Sleep paralysis, also known as sleep paralysis, can occur in people with narcolepsy, a mental health disorder.
As the body falls asleep, the brain sends signals to relax the muscles in the arms and legs. This results in a loss of muscle tone and automatic paralysis during rapid eye movement (REM) sleep, which begins 70 to 90 minutes after falling asleep.
If part of the brain is awakened, sleep paralysis (also known as sleep paralysis) occurs, the sleeper is aware of their surroundings but cannot move or speak, and gradually hallucinates for several minutes. According to WebMD , 4 out of 10 people have experienced sleep paralysis at some point in their lives, most commonly in adolescence.
Sleep disorders
A 2010 study by Kaohsiung Medical University in Taiwan, involving 100 participants, found that sleep paralysis was common among people with chronic insomnia, circadian rhythm disorders, and nocturnal leg cramps. Of these, 38% had obstructive sleep apnea.
Scientists explain that sleep disorders can affect the quality, quantity, and duration of sleep; thereby, leading to daytime discomfort and impaired cognitive function at night. Sleep paralysis is more common when lying on your back. Because sleeping in this position can easily cause snoring and sleep apnea.
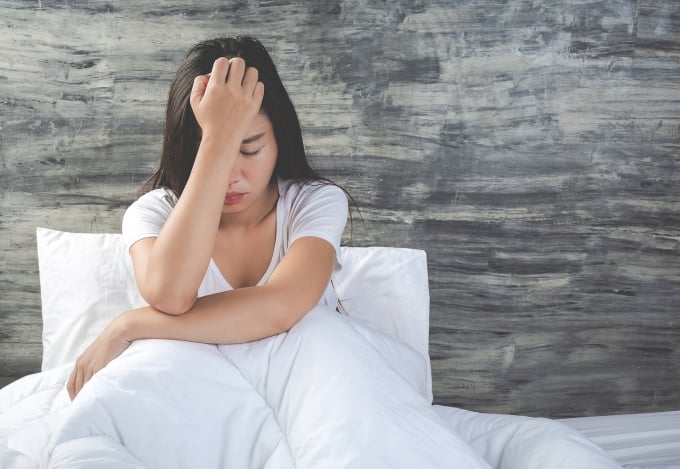

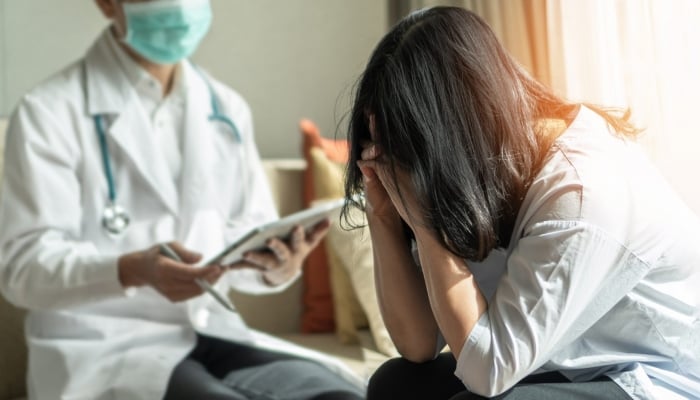
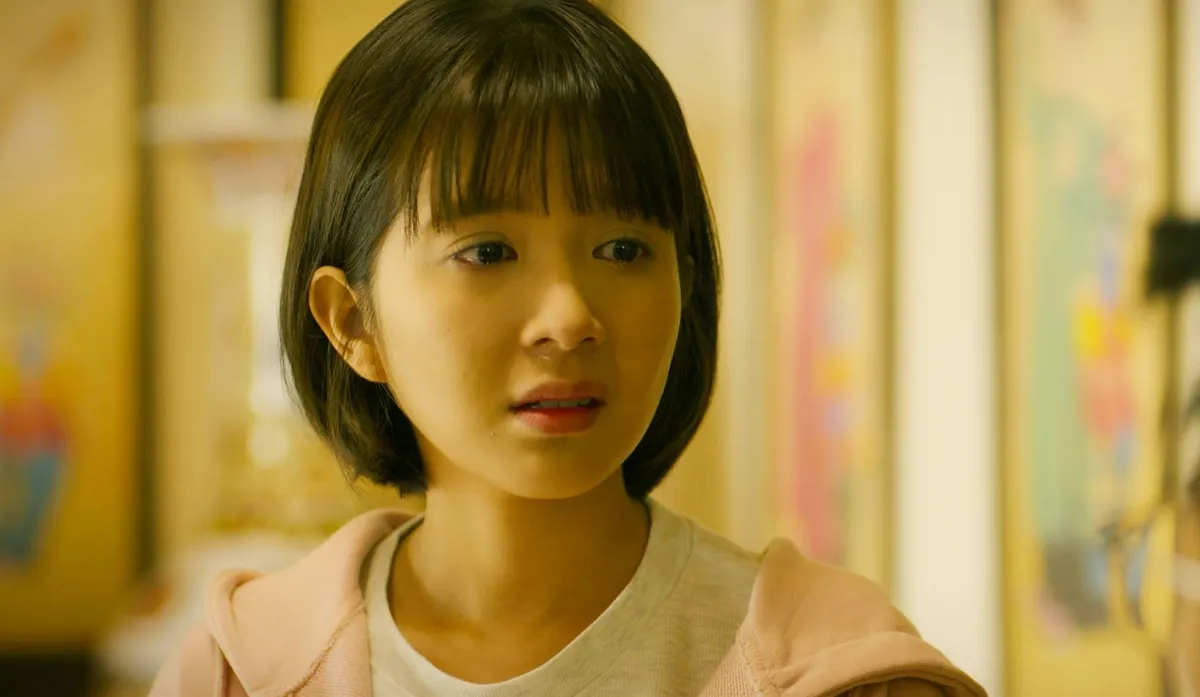
Sleep paralysis affects sleep, makes you wake up easily and causes fatigue. Photo: Freepik
Narcolepsy
The brains of people with narcolepsy often have difficulty controlling their sleep-wake cycles due to the loss of brain cells that produce a neurotransmitter called orexin. This substance plays a role in reinforcing wakefulness and inhibiting REM sleep. As a result, the brain can fall into a state of paralysis after falling asleep more often.
Signs of narcolepsy include intermittent sleep, hallucinations, daytime sleepiness, or muscle weakness. Risk factors for narcolepsy include jet lag and shift work.
Mental health disorders
People with post-traumatic stress disorder, who have experienced physical and mental suffering, and anxiety disorders are susceptible to sleep paralysis. The cause is a combination of hallucinations, disordered thoughts and behaviors that impair daily activities, thereby developing anxiety, leading to sleep paralysis.
Daydreamers are also more likely to suffer from sleep paralysis, scientists say, explaining that supernatural beliefs increase hallucinations.
Sleep paralysis is not harmful but can affect mental health, easily causing negative thoughts when going to bed, reducing the number of hours of good sleep. To avoid this situation, everyone should keep a regular sleep schedule and get enough sleep.
In daily life, avoid caffeine, limit evening snacks and do not use phones or computers before going to bed to reduce exposure to blue light. Relax before going to bed by taking a bath, reading a book, listening to soothing music.
Huyen My (According to Sleep Foundation, Healthline )
| Readers ask neurological questions here for doctors to answer |
Source link



























































































Comment (0)