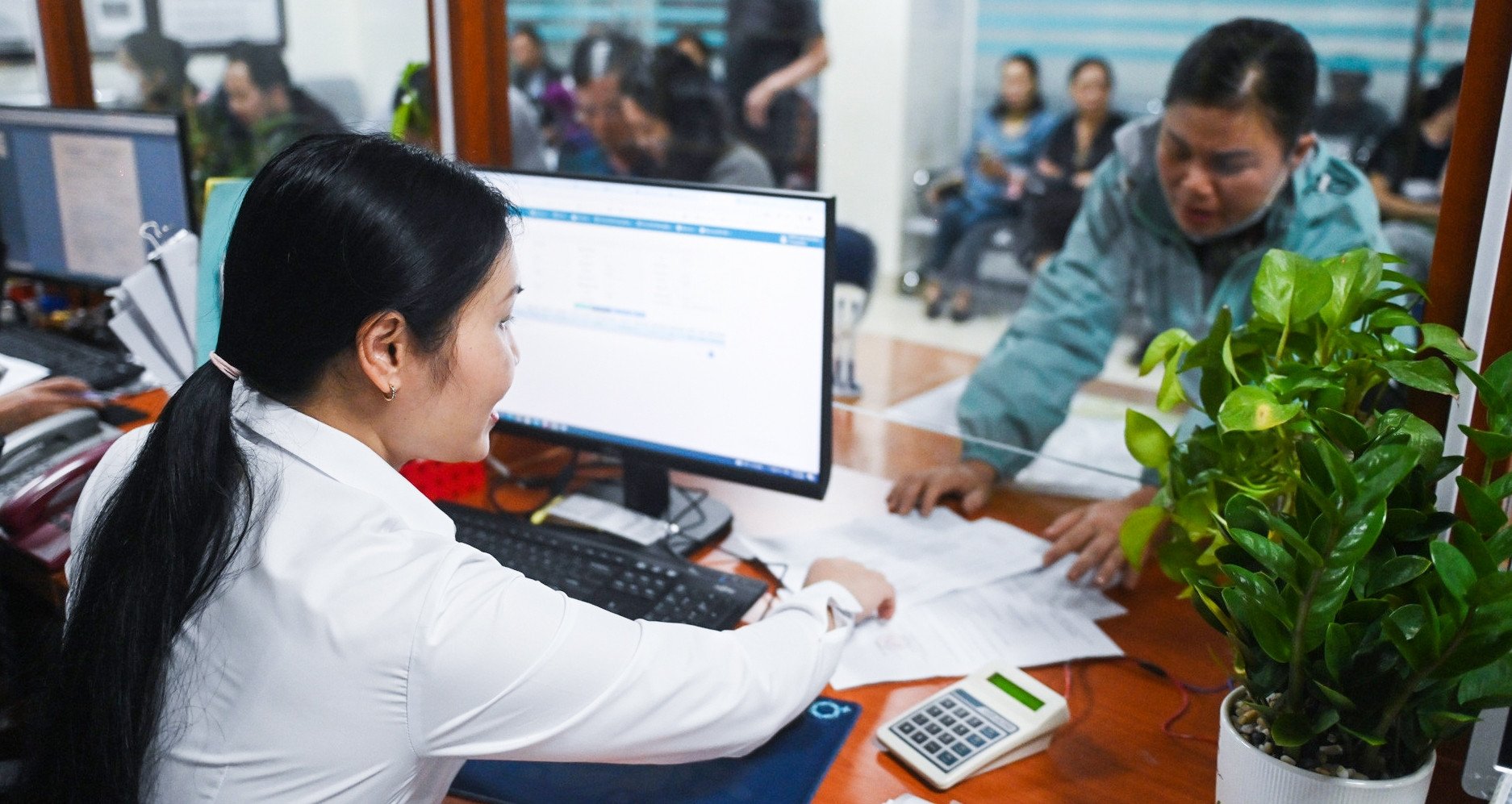
The Social Insurance Law 2024, effective from July 1, 2025, stipulates that employees can receive sick leave benefits calculated on a half-day basis. Specifically, sick leave of less than half a day is counted as half a day, from half a day to less than one day is counted as one day.
