How General AI Works
The first challenge in teaching about general AI is that most people misunderstand what it actually means — so addressing those misconceptions is a top priority.
A common misconception is that general AI tools can be used the way search engines are: type in a question; get an answer. However, tools like ChatGPT are more properly thought of as storytellers, with a preference for plausible stories over facts.

A general approach to AI is essential for journalism students. Photo illustration: GI
This doesn’t mean that answers from general AI tools should be ignored, the way some people tell journalists not to use Wikipedia. It means that it is a source of information to be consulted, verified, and re-verified.
You can also compare the responses of chatbots like ChatGPT to a book or a movie “based on a true story”. You need to know which elements are real and which elements are added for dramatic effect.
Second, general AI tools are trained. This shapes the style and tone of the stories they tell, meaning that chatbots trained in China will have a different tone than chatbots trained in the US, and will introduce some bias.
For example, at the most basic level, most algorithms will be trained on more English text than other languages, as well as exposed to more Western images. Why? Because there are more documents in English than other languages (90% of them are in English for ChatGPT's GPT-3 model).
Another point to note about the training data is its up-to-dateness: ChatGPT's training data was only recently updated to 2021.
General AI Usage Rules
Plagiarism is one of the biggest concerns with ChatGPT and similar tools. Since these technologies can garble multiple sources of information, it can become an attractive option for cheaters.
But asking journalism students not to use ChatGPT is unreasonable, what is important is how to help them do it better and more correctly. Many universities around the world have started publishing guides on their websites on how to use tools like ChatGPT.
One of the more well-regarded applications of general AI is proofreading. For example, you can ask tools like ChatGPT to “tell me any errors I need to fix in this paragraph, explain what you changed and why?” That’s where AI comes in handy.
As journalists, we all know how much of a difference it makes when your work is well-edited. And it’s great if you have an editor who is willing to proofread, edit, and explain the changes they make.
How to ask questions and ethical issues
As AI becomes part of journalism, journalists will need to have the skills to work with AI tools, just as we did before we had to work with computers and the internet. AI is essentially a tool that will speed up and improve the work of journalists.

