Artificial Intelligence
One of the most common applications of artificial intelligence (AI) in retail is demand forecasting. Algorithms have learned to understand what products customers like, as well as when and where they want to buy them. This allows stores to manage their supply chains, optimize inventory levels, and avoid markdowns.
The AI market in retail is expected to grow from $5.5 billion (in 2022) to more than $55.5 billion by 2030. Demand forecasting is so valuable that Nike acquired AI startup Celect for $110 million in 2019 to better understand its customers.
AI technology helps stores not only analyze demand, but also electronically order the necessary goods from suppliers. The store's information system communicates with the supplier's information system and prepares packages according to the required volume of products to be shipped.
Additionally, AI can even determine the optimal price for a product. Retail is a competitive business, and prices vary from store to store depending on a variety of factors. The algorithms themselves compare these prices and suggest their own options.
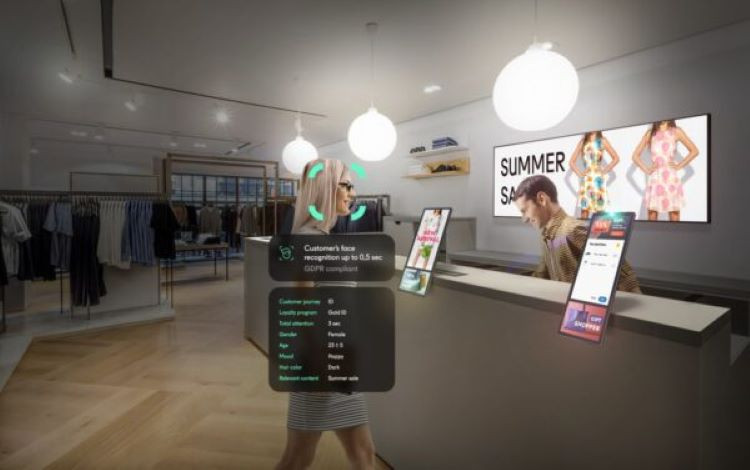

Biometric technology is also being introduced in shops. Smile recognition systems can allow you to withdraw money without a physical card. Biometrics are also being used extensively in banks and public transport, where you can pay with your face.
Video Analytics
While in-store camera use was once limited to security, today the retail industry uses computer vision technology for a variety of business needs, as simple as just controlling shelf displays.
According to the IHL Group (USA), the global retail industry loses 900 billion euros each year due to out-of-stock and untimely replenishment of products on display. The US retail chain Walmart solves this problem by attaching cameras to floor cleaning machines for store employees, then sending them to clean hallways and warehouses.
Cameras record shelf inventory and send the information to a data center, where AI analyzes shortages and decides on restocking. Such machines take more than 20 million photos of products on shelves every day.
Other retailers use a robotic scanner that moves down the aisles of a distribution center, scanning every pallet and helping to prevent out-of-stock situations. There are also cameras in the hallway, such as a video analytics system, that monitor the availability of products on the shelves and send signals to the manufacturing facility about how much product is left.
Computer vision is not only used in stores, but also in delivery trucks. Delivery trucks move around the clock, so it is important to monitor the driver's condition at any time of the day.
The Antison system (Russia) operates directly in the cabin and monitors whether the driver has fallen asleep at the wheel. If this happens, the system wakes the driver up and then informs the control center that the driver needs to stop and rest.
Video analytics helps monitor safety in stores, as well as service standards and procedures at checkout. If an incident suddenly occurs at the checkout, the system will immediately recognize it and notify the relevant department of the incident.
In addition, cameras monitor queues in the hall: the system notifies staff of crowds and gives a signal to quickly open an additional cash register. According to a study by Honeywell's Group in the UK, limiting long queues increases customer loyalty by 35%.

Cyber Security
In 2022, 67% of companies in Russia and the CIS in the retail sector reported experiencing threats of information leakage. The most common leaks concerned customer and transaction data (71%), financial information (41%), and technical documentation (21%). Such data sets are of great interest to cyber attackers.
Stores are often equipped with a large number of “smart” devices, making them easy targets for hackers. These threats are recorded and prevented by Information Security Incident Response and Monitoring Centers, whose main task is to maintain customer trust and protect their personal data.
Retailers’ serious approach to information security is a constant in their business processes, allowing stores to operate smoothly and attract customers. Customers know their data is protected and that the shelves will always have the products they need.
(according to RBK)
Source































































































Comment (0)