Many times, public opinion has mentioned that many scientific research topics have poor applicability, and some research topics are even put away in a drawer, causing waste of state budget. However, there are also opinions explaining that delays and risks are part of scientific research. Reporters of the People's Army Newspaper had an interview with Ms. Nguyen Thi Thu Hien, Deputy Director of the Department of Planning and Finance, Ministry of Science and Technology (MOST) about this issue.
What is lag in scientific research?
Reporter (PV): Recently, there have been many concerns about scientists using delays and risks as excuses for research topics that are then put in drawers, have no practical value, and waste the state budget. Can you explain more clearly about the concepts of delays and risks in scientific research?
 |
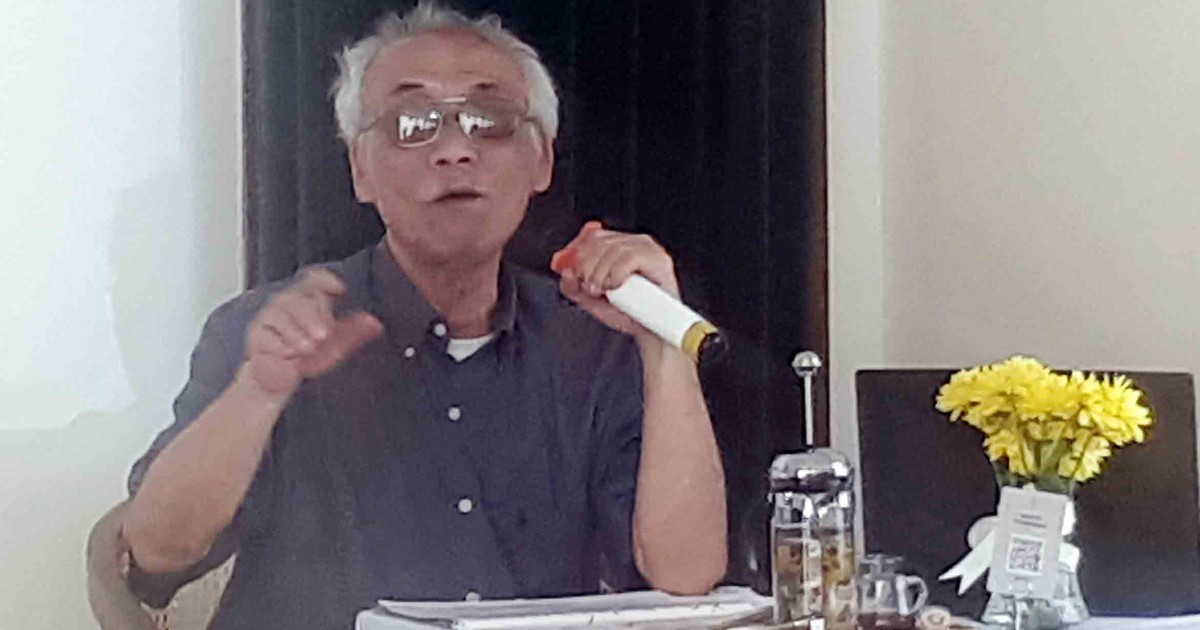
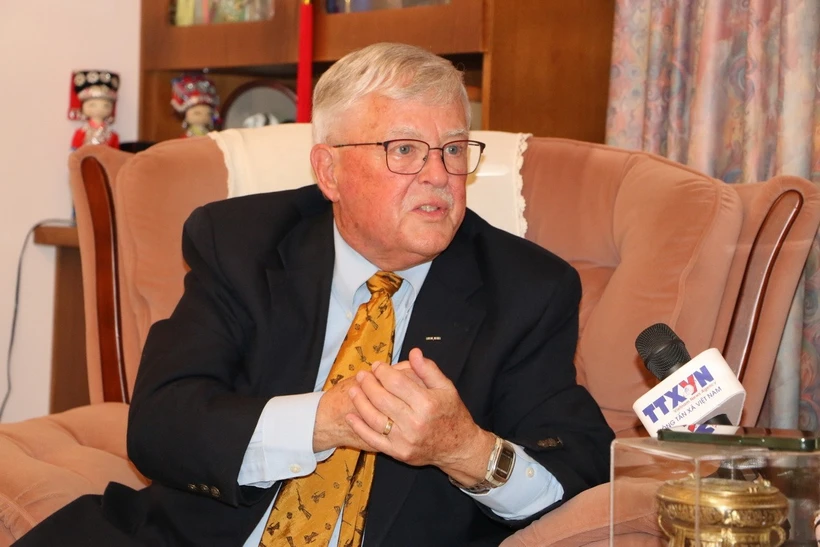
| Mrs. Nguyen Thi Thu Hien. |
Ms. Nguyen Thi Thu Hien: The delay in scientific research is the time from when the research results are available until the research is effective and applied in life and production. Thus, the time to implement the research topic is not included in the delay time. The delay in application is due to the users of the research results, the manufacturers using the researched technology, not the researchers.