A composite image of female beauty created by AI software Midjourney with just a few prompts. Photo: Twitter/Nicolas Neubert
Tools like ChatGPT can help students grasp the basics of journalism, such as what readers want, style, format, and length. And just like Google, asking the right questions and using the right keywords are important when using general AI tools to find the right information.
Teaching the right questions also helps address ethical journalism issues. Journalists should be looking for clarity, through questions, so that AI models can provide the most accurate answers. Without the right questions, it is difficult to get the right answers.
FlowGPT is an AI application that has a database of questions that can be searched and used. Another journalistic ethics principle when using general AI is that we should also always remind chatbots to cite the sources they use and explain what they did and why?
Generate ideas for topics
Generative AI tools can also generate different ideas about a given topic. For example, a common mistake new reporters make is coming up with an idea to cover an issue, rather than a story. For example, “I’m going to write about homelessness” is not a good story.
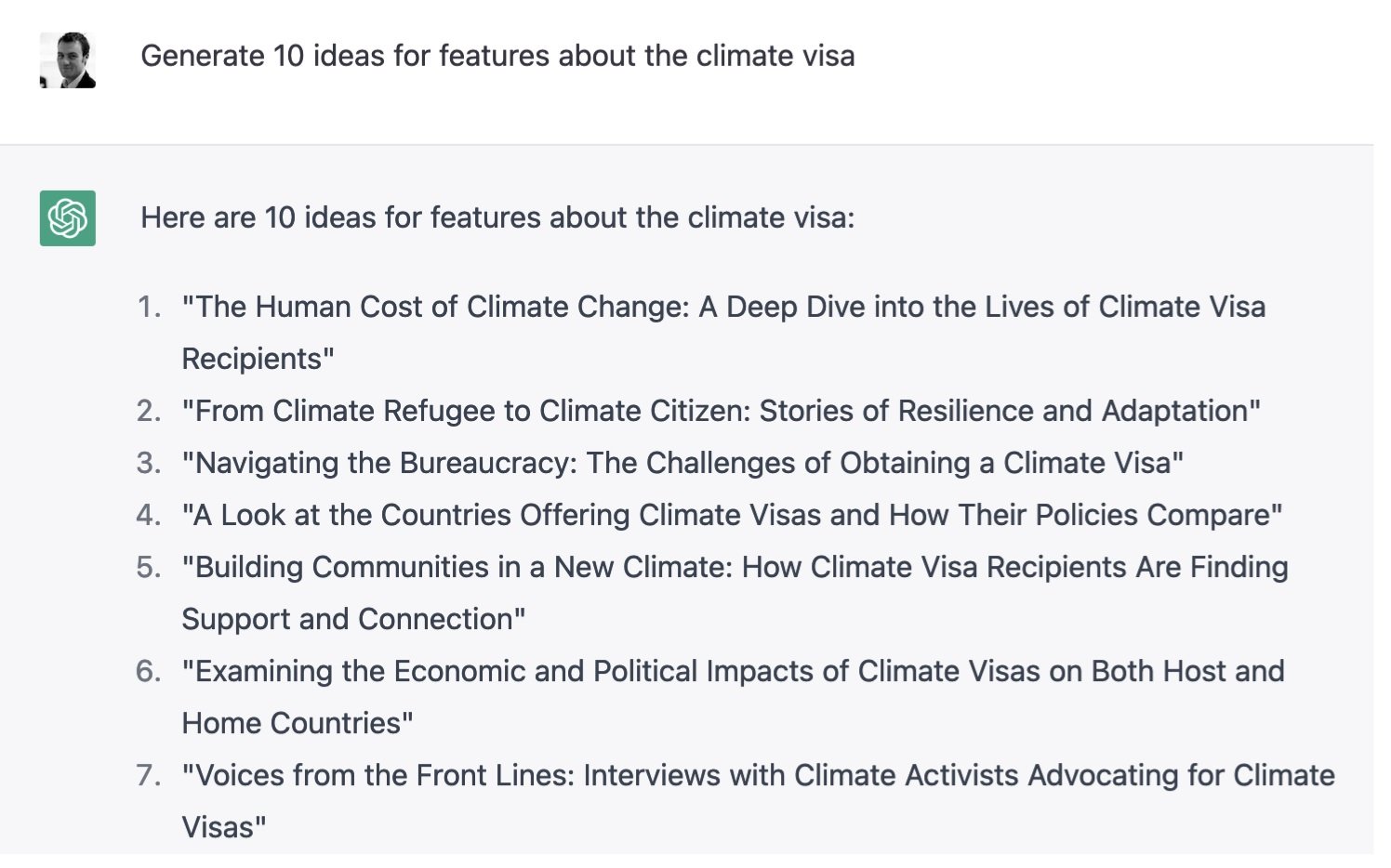
ChatGPT can provide suggestions that journalists can explore on a given topic. Photo: Twitter/Paul Bradshaw
However, tools like ChatGPT understand that feature stories need to have a clear angle and articles need to have something new going on, so asking it to generate ideas about an issue can help journalism students understand what a ‘feature idea’ really is.
Another useful suggestion is to ask what aspect of an issue might be relevant to a journalistic investigation or what aspect of an issue might be relevant to a news story. When asked to provide sources, generative AI models can suggest types of sources that journalism students might not have considered.
Summarize, filter and organize information
One of the most common ways people use general AI is as a tool to provide background information about a topic they need to understand. For example, ChatGPT can be used to explain different parts of a complex system to get a quick overview of it, so you can then dig deeper. AI tools can also be used to summarize long documents or reports.
AI's ability to filter and prioritize information also has obvious potential for journalists. Among other things, some AI tools also allow you to extract newsworthy information from press releases or scientific papers.
Finally, AI tools can automate the writing process. Specifically, a user can input a dataset and ask it to generate a story.
In all of these cases, it's important to remember that AI has the potential to hallucinate and make up things that aren't in your data. You'll have to figure out all the facts and check them.
Hoang Hai (according to OJB)
Source


![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)
![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)




















































































Comment (0)