TPO - The James Webb Space Telescope has discovered a supernova dating back just 1.8 billion years after the Big Bang, as well as 80 other supernovae in the early universe. These ancient explosions could help scientists uncover the mysteries of how the universe evolved.
 |
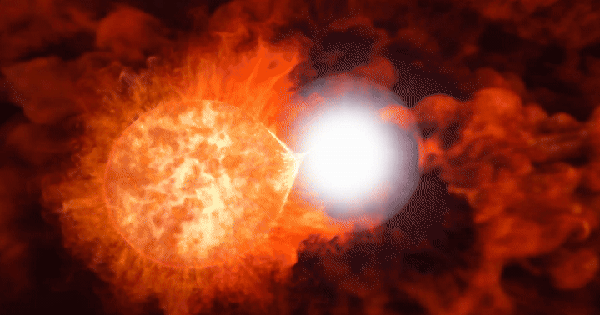
Illustration |
It is the oldest and most distant supernova ever discovered - a stellar explosion that occurred when the universe was just 1.8 billion years old.
Supernovae are transient objects because their brightness varies over time. This makes the new series of distant stellar explosions particularly interesting, as studying them could provide important insights into unanswered questions about how the early universe evolved.
“We’re essentially opening a new window on the temporal universe,” said Matthew Siebert, an astronomer who is leading the spectroscopic analysis of the supernovae. “Historically, whenever we’ve done this, we’ve found incredibly interesting things — things we didn’t expect.”
There are two main types of supernovae: core collapse and thermonuclear runaway supernovae.
Explosions of the first type occur when stars at least eight times more massive than the Sun run out of fuel and collapse in on themselves before expanding outward again in a giant explosion.
According to Live Science
Source: https://tienphong.vn/phat-hien-sieu-tan-tinh-xa-nhat-tu-truoc-toi-gio-post1646635.tpo


![[Photo] Warm meeting between the two First Ladies of the Prime Ministers of Vietnam and Ethiopia with visually impaired students of Nguyen Dinh Chieu School](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/b1a43ba73eb94fea89034e458154f7ae)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives Lao Prime Minister Sonexay Siphandone](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/337e313bae4b4961890fdf834d3fcdd5)
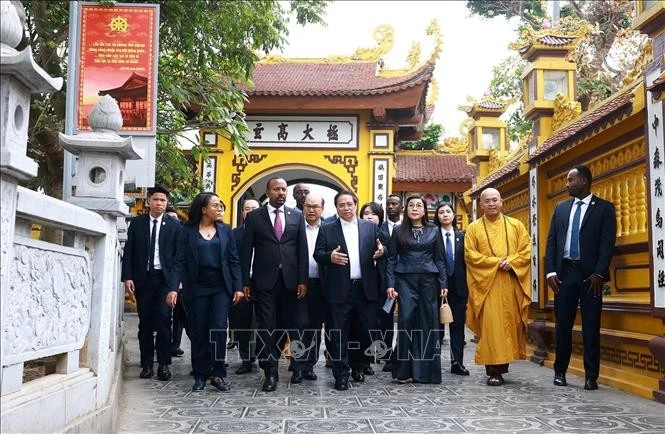
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh and Ethiopian Prime Minister visit Tran Quoc Pagoda](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/18ba6e1e73f94a618f5b5e9c1bd364a8)
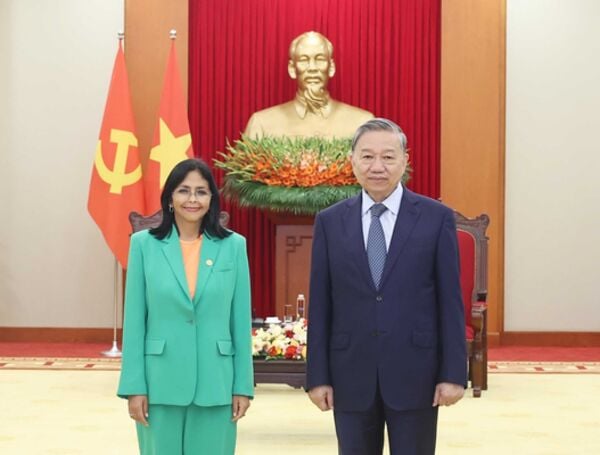
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives UN Deputy Secretary General Amina J.Mohammed](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/72781800ee294eeb8df59db53e80159f)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong receives Kenyan Defense Minister Soipan Tuya](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/0e7a5185e8144d73af91e67e03567f41)
![[Photo] Hundred-year-old pine trees – an attractive destination for tourists in Gia Lai](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/25a0b7b629294f3f89350e263863d6a3)























![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam attends conference to meet voters in Hanoi city](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/889ce3da77e04ccdb753878da71ded24)






















![[Video] Viettel officially puts into operation the largest submarine optical cable line in Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/17/f19008c6010c4a538cc422cb791ca0a1)










































Comment (0)