Risk in scientific research is often understood as failure, but in fact it is just not achieving the expected research product. All types of research have more or less risks, that is, not achieving the expected product, due to many reasons. It can be seen that the risk increases from basic research to implementation. Risk in scientific research should not be understood simply as failure, because failure in the research process also has great reference value. Delay and risk are the nature of scientific research, which need to be accepted in research activities.
PV: Can you give some examples of delays in scientific research?
Ms. Nguyen Thi Thu Hien: For example, to find a solution to restore a coral reef, scientists must use the basic research results that have been accumulated for many years on the characteristics and structure of corals and the results of research on the marine environment in that area. Or to create a new material, scientists must also use the basic research results that have been accumulated for many years on the characteristics and structure of basic materials and a series of other knowledge to be able to find a solution to create a new material with the required properties.
To date, Vietnam has produced a number of vaccines and has become the fourth country in the world to produce its own vaccine against rotavirus diarrhea. To achieve this, since 1998, Vietnam has carried out exploratory research and basic research oriented to application. By the end of 2017, Vietnam had fully mastered the technology and was able to produce its own vaccine against diarrhea to meet domestic and export needs. Thus, it took nearly 20 years of research for Vietnam to produce a vaccine against diarrhea.
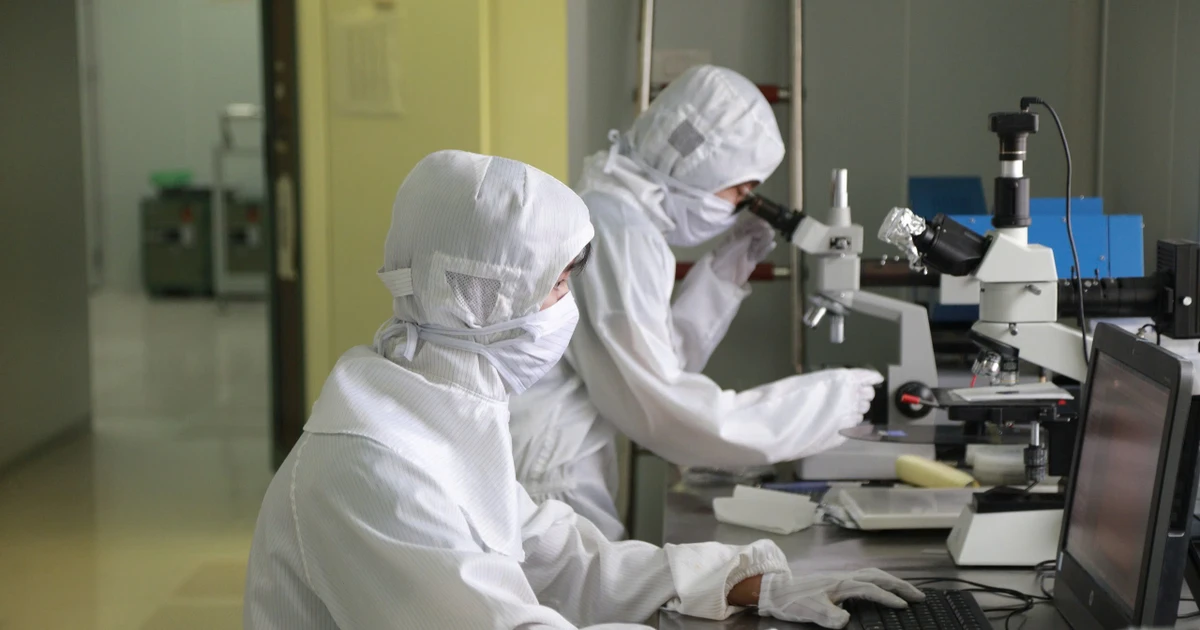
 |
| Lecturers and students of Hanoi University of Science and Technology do research in the laboratory. Photo: KIM NGOC |
Need appropriate reward and punishment mechanism
PV: So what solutions does the Ministry of Science and Technology have so that research results can be quickly applied to life?