Specifically, Article 42 of this Law stipulates that employees are entitled to sick leave benefits when they are off work in one of the following cases:
Treatment for illnesses that are not occupational diseases; treatment for accidents that are not work-related accidents; treatment for accidents while traveling from home to work or from work to home by a reasonable route and time in accordance with the provisions of law on occupational safety and hygiene;
Treatment and rehabilitation of occupational functions when injuries or illnesses recur due to work-related accidents, occupational diseases or accidents; donation, removal, and transplantation of human tissues and organs according to the provisions of law; care for sick children under 7 years old.

The maximum time to enjoy sick leave in a year (from January 1 to December 31) for employees is calculated by working days, excluding holidays, Tet, and weekly days off, and is regulated as follows:
Working under normal conditions, you are entitled to 30 days if you have paid compulsory social insurance for less than 15 years; 40 days if you have paid from 15 years to less than 30 years; 60 days if you have paid from 30 years or more;
Those who work in arduous, toxic, dangerous or especially arduous, toxic, dangerous occupations or jobs on the list of arduous, toxic, dangerous or especially arduous, toxic, dangerous occupations or jobs issued by the Minister of Labor, War Invalids and Social Affairs or work in areas with especially difficult socio-economic conditions are entitled to 40 days if they have paid compulsory social insurance for less than 15 years; 50 days if they have paid from 15 years to less than 30 years; 70 days if they have paid for 30 years or more.
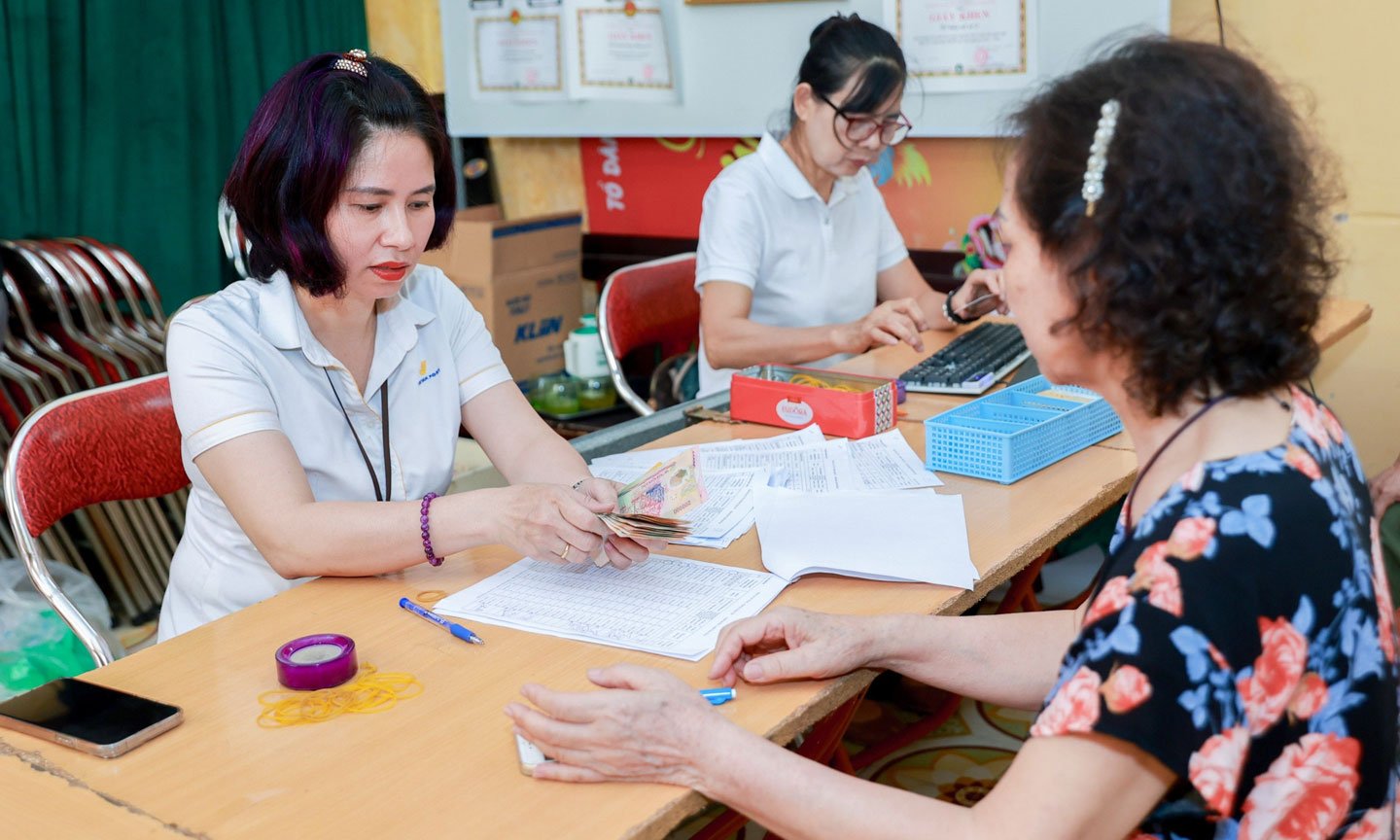
Regarding the level of sickness allowance, it is calculated monthly and based on: Salary used as the basis for social insurance payment of the month most recent before the month of sick leave; salary used as the basis for social insurance payment of the first month of participating in social insurance or the month of re-participation if having to take sick leave in the first month of participation or the month of re-participation.
Compared to current regulations, the Social Insurance Law 2024 has added regulations on sick leave to meet the needs of protecting the rights of employees.
