Starting the day with health news , readers can also read more articles: Doctors warn about dangerous eye injuries in daily life and work; What happens to the body if you stop exercising?; Science shows that sleeping positions can be harmful, the elderly should avoid...
3 health problems that cause sudden weight gain
Weight gain is often caused by an unhealthy diet, such as eating a lot of sugary foods, drinking a lot of alcohol, and a sedentary lifestyle. However, there are cases where people gain weight despite eating a balanced diet and exercising. The cause is a number of underlying health problems.
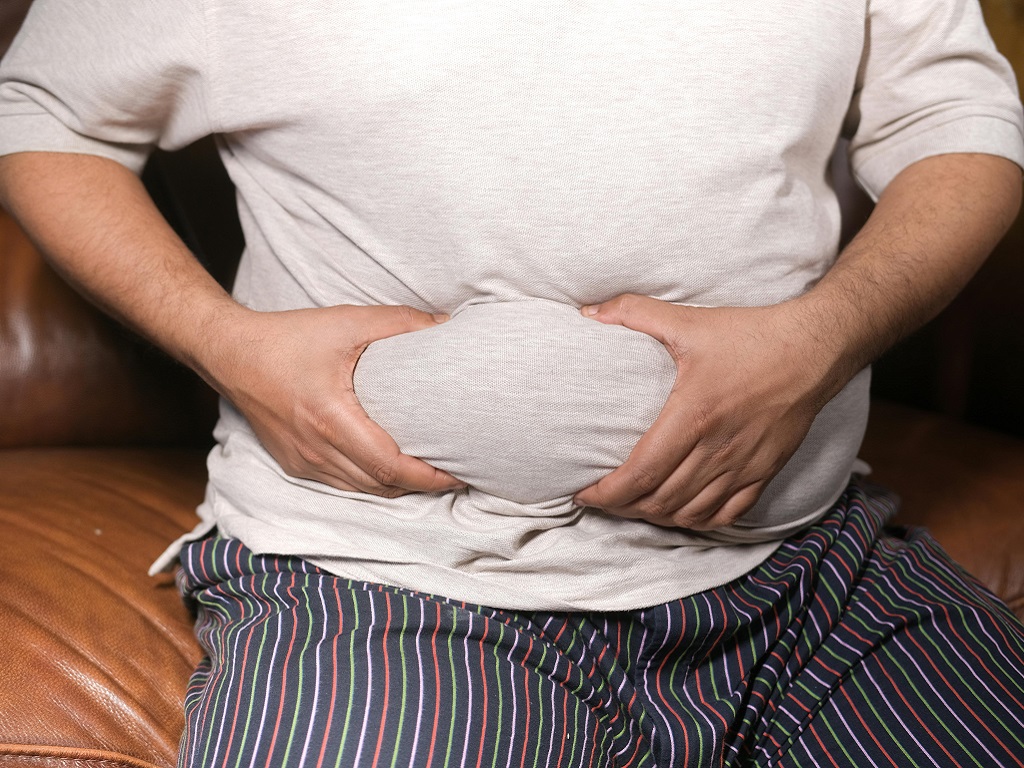

Hormonal imbalances can cause weight gain without any changes in diet and exercise.
Common causes of unexplained weight gain that people should not ignore include:
Hormonal imbalance. Hormones play an important role in regulating body weight. Health problems that affect the body's hormonal balance, such as hypothyroidism, can lead to weight gain. Untreated hypothyroidism slows down the body's ability to burn calories. This can lead to weight gain despite no changes in diet or exercise.
Similarly, polycystic ovary syndrome, a common hormonal disorder in women, can cause insulin resistance and weight gain.
Medication side effects. Some medications can contribute to weight gain. Antidepressants, antipsychotics, and corticosteroids have the side effect of increasing appetite, which can lead to weight gain.
Research published in The Lancet Psychiatry found that antipsychotics such as olanzapine and clozapine are more likely to cause weight gain than other drugs. Readers can read more about this article on the health page on September 15.
What happens to your body if you stop exercising?
Regular exercise helps maintain overall mental and physical health. If you stop exercising, your body will no longer receive those benefits. This can cause a number of negative health effects over time.