Ms. Nguyen Thi Thu Hien: The nature of science is that it has delays and risks. There are tasks that, after research, must wait for a period of time to be completed and prepare infrastructure conditions before they can be applied to production and business practices to serve socio-economic development. In order for research results to be quickly applied to life, the Ministry of Science and Technology has been coordinating with ministries, branches and localities to focus on reviewing and restructuring the chain of scientific and technological research associated with basic research. The mechanisms and policies of science and technology in the coming time will focus on supporting and promoting innovation activities in all sectors and fields. The Ministry of Science and Technology will develop and supplement criteria on the application and commercialization of research and development results into current state management mechanisms on science and technology. In particular, it is necessary to perfect the management system of scientific and technological programs and tasks to ensure publicity and transparency of all processes and procedures. Investigate, publicly announce application results and have appropriate reward-punishment mechanisms.
In addition, state budget resources need to continue to maintain and gradually increase the proportion of funding for implementing science and technology tasks. Science and technology tasks focus on prioritizing the development of key, key products and national products according to the value chain and must be linked to enterprises, with enterprises as the center. Build a reasonable proportion of expenditure for basic research, applied research, experimental development and commercialization; invest sufficiently, up to the threshold for science and technology tasks eligible for commercialization. Increase the proportion of investment in science and technology, innovation from socialization to a higher level than investment from the state budget.
The Ministry of Science and Technology will continue to build and improve the legal framework, create favorable conditions to promote the formation and development of venture capital funds in the field of science and technology, increase projects in the form of PPP (public-private partnership investment), contributing to diversifying investment capital sources for science and technology activities. In addition, the Ministry of Science and Technology will promote the development of high-quality science and technology human resources; focus on developing a team of leading experts, scientists, and strong research groups. At the same time, the Ministry of Science and Technology will continue to improve mechanisms and policies to attract and promote domestic and foreign science and technology talents and experts; strengthen international cooperation to learn from experiences, support the development of an innovative startup ecosystem.
PV: Thank you very much!
LA DUY (performed)
*Please visit the Science Education section to see related news and articles.
Source































![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)












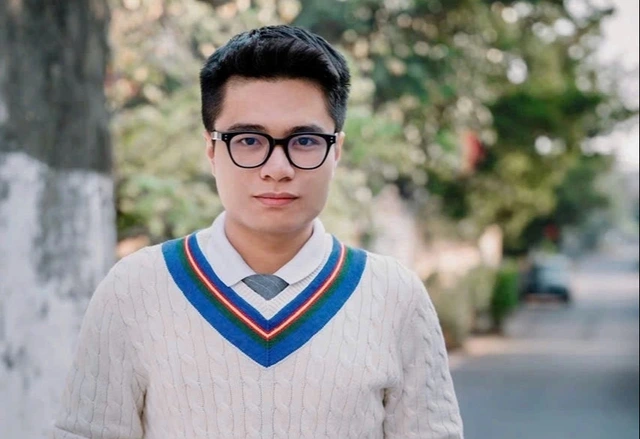















































Comment (0)