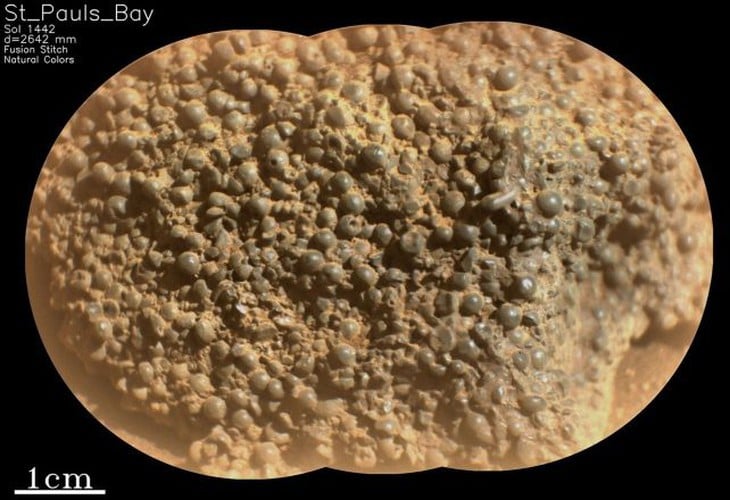
The rock structure looks like a deposit of frog eggs - Photo: NASA/JPL-Caltech/LANL/CNES/IRAP
Ship Perseverance discovered the rock while it was moving around Broom Point, on the lower slopes of Witch Hazel Hill on the edge of Mars' Jezero Crater.
Strange and mysterious rock on Mars
The rock consists of hundreds of small dark gray spheres, each about a millimeter in diameter, some of which have tiny holes. All of them are clumped together into a structure that looks like a mass of deposited frog eggs.
Scientists have named this rock St. Pauls Bay and described it as “shocking”. There is nothing similar in the surrounding area. Furthermore, the composition, formation and origin of St. Pauls Bay are also a mystery.
The rock is not attached to the bedrock, but was somehow moved from its original location. Without knowing where St. Pauls Bay came from, scientists cannot determine the context in which it was formed, a key factor in determining whether it was created by fire or water. However, orbital observations have detected a dark layer of rock nearby that may be where St. Pauls Bay was born.
On Earth, minerals crystallize in spherical clusters called botryoidal structures. Many minerals can form this form by a well-understood formation mechanism.
However, the way such structures form on Mars may be entirely different, especially since St. Pauls Bay appears to be unlike botryoidal structures on Earth, such as grape agate or hematite.
Evolutionary significance
According to Space , determining the geological origin of features in this area could provide valuable insights into how the rocks here have evolved over billions of years.
One way these little balls could form is from molten lava that cools rapidly. This could happen during a meteorite impact, where the heat from the impact with the planet’s surface melts the material, creating droplets that are then scattered. Another possibility is that they could also occur during volcanic activity.
The Witch Hazel Hills area is scientifically significant, with each rock layer like a page in the history of Mars.
The samples Perseverance has collected also include one with interesting features resembling leopard spots and poppy seeds, which scientists suspect could be evidence of ancient microbial activity.
Previously, a study published on March 24 in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States showed the development of prebiotic chemical reactions on Mars.
While analyzing a rock sample in a miniature laboratory built into the Curiosity rover, scientists discovered the largest organic molecules ever found on Mars.
In the past, the Curiosity rover has detected small, simple organic molecules. However, this discovery suggests that chemical reactions on Mars may have progressed enough for life to form.
Source: https://tuoitre.vn/tau-tham-do-nasa-phat-hien-tang-da-bi-an-tren-sao-hoa-20250331202541743.htm


![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)




![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)












































































Comment (0)