Regular exercise improves cardiovascular health, lowers blood pressure and improves circulation. Exercise also helps control weight, boosts metabolism, burns calories, and prevents obesity and chronic diseases such as diabetes and high blood pressure.
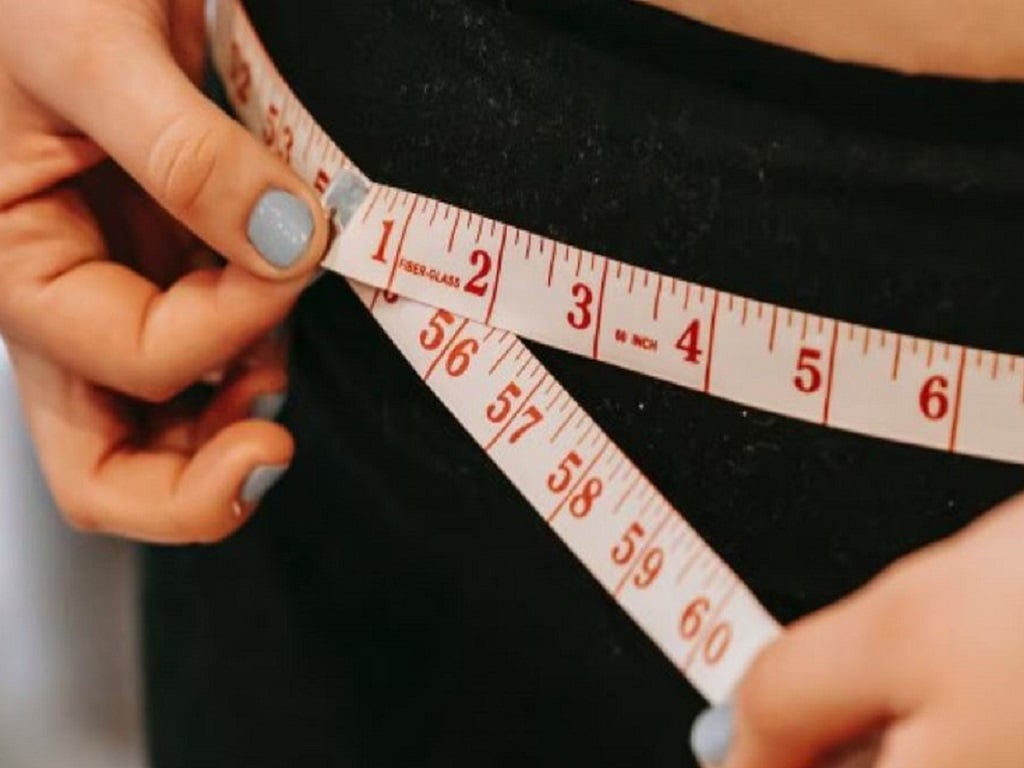

Skipping regular exercise for a long time will make the body more likely to accumulate excess fat and gain weight.
When you stop exercising for a long time, the body will experience the following adverse effects:
Loss of muscle and strength. When you stop exercising, within just a few weeks, your muscles will be out of shape. Both muscle mass and tone will decrease. As a result, your muscles will weaken, leading to a loss of strength and endurance. Over time, activities that were once easy, such as climbing stairs or carrying heavy objects, will become more difficult to perform.
Weight gain. Without regular physical activity, your body's metabolism slows down. Your ability to burn calories decreases. As a result, your body stores excess fat and gains weight. Excess fat around your abdomen increases your risk of high blood pressure and diabetes. The next part of this article will be on the health page on September 15 .
Science shows sleeping positions can be harmful, older people should avoid
New research presented at the 2024 Alzheimer's Association International Conference has found a link between the supine sleeping position and neurodegeneration — a common condition in older adults.
From side sleeping, stomach sleeping to back sleeping, everyone has a favorite sleeping position.
Previous studies have linked the back sleeping position to a number of potential health risks, including high blood pressure and obstructive sleep apnea, and to people with nocturnal reflux or pregnancy. Now, a new study has found another potential downside to this sleeping position.
