US International research team completely decodes the sequence of the human Y chromosome, which is closely related to male development.
The work was conducted by the Telomere-to-Telomere Consortium (T2T), a group of experts from the National Genome Research Institute (NHGRI), US National Institutes of Health, and published in the journal Nature on August 23.
It is the last human chromosome to be fully sequenced, which could shed light on everything from fertility to risk of developing disease. Scientists have also identified 41 genes that make new proteins.
Researchers first completed the sequence of the human genome 20 years ago, but many chromosomes still have gaps. The gap on the Y chromosome is the largest.
The new study fills this large gap, which is more than 50% of the length of the Y chromosome. According to the study, although both the X and Y chromosomes play a central role in sexual development, the factors involved are complex and spread across the genome.
The Y chromosome is repetitive, which makes its sequencing particularly difficult. To explain, the study authors likened the Y chromosome to a book in which lines of text are repeated thousands or millions of times. This would make it difficult to sequence the contents. In the Y chromosome, about 30 million letters are repeated.
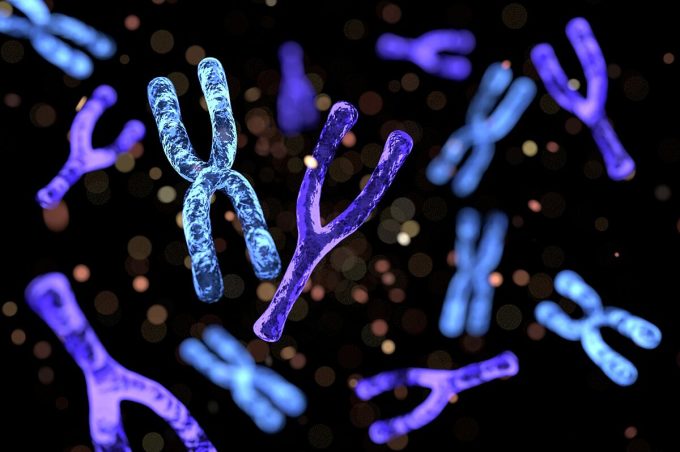
Illustration of X and Y chromosomes in the human body. Photo: IAI
The T2T Consortium applied new gene decoding technology and sequencing methods, along with the knowledge obtained from the remaining 23 chromosomes, to clarify the mysterious chromosome.
The study revealed information about the azoospermia region, a stretch of DNA that contains several genes involved in sperm production, affecting fertility. With the Y chromosome complete, scientists were able to more accurately analyze the DNA deletions and their effects on sperm.
The new technique also adds 30 million base pairs missing from the current Human Genome Project, bringing the total to 62,460,029 base pairs in the Y chromosome.
Other research shows that genes on the y chromosome contribute to many aspects of human biology, including cancer risk.
Thuc Linh (According to US News )
Source link




![[Photo] Closing of the 11th Conference of the 13th Central Committee of the Communist Party of Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/114b57fe6e9b4814a5ddfacf6dfe5b7f)

![[Photo] Overcoming all difficulties, speeding up construction progress of Hoa Binh Hydropower Plant Expansion Project](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/bff04b551e98484c84d74c8faa3526e0)








![[Video] First time in Vietnam: Successful implantation of 3rd generation partial artificial heart](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/12/8817412224094c68ba2c744b7bd5cfea)












































































Comment (0)