Getting enough sleep, reducing stress, eating healthy and exercising moderately will help the next shot produce better immunity.
Some scientists believe that a healthy lifestyle helps the body respond to vaccines more effectively. A study published in 2022 in the British Journal of Sports Medicine showed that two and a half hours of exercise a week increased the protection of vaccines, reduced the risk of hospitalization, severe illness...
Get enough sleep
Getting enough sleep has many benefits, including boosting immunity. Good sleep increases the activity of specialized white blood cells (called T cells), improving the response to many vaccines such as influenza, hepatitis A and B.
A study published in March in the journal Current Biology found that people who slept less than six hours a night had a lower immune response than those who slept enough. Another study in 2012 on people who had received the hepatitis B vaccine found that sleeping less than six hours a night reduced the immune response 11 times more effectively than sleeping more than seven hours a night.
Stress Relief
According to a 2021 scientific paper published in the journal Sage , there have been many studies demonstrating the link between stress, depression, loneliness and how the immune system responds to vaccines. People who care for patients with dementia or who are chronically stressed, respond less to influenza and pneumococcal vaccines than those who are less stressed.
Therefore, experts suggest that people exercise regularly, get enough sleep, and practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing, meditation, and yoga to reduce stress and increase vaccine effectiveness.
Increase movement
Regular physical activity also helps boost immunity. According to a 2007 study, physically fit older adults responded better to tetanus and influenza vaccines than their less fit peers. Older adults who exercised vigorously for at least 20 minutes three or more times a week had a stronger immune response to the flu vaccine than older adults who were moderately or sedentary.
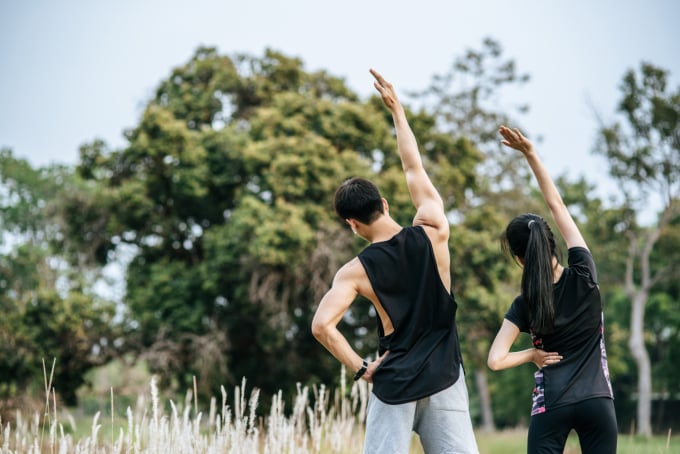

Exercise helps reduce stress, increase immunity, and respond better to vaccines. Photo: Freepik
Anti-inflammatory diet
An anti-inflammatory diet also supports the immune system. People should eat more fruits, vegetables, whole grains, whole soy foods and fish; eat less processed foods, fats, sugar. While eating, people should supplement with fiber-rich foods, which help promote gut bacteria and avoid excessive alcohol and tobacco use because they negatively affect immunity.
Chile (According to Prevention )
Source link


![[Photo] Comrade Khamtay Siphandone - a leader who contributed to fostering Vietnam-Laos relations](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/3d83ed2d26e2426fabd41862661dfff2)

![[Photo] Special relics at the Vietnam Military History Museum associated with the heroic April 30th](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/a49d65b17b804e398de42bc2caba8368)

![[Photo] Moment of love: Myanmar people are moved to thank Vietnamese soldiers](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/9b2e07196eb14aa5aacb1bc9e067ae6f)














![[Video] Hanoi strengthens food safety control at schools, tightens handling of violations](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/3/c9a2202768fb4d6dbd70deaf3f28979f)







































































Comment (0)