many difficulties. First of all, the problem is that Washington is dominant and therefore does not want to negotiate. Perhaps only the emergence of a Russian-Chinese defense alliance in the space field will convince the Americans.
It is important to understand that the unwillingness to negotiate puts the opponent in an uncomfortable position. The presence of numerous enemy satellites in near-Earth orbit has a negative psychological and moral impact on the top Russian leadership. And this will increase the pressure on decision-making.
Then there ’s the difficulty of identifying malicious devices in orbit. Dozens of civilian satellites are now flying in space that also function quite effectively for the military, like Starlink.
The second step for Russia and China is to demand that all respect each other's space sovereignty.
There is no difference between a U-2 reconnaissance aircraft or a Lacrosse satellite flying over the territory of another country. In this case, it is difficult to talk about sovereignty. Russia has a complex "Peresvet", which is used to cover the operations of mobile missile systems, but its operation is quite simple. It is just a camouflage and then a deliberate shutdown mode from enemy satellites.
In this connection, we can recall the Starfish nuclear test in 1962, when the Pentagon conducted a 1.4 megaton nuclear explosion in space. There were many explosions 1,500 km from the epicenter, an electromagnetic pulse that knocked out the power, disrupting telephone and radio communication systems.
Three satellites were destroyed immediately, including the first television relay satellite Telstar-1 and Britain's first satellite Ariel-1. Seven more satellites were later decommissioned due to damage to their solar panels and electronics.
If that were to happen today, up to 90 percent of all satellites would be destroyed. But perhaps this extreme scenario would quickly and effectively solve the problem of spy and communication satellites in a future war.
Of course, Russia's own Global Positioning Satellite System will also cease to function. But an alternative is to deploy a communications system based on hundreds of high-altitude drones and satellite-free navigation.
And finally, the third and most expensive way out of this situation is to build its own satellite system, on par with the Americans. These are priority cooperation programs with China and India, including financial sharing by businesses on a commercial basis. Without these approaches, the problem of low-Earth space will always haunt Russia.
Source




![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)
![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)























































































Comment (0)