People with diabetes, if their blood sugar levels are too low, will experience tremors, dizziness, irregular heartbeat, headaches, and even fainting. If their blood sugar levels are too high, they will feel thirsty, hungry, and urinate frequently.
If diabetes is not treated, it can lead to coma, damage to organs such as the eyes, kidneys, nerves, and heart, according to Channel News Asia .

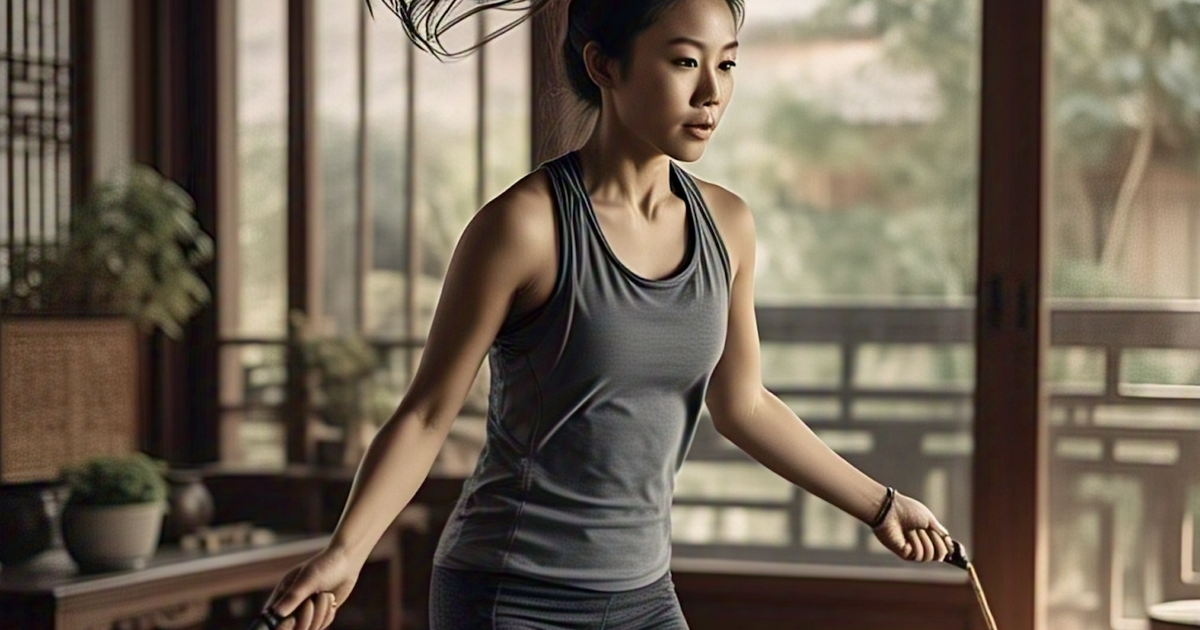
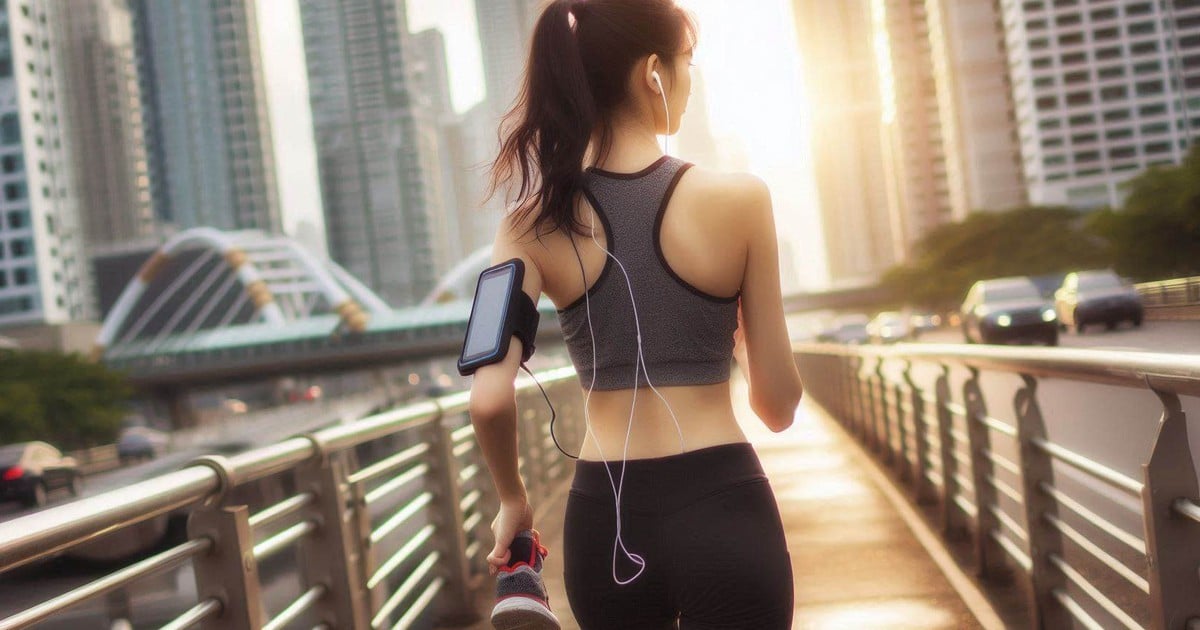
People with diabetes should exercise at a moderate intensity, at least 150 minutes per week.
Exercise can control glucose
According to experts, exercise is key to managing blood sugar levels.
"Overweight people with type 2 diabetes will improve their blood sugar levels if they lose 7% to 10% of their body weight," said Tai Ee Shyong , a professor at the National University of Singapore.
"Muscle contraction during exercise allows cells to take up glucose for energy, regardless of whether insulin is available," said Cheryl Tan, from Alexandra Hospital in Singapore.
When cells respond quickly to insulin, they are better able to absorb glucose from the blood, resulting in lower blood sugar levels, says Chermine Tan, a physiotherapist in Singapore.
Glucose is used by the body for energy both during and after exercise. After exercise, the muscles take up glucose to restore, replenish and stabilize blood sugar levels.
How to exercise effectively?
Many people with diabetes may also have joint pain, heart disease, kidney disease or poor vision, which can make it difficult for them to exercise, Tai said.
In addition, people with diabetes are often older and less active. They do not have the habit of exercising and even lack the motivation to exercise.
According to the American Diabetes Association, people with diabetes should exercise at a moderate intensity, at least 150 minutes per week. The form of exercise is very diverse, such as climbing stairs, walking... as long as they affect large muscles and increase the heart rate.
However, people with diabetes need to follow a specific exercise plan and schedule.
Source link





![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)

![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)




















![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)






























































Comment (0)