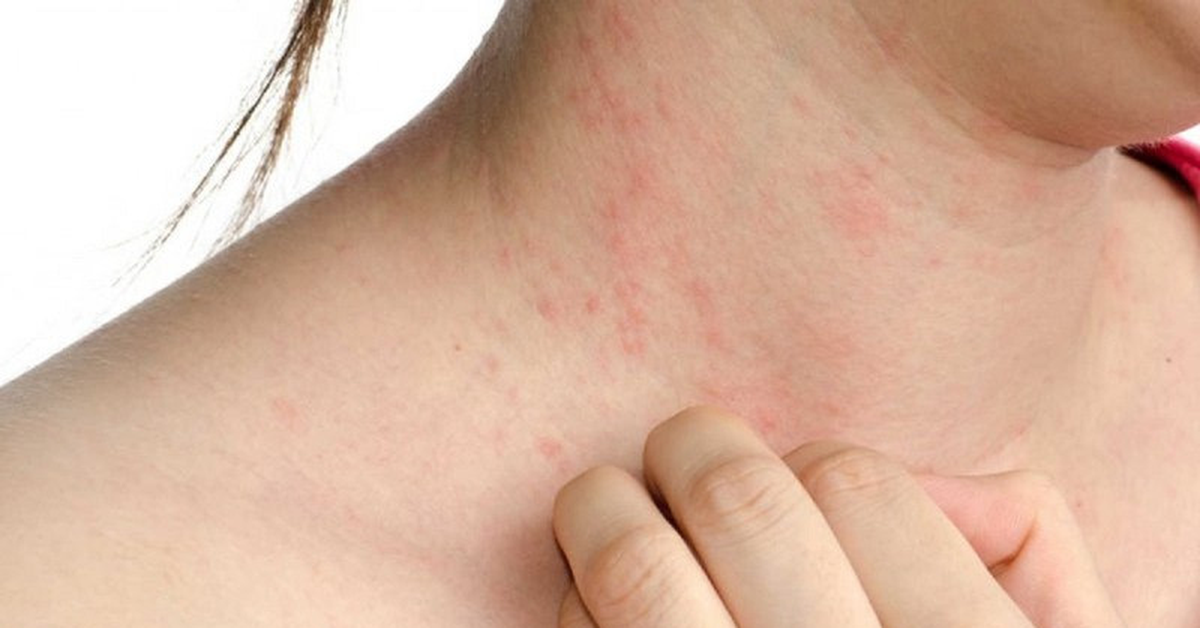
When biting humans, lone star ticks can cause a nasty disorder called Alpha-gal Syndrome (AGS), which makes victims allergic to red meat.
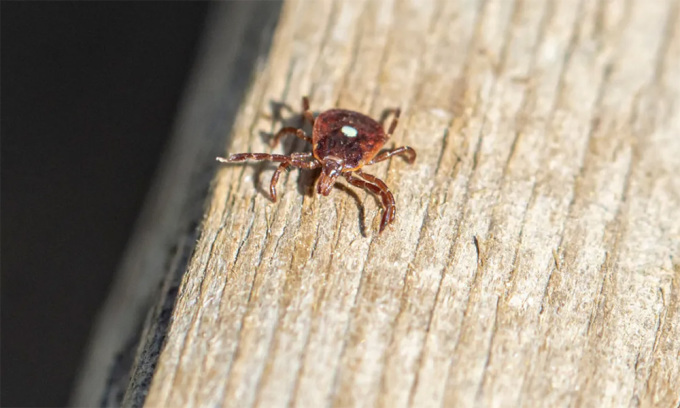

