 |
The Ministry of Health issued Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and prevention of monkeypox in humans with Decision 2099/QD-BYT.
1. What is monkeypox?
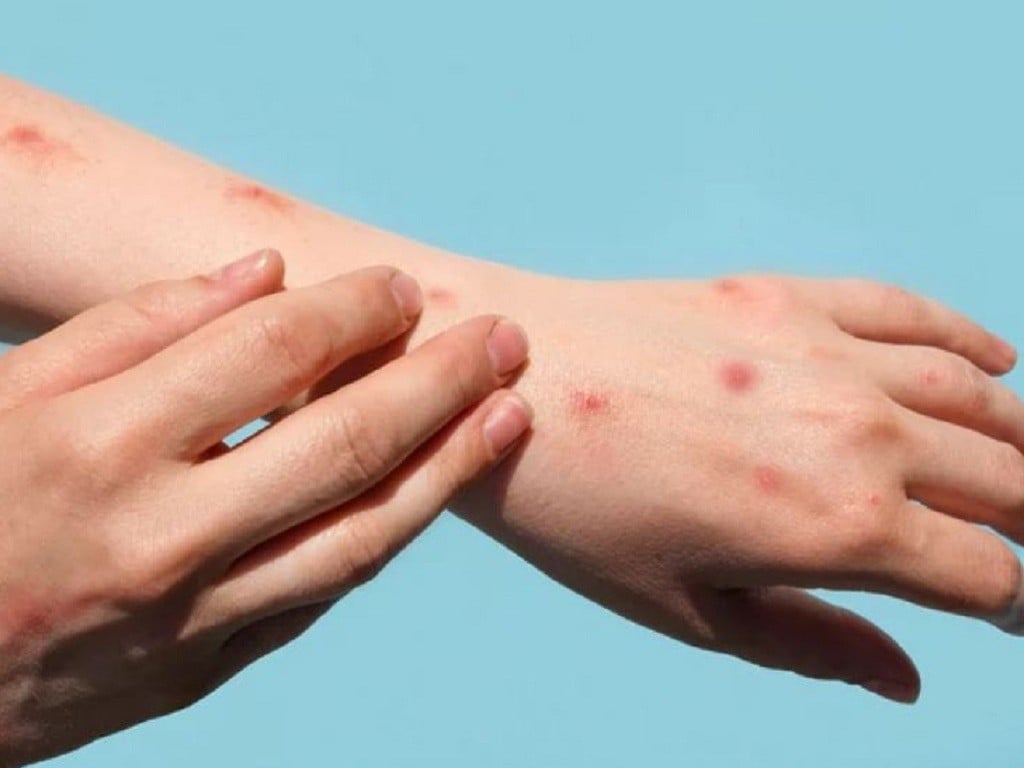
Monkey pox is an acute infectious disease with the potential to cause epidemics caused by the monkeypox virus. The disease originates in Africa and is transmitted from animals to humans and from humans to humans through direct contact with skin lesions, body fluids, sexual contact, respiratory droplets, objects of infected people, and from mother to child. The main symptoms of the disease are fever, blister-like rash, and peripheral lymphadenopathy, which can cause serious complications leading to death.
On July 23, 2022, the World Health Organization (WHO) declared a public health emergency of international concern over monkeypox.
2. Instructions for preventing monkeypox
* Non-specific prevention:
General precautions to avoid monkeypox infection include:
- Avoid contact with people/animals that may be sick (including sick or dead animals in areas where monkeypox occurs).
- Avoid contact with objects and surfaces that may be contaminated with monkeypox virus, such as bed sheets and clothing of sick people.
- Isolate and treat patients at medical facilities.
- Regularly wash hands with soap and common antiseptic solutions after contact with people/animals suspected of being infected.
- Use personal protective equipment when caring for sick people.
- Conduct exposure risk assessments according to regulations to take appropriate action.
* Specific disease prevention with vaccines:
Use of monkeypox vaccine to prevent monkeypox in high-risk groups.
* Infection prevention at treatment facilities:
Strictly implement isolation of suspected, possible and confirmed cases. Comply with infection control and prevention measures for medical staff, caregivers and other patients at treatment facilities according to the instructions of the Ministry of Health.
3. Instructions for treating monkeypox
3.1. Treatment principles
- Monitor and isolate suspected/confirmed cases;
- Treatment is mainly symptomatic;
- Ensure nutrition, electrolyte balance and psychological support;
- Use specific treatment drugs in severe cases and special conditions (infants, the elderly, people with immunodeficiency, etc.) according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization and Vietnamese regulations.
- Monitor, detect and promptly treat serious conditions and complications of the disease.
3.2. Specific treatment
* General treatment measures :
- Isolate suspected/confirmed cases at medical facilities according to the Ministry of Health's temporary guidelines for monitoring and preventing monkeypox.
- Personalize treatment for each patient.
* Mild :
Treat symptoms such as:
- Fever reducer, pain reliever.
- Care for skin, eye and mouth injuries.
- Ensure nutrition and electrolyte balance.
- It is necessary to monitor and detect early complications if any: pneumonia, skin infection, sepsis, encephalitis... for treatment in the isolation room in the intensive care unit.
- Prevent and control infection according to regulations
* Heavy :
Need to be treated in an isolation room in the intensive care unit, treat complications (if any) according to issued protocols.
* Specific treatment drugs :
- Indication
+ People with severe complications (sepsis, pneumonia, encephalitis...).
+ People with weakened immune systems (HIV, cancer, being treated with immunosuppressants or high-dose corticosteroids...).
+ Children, especially children under 8 years old.
+ Pregnant or breastfeeding women.
+ People with progressive acute illness.
- Treatment drugs are used according to the recommendations of the World Health Organization (refer to Appendix 2)
+ Tecovirimat
+ Cidofovir
+ Brincidofovir
+ Intravenous immune globulin
Source





![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)
![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)



















![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)





























































Comment (0)