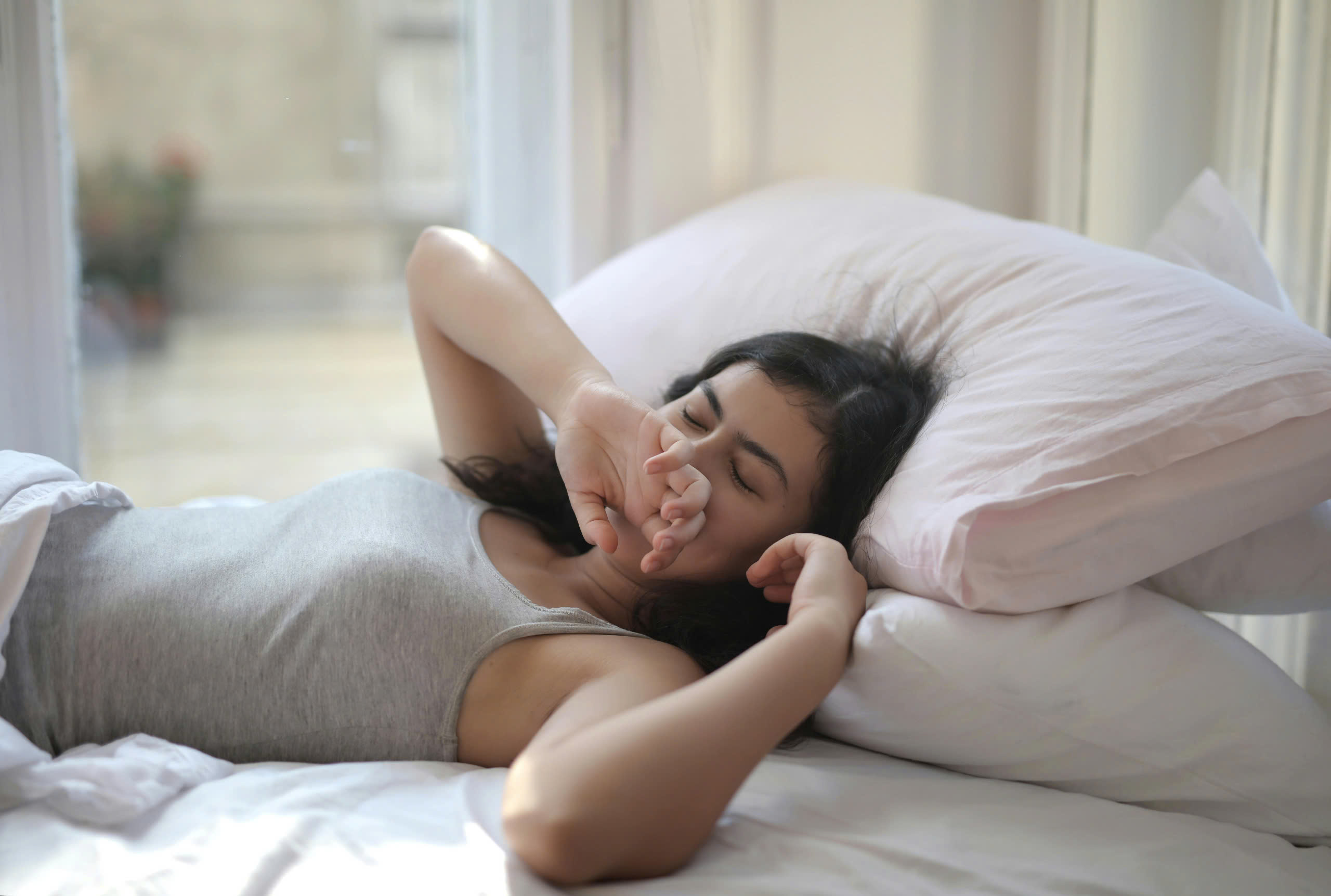

Many studies show that sleeping on your back causes some potential harmful effects on health.
The new research builds on a 2019 study that found that sleeping more than 2 hours a night on your back increases your risk of neurodegenerative disease .
