According to information from the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology, scientists have just completed a research project on the use of a combination of Silic algae and symbiotic cyanobacteria to indicate water masses in the East Sea.
This work was carried out with scientific cooperation from the Institute of Oceanography (Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology), Georgia Institute of Technology (USA) and the Baltic Sea Research Institute (Rostock, Germany).
The research aims to clarify the distribution characteristics of diatoms carrying Cyanobacteria symbionts in different water masses such as: coastal water masses affected by the Mekong River, coastal water masses in the South Central region and water masses affected by upwelling.
According to the Information and Documentation Center (Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology), the East Sea is a sea with complex and dynamic hydrological terrain and is of great economic importance.
Primary production in the South China Sea is strongly seasonally pressured, through the monsoon cycle, which affects both riverine flows and basin circulation.
In particular, the summer monsoon creates a combination of waters influenced by the Mekong River outflow and coastal upwelling, within the wind-driven surface dynamic circulation.
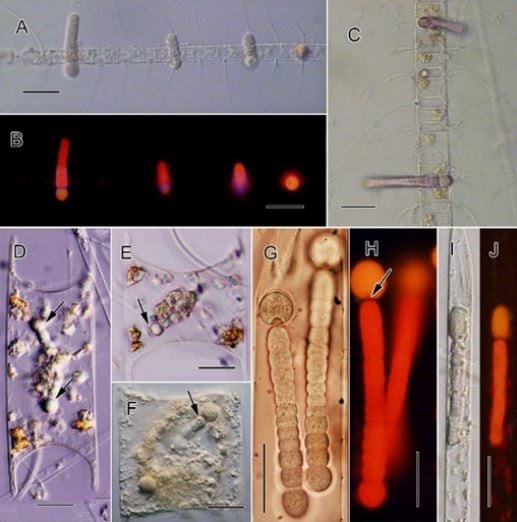
Distribution, abundance and symbiotic status of a group of diatoms and diatom-diazotroph (DDA) assemblages in different habitats determined by physical and biological characteristics of the South China Sea during the early stage of the southwest monsoon.
Prof. Dr. Nguyen Ngoc Lam, Institute of Oceanography (Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology) said that Silic algae is the host of DDA and is widely distributed throughout the research area.
The research team of Prof. Dr. Nguyen Ngoc Lam found symbiotic Cyanobacteria in all sample collection environments, although the infection rate (abundance of hosts carrying symbiotic Cyanobacteria) and infection intensity (number of symbiotic Cyanobacteria colonies per host) were lowest in waters affected by coastal upwelling.
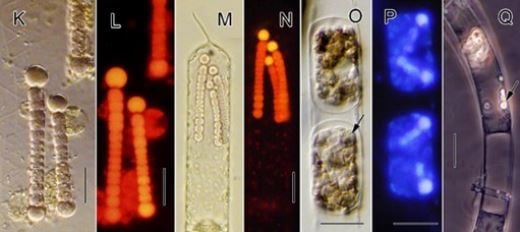
Host infection rates tend to be highest in offshore waters and DDA host diatoms often vary widely in size and infection intensity both within and between defined habitats.
These differences may reflect different optimal strategies for biomass and energy allocation between host and symbiont.
This is the first report by scientists from the Institute of Oceanography in particular, the whole country in general and the Southeast Asian region on the genus of Silic algae carrying symbionts of Cyanobacteria that fix nitrogen in the water masses of the East Sea, thereby contributing to clarifying the biological productivity of the East Sea.
As one of the outstanding works of the Institute of Oceanography published in prestigious SCIE journals ranked Q1: Journal of Phycology IF=3.2 and Hydrobiologia, IF=2.8, this study is one of the few reports on marine biology in the East Sea of Vietnam conducted by Vietnamese main authors.
By successfully determining biological productivity, the results of the research project can help improve exploitation efficiency, contributing to promoting economic development in the East Sea region.
The research work of the Institute of Oceanography also contributes to showing the role and contributions of Vietnamese scientists in marine research activities and promoting the marine economy.
This is considered one of the outstanding achievements of scientists from the Institute of Oceanography in particular and the Vietnam Academy of Science and Technology in general this year.

Source




![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)


![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)

















































































Comment (0)