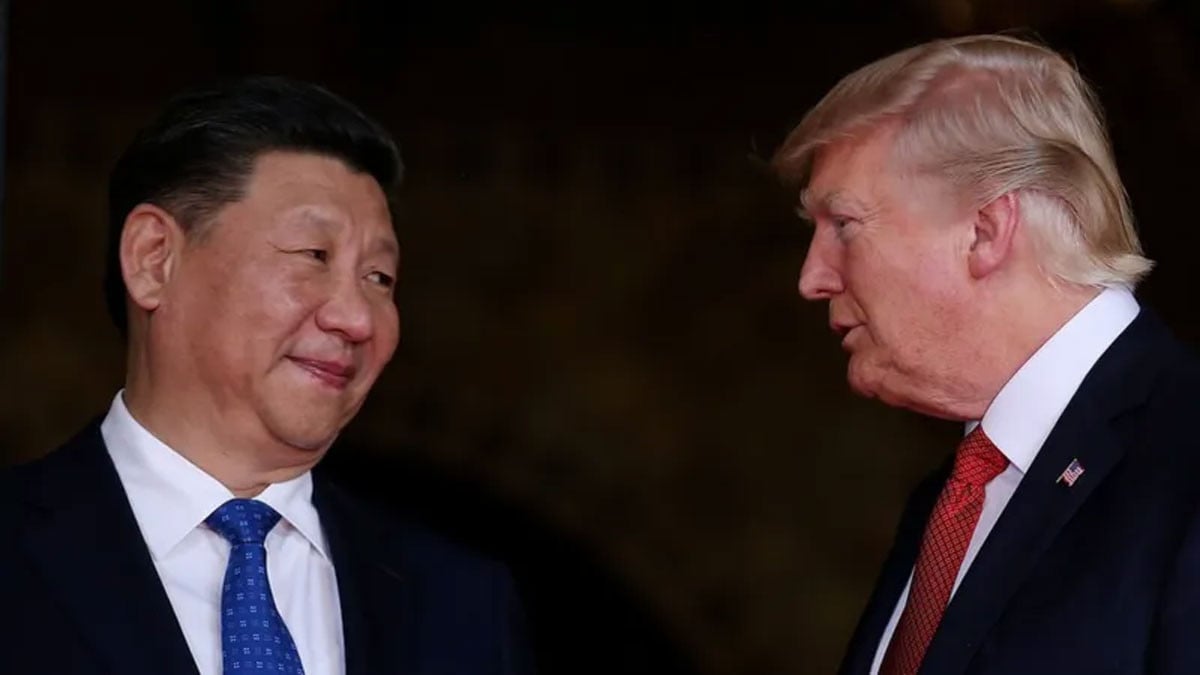
China has just introduced a series of solutions to strive to achieve ambitious economic growth targets in the context of the Donald Trump administration escalating trade tensions.
At the opening session of the National People's Congress on March 5, Beijing set a GDP growth target of "around 5%" for 2025. The figure comes as the world's second-largest economy faces a series of challenges, including President Donald Trump's escalating tariffs - doubling to 20% on Chinese goods imported into the US.
Increase spending, stabilize domestic market
Faced with great pressure from the US and the difficulty in changing the Trump administration's "America First" will, Beijing has gradually shifted its focus to domestic demand, reducing its dependence on exports, especially the US - a market that accounts for a large proportion of the country's trade turnover.
One notable point in the Chinese government's report is the increase in the budget deficit target to "around 4%" of GDP. This is the highest level in the past 15 years, far exceeding the 2024 figure of 3%, and even higher than the 2020 pandemic-era level of 3.6%.
In particular, China also launched a plan to issue 1.3 trillion yuan (CNY) of super-long-term special government bonds in 2025, 30% higher than last year. In addition, a support package worth 500 billion CNY provided to large state-owned commercial banks to increase lending.

Thus, Beijing's policy is to loosen fiscal policy, "more proactively" and monetary policy "appropriately loose". The Chinese government also pledged to "timely cut" both interest rates and banks' reserve requirement ratios.
Money will be pumped into the economy aggressively to boost growth.
However, the inflation target was set to fall to “around 2%” – the lowest in more than two decades and significantly lower than the above 3% of previous years. It reflects weak domestic demand and gives Beijing room to pump more money into infrastructure projects, support businesses and boost household consumption.
Stabilizing the property market, which accounts for nearly a third of China’s economy, has been a priority. After years of crisis with a housing surplus and falling prices, China has rolled out supportive policies such as cutting mortgage interest rates and pumping capital into property developers.
However, the root problem lies in the fact that consumer confidence among businesses and people remains low, and the yuan weakens...
Diversify markets, focus on technology
In addition to imposing retaliatory tariffs, adding 15% to some US goods from March 10 and putting some US businesses on the unreliable entity list,... Beijing is stepping up its efforts to diversify its export markets.
In response, China has strengthened cooperation with Asian, African and European countries, and promoted the “Belt and Road” initiative to expand its consumer market.
For example, China has pledged to support export insurance and increase trade with countries not affected by Mr. Trump’s protectionist policies. This not only helps to offset some of the damage from the US market but also strengthens Beijing’s geopolitical position. However, trade barriers from the EU (such as high tariffs of up to 35% on Chinese EVs, etc.) or Indonesia show that this path is not easy.
In addition, China is also promoting technological autonomy to reduce dependence on the US in strategic areas such as semiconductors and artificial intelligence (AI).
China's stock market has recently rebounded after a rare meeting between President Xi Jinping and some of the country's top tech entrepreneurs last month, including Alibaba's Jack Ma and AI DeepSeek's Liang Wenfeng... The country is betting on technology as a long-term savior.
However, if Mr. Trump continues to impose tariffs of up to 60% as threatened, Chinese exports could fall sharply and could cause China's GDP growth to lose 0.5-1%, forcing China to balance short-term stimulus with long-term investment, not to mention facing the risk of trade retaliation from other partners.

Source: https://vietnamnet.vn/ung-pho-muc-thue-rat-cao-cua-donald-trump-trung-quoc-dat-cuoc-vao-van-bai-moi-2377869.html



![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Mr. Jefferey Perlman, CEO of Warburg Pincus Group (USA)](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/18/c37781eeb50342f09d8fe6841db2426c)





















































































Comment (0)