The lone star tick with the ability to cause meat allergy. Photo: Maria T Hoffman
The anaphylactic shock in AGS is not caused by meat but by the sugar molecule galactose-α-1,3-galactose, or alpha-gal, which is found in certain foods, mainly red meat, but also milk and gelatin, IFL Science reported on June 14. Alpha-gal is limited to mammals, meaning not all meats cause allergies because alpha-gal is not found in fish, birds, or reptiles, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
If bitten by a lone star tick and infected with AGS, symptoms can appear within about two hours of eating the offending food. Symptoms include coughing, nausea, vomiting, rash, difficulty breathing, and low blood pressure.
The severity of AGS varies from person to person. They may experience only mild symptoms or struggle with life-threatening symptoms such as anaphylaxis. The severity of the reaction varies, but in severe cases, patients may have difficulty breathing and feel like they are on fire every time they eat meat.
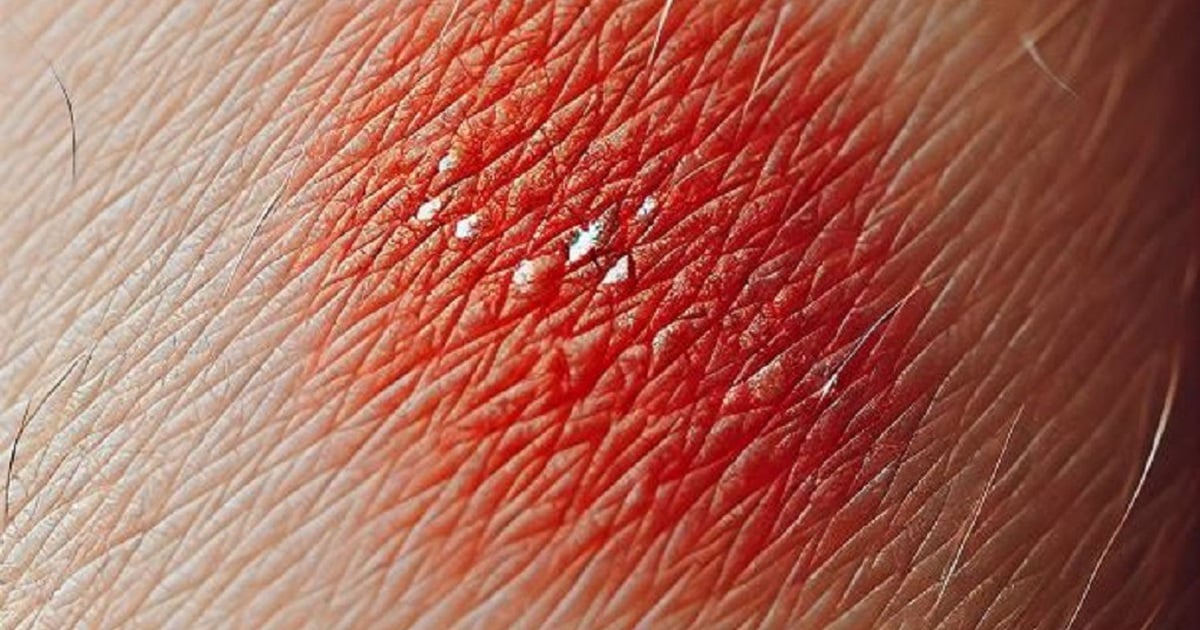
The mechanism of allergy is thought to involve tick saliva, which contains proteins with alpha-gal molecules. Their presence leads to IgE antibody hypersensitivity to sugar, causing subsequent exposure to alpha-gal to cause an allergic reaction. An increase in certain B cells is also associated with an exaggerated immune response to alpha-gal. Just one bite from a lone star tick can cause a lifelong allergy to red meat.
The lone star tick ( Amblyomma americanum ) is common in the eastern United States and Mexico. It needs blood to develop at every stage of its life cycle, so it has evolved the ability to attach itself to everything from turkeys to deer to humans. It is easily identified by its color and markings. It is reddish brown with an oval body, and females have a white spot on their back. In addition to causing meat allergies, the lone star tick also transmits the bacterial infection ehrlichiosis.
Thu Thao (According to IFL Science )
Source link




![[Photo] Military doctors in the epicenter of Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/6/fccc76d89b12455c86e813ae7564a0af)
























![[Photo] Quang Binh: Bright yellow vermicelli flowers in Le Thuy village](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/6/80efad70a1d8452581981f8bdccabc9d)





























































Comment (0)