Thanks to its high protein and fiber content, cereals help people feel full for a long time, making it easier to maintain a diet. If eaten properly, cereals not only support weight loss but also help control blood sugar, improve intestinal health and many other benefits, according to the health website Medical News Today (UK).
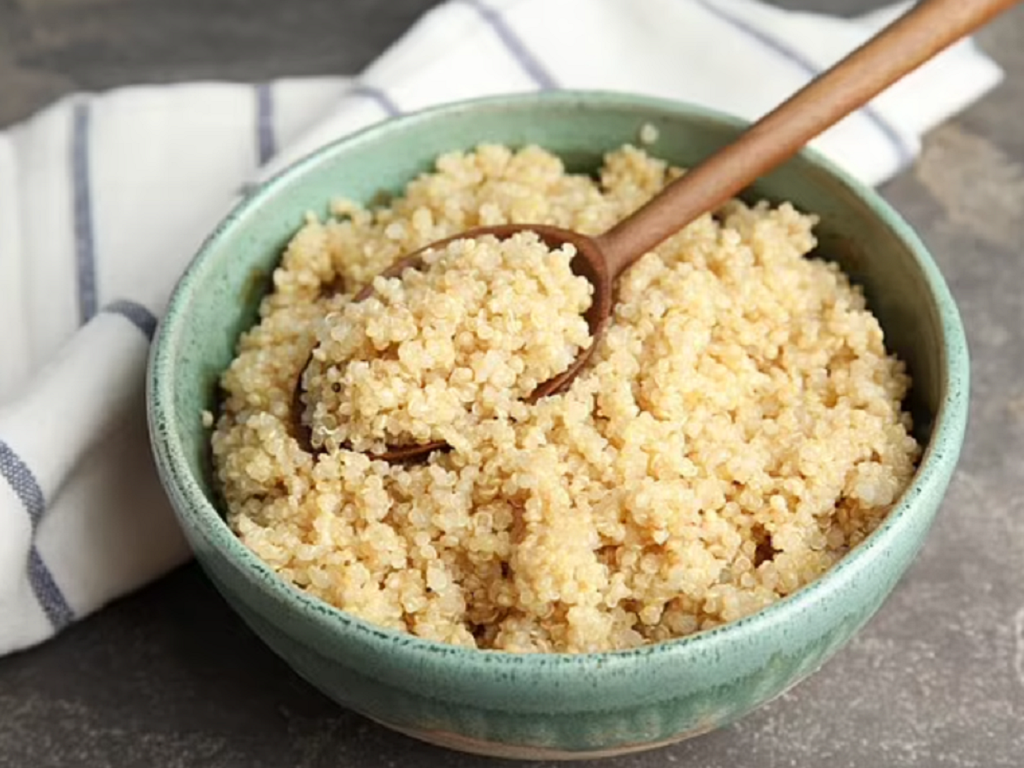

Quinoa can be used to replace part of rice in daily meals.
Protein-rich grains include:
Quinoa
One cup of quinoa has about 8 grams of protein. Not only that, quinoa is also a rich source of complete amino acids, containing all 9 essential amino acids for the body.
Quinoa also contains fiber, iron, magnesium, and B vitamins. People can add quinoa to their daily diet in many ways, from adding it to salads, baking, or using it as a rice substitute in meals.
Amaranth
Amaranth is a whole grain that is very high in protein. One cup of amaranth has about 9.4 grams of protein. Amaranth is technically a seed. However, in everyday life, it is still classified as a whole grain.
In addition to being rich in protein, amaranth is also rich in manganese. Just one cup of amaranth provides you with your daily dose of manganese. Manganese is a mineral that is essential for bone health and helps the body absorb certain nutrients.
Like quinoa, amaranth is one of the few whole grains that contains all nine essential amino acids that the body needs. People can cook amaranth similar to rice or grind it into flour.
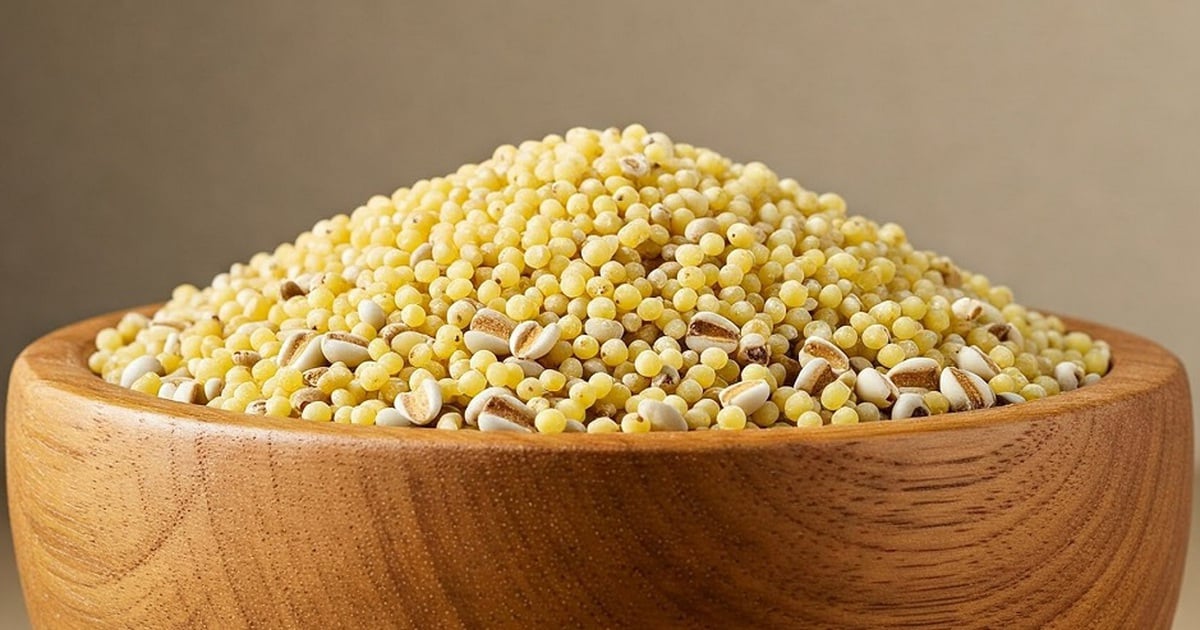
Millet
Millet is a gluten-free grain that is rich in protein, fiber, and essential minerals such as magnesium, phosphorus, and manganese. Each cup of millet has about 6 grams of protein. Not only is it nutritious, millet also tastes good. People can boil it, stew it, or cook it in soup.
Buckwheat
One cup of buckwheat has nearly 6 grams of protein. This whole grain has been called a “superfood” because of its high fiber, essential amino acids, and antioxidants. Several studies have shown that buckwheat can improve heart health, promote weight loss, and control blood sugar, according to Medical News Today .
Source link


![[Photo] Looking back at the impressive moments of the Vietnamese rescue team in Myanmar](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/5623ca902a934e19b604c718265249d0)
![[Photo] "Beauties" participate in the parade rehearsal at Bien Hoa airport](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/155502af3384431e918de0e2e585d13a)
























![[Photo] Summary of parade practice in preparation for the April 30th celebration](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/11/78cfee0f2cc045b387ff1a4362b5950f)





























































Comment (0)