Specifically, supplementing the partial sick leave regime. Accordingly, employees can receive sick leave benefits calculated on a half-day basis. Specifically, for employees who take sick leave for a partial day, the absence from work of less than half a day is counted as half a day; from half a day to less than one day is counted as one day.
This regulation ensures that employees still enjoy benefits when taking time off for health reasons without having to take the entire day off.
In cases of sickness benefits, the Law supplements benefits for employees to take time off work to treat non-occupational diseases, accidents on the way to work, tissue or body part transplants, or when using precursor drugs as prescribed by a doctor.
Cases where employees are not entitled to sick leave
The Social Insurance Law 2024 also stipulates 4 cases in which employees participating in social insurance are not entitled to receive sick leave benefits. Specifically, this law stipulates that employees are not entitled to receive sick leave benefits in the following cases:
Self-injury or self-harm.
Use of narcotic substances and drug precursors according to the list prescribed by the Government, except for the use of precursor drugs or combination drugs containing precursors as prescribed by medical practitioners at medical examination and treatment facilities.
During the first time having to take time off work for treatment and rehabilitation due to work-related accidents or occupational diseases.
During the leave of absence coinciding with the leave of absence prescribed by the law on labor or during the leave of absence with full pay prescribed by other specialized laws or during the leave of absence to enjoy maternity benefits or recuperation benefits prescribed by the law on social insurance.
Source: https://vietnamnet.vn/om-dau-nua-ngay-nguoi-lao-dong-duoc-bhxh-chi-tra-che-do-2348653.html



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh chairs the Government's special meeting on law-making in April](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/13/8b2071d47adc4c22ac3a9534d12ddc17)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the Policy Forum on Science, Technology, Innovation and Digital Transformation](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/13/c0aec4d2b3ee45adb4c2a769796be1fd)

![[Photo] National Assembly Chairman Tran Thanh Man attends the ceremony to celebrate the 1015th anniversary of King Ly Thai To's coronation](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/13/6d642c7b8ab34ccc8c769a9ebc02346b)
















































































Comment (0)