According to the China Manned Space Administration, the Long March-7 rocket, carrying the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft, lifted off from the Wenchang Space Launch Center in the southern province of Hainan.
On November 15, China launched the Tianzhou-8 cargo ship to deliver equipment to the Tiangong space station.
According to the China Manned Space Administration, the Long March-7 rocket, carrying the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft, lifted off from the Wenchang Space Launch Center in the southern province of Hainan.
After about 10 minutes, the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft separated from the rocket and entered its designated orbit. The spacecraft's solar panels opened. The Chinese Manned Space Agency declared the launch a success.
The Tianzhou-8 spacecraft will automatically land and dock with the rear port of the Tianhe main module of the Tiangong space station about three hours after launch.
China's Tianzhou cargo ship is 10.6 meters long and has a maximum diameter of 3.35 meters, consisting of 1 cargo module and 1 fuel module, mainly responsible for transporting supplies and fuel to the Tiangong space station and returning waste from the space station to the atmosphere for incineration and disposal.
During this mission, the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft carried essential supplies for astronauts in orbit, including daily necessities, medical supplies, and support materials for spacewalks.
These supplies are mainly intended to support future Shenzhou-19 and Shenzhou-20 astronauts.
Notably, the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft also carried “lunar bricks”, created by scientists from the Huazhong University of Science and Technology (HUST). Scientists used materials simulating lunar soil brought back by the Chang’e-5 spacecraft to create bricks that are three times more durable than conventional red bricks or concrete bricks.
In addition, scientists have also developed a construction method using additive manufacturing technology, also known as 3D printing technology - a process of creating objects in 3D space, in which materials are applied and formed under computer control.
Therefore, the purpose of sending “Moon bricks” into space this time is to test the mechanical performance and heat resistance, as well as the ability to withstand cosmic radiation of the bricks to see if they can be used to build houses on the Moon. It is expected that after the space experiment, “Moon bricks” will return to Earth at the end of 2025.
In addition, the Tianzhou-8 spacecraft also carries fruit flies to conduct scientific experiments in a mixed microgravity environment.
Source: https://nhandan.vn/trung-quoc-chinh-thuc-dua-gach-mat-trang-len-vu-tru-post845342.html
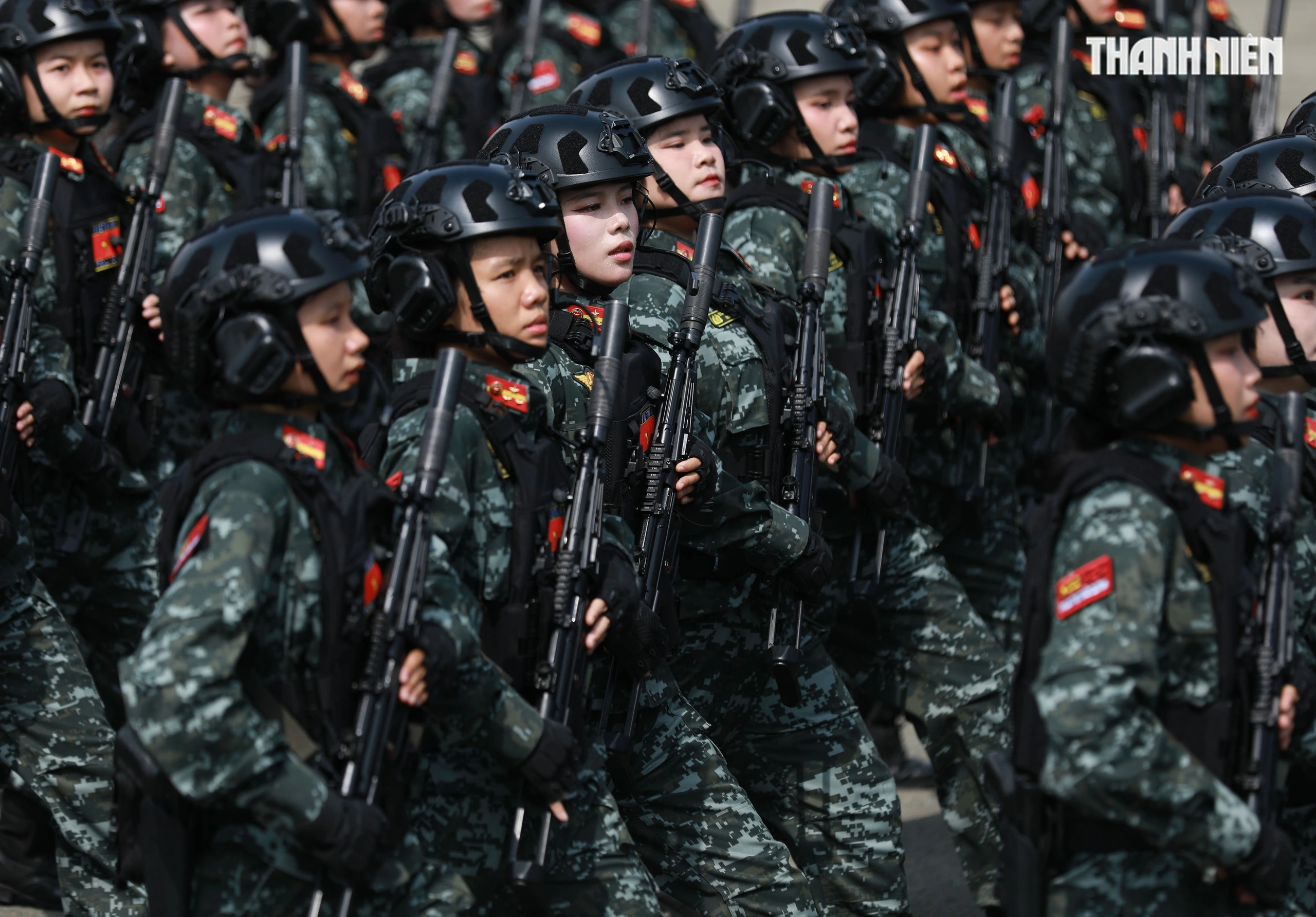






























![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)

























































Comment (0)