The new study, by a team of scientists from the University of California San Francisco, Mayo Clinic School of Medicine (USA) and Saint Mary's General Hospital in Toronto (Canada), included people with mild cognitive impairment, progressive supranuclear palsy - a late-onset neurodegenerative disease, Parkinson's disease, Alzheimer's dementia and a control group.
Participants wore devices that calculated the number of hours they slept in a supine position each night, and assessed nine sleep biomarkers to distinguish the risk of neurodegenerative disorders.
Results found that people who slept more than 2 hours in a supine position had four neurodegenerative conditions compared with the control group.
Researchers believe this provides further evidence of a strong link between sleeping on your back and neurodegeneration in Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and mild cognitive impairment. Start your day with health news to see more of this article!
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/ngay-moi-voi-tin-tuc-suc-khoe-vi-sao-tap-the-duc-dieu-do-van-tang-can-185240914220947303.htm


![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the first meeting of the Steering Committee on Regional and International Financial Centers](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/47dc687989d4479d95a1dce4466edd32)
![[Photo] Capital's youth enthusiastically practice firefighting and water rescue skills](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3f8481675271488abc7b9422a9357ada)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs meeting after US announces reciprocal tariffs](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/ee90a2786c0a45d7868de039cef4a712)

![[Photo] Ho Chi Minh City speeds up sidewalk repair work before April 30 holiday](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/17f78833a36f4ba5a9bae215703da710)
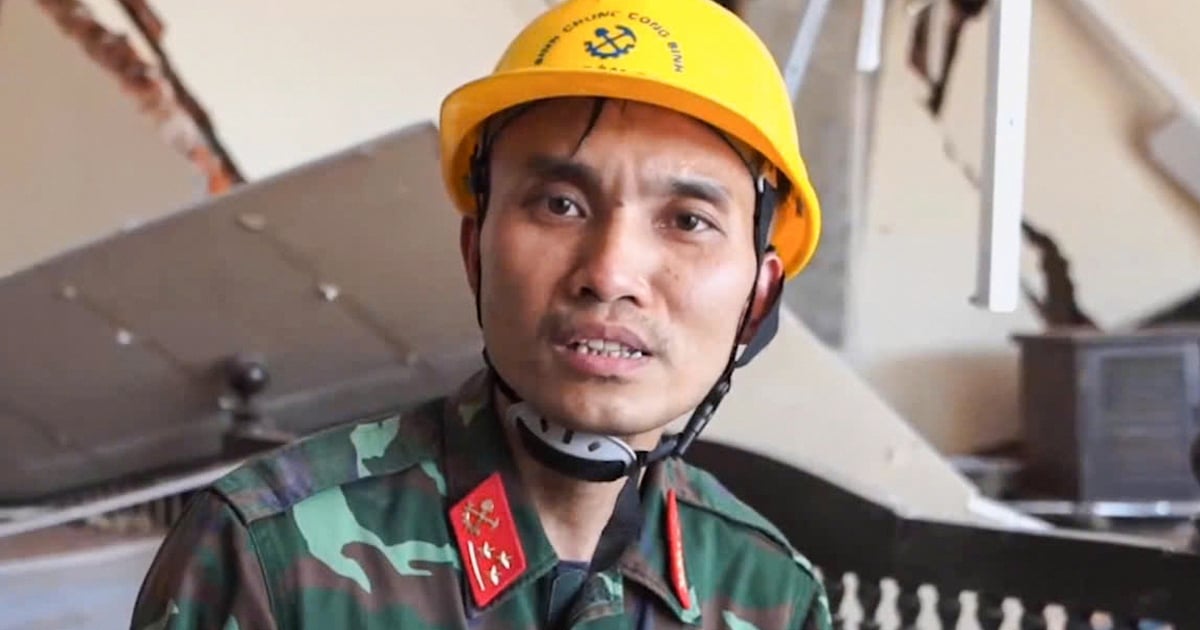
![[Photo] A brief moment of rest for the rescue force of the Vietnam People's Army](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/a2c91fa05dc04293a4b64cfd27ed4dbe)




















































































Comment (0)