Many people often consider age spots as an 'obvious' skin condition when getting older, so they pay little attention. However, understanding age spots can also help prevent and control their development, and even predict dangerous skin diseases.
Age spots (brown spots) are flat or slightly raised pigmented lesions on the skin that occur in both men and women of all races and ages. Age spots are usually permanent and may increase in number with age or with increased sun exposure. Some spots on areas protected from the sun may fade and disappear.
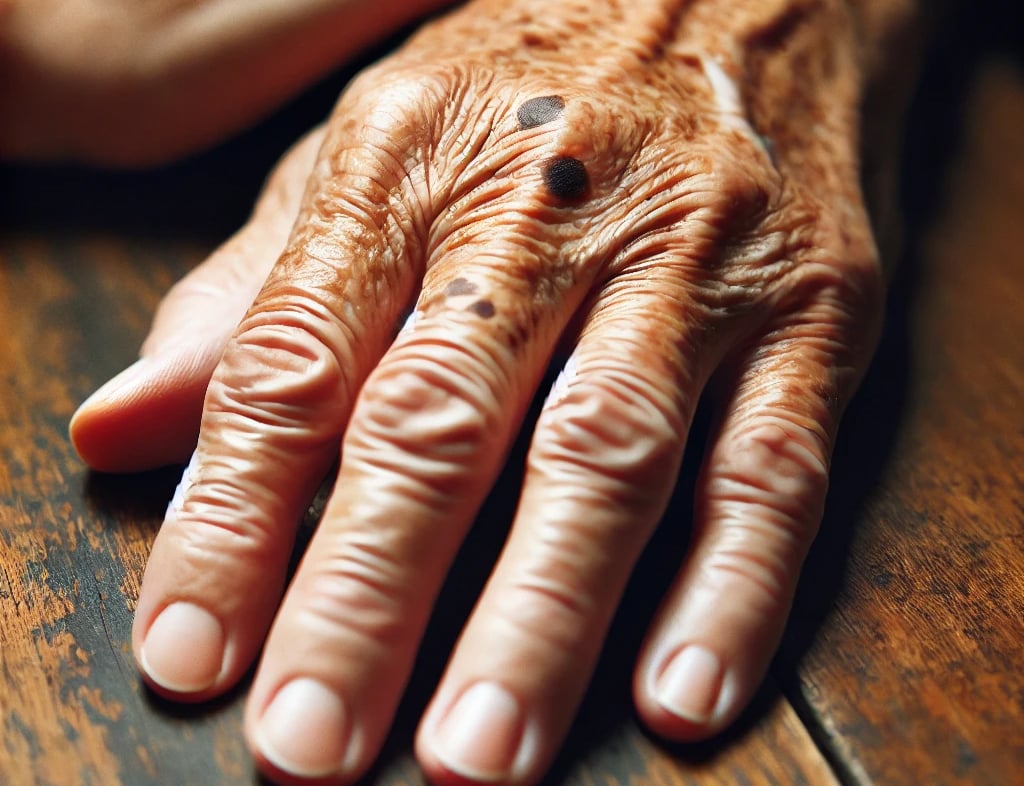
Age spots are often permanent and may increase in number with age.
Classify age spots, monitor closely to detect signs of skin cancer
According to Dr. Le Cao Tri, University of Medicine and Pharmacy Hospital, Ho Chi Minh City - Facility 3, the common types of freckles are:
Lentigo Simplex : Appears in the first few years of life and early adulthood; occurs on the trunk and extremities. Small, brown, round or oval macules or thin plaques, with regular or serrated borders, may have a dry surface and disappear over time.
Due to sunlight : Most common from middle age, appearing in areas exposed to sunlight for a long time such as the face, neck, shoulders, hands, forearms, and lower legs. Thin plaques or patches, yellow, light or dark brown, regular or irregular borders, may have a dry surface. Usually 5 mm in diameter, can spread to several centimeters or combine together. May disappear through lichenification. When in atypical form, it can be difficult to distinguish from melanoma in situ.
Ink spots : Less numerous than sun spots, appear after sunburn in people with very fair skin. Color is uneven, ranging from dark brown to black.
Post-PUVA (photochemotherapy) lentigo, skin darkening : Similar in appearance to ink-like brown spots, present anywhere exposed to PUVA, tanning beds.
Radiation dermatitis : Occurs at the site of radiation (accidental or iatrogenic). Associated with late-stage radiation dermatitis.
Melanotic macule : Found on mucosal or semi-mucosal surfaces such as the lips, vulva, penis, anus, light brown to dark brown.
Lentigo is associated with other organ abnormalities : Cluster type (associated with neurological abnormalities, mental development); patterned type; central lentigines of the face, neurological abnormalities (associated with intellectual disability); lentigines associated with genetic syndromes...
“Any change in the shape, color, or size of a mole compared to the original can be a sign of a serious abnormality such as skin cancer. For example: rapid increase in size, uneven color, multiple colors, uneven edges, bleeding, or pain,” said Dr. Cao Tri.
Therefore, people with age spots need to have certain knowledge and not be subjective with the appearance or changes of age spots all over the body to promptly visit and receive treatment at a reputable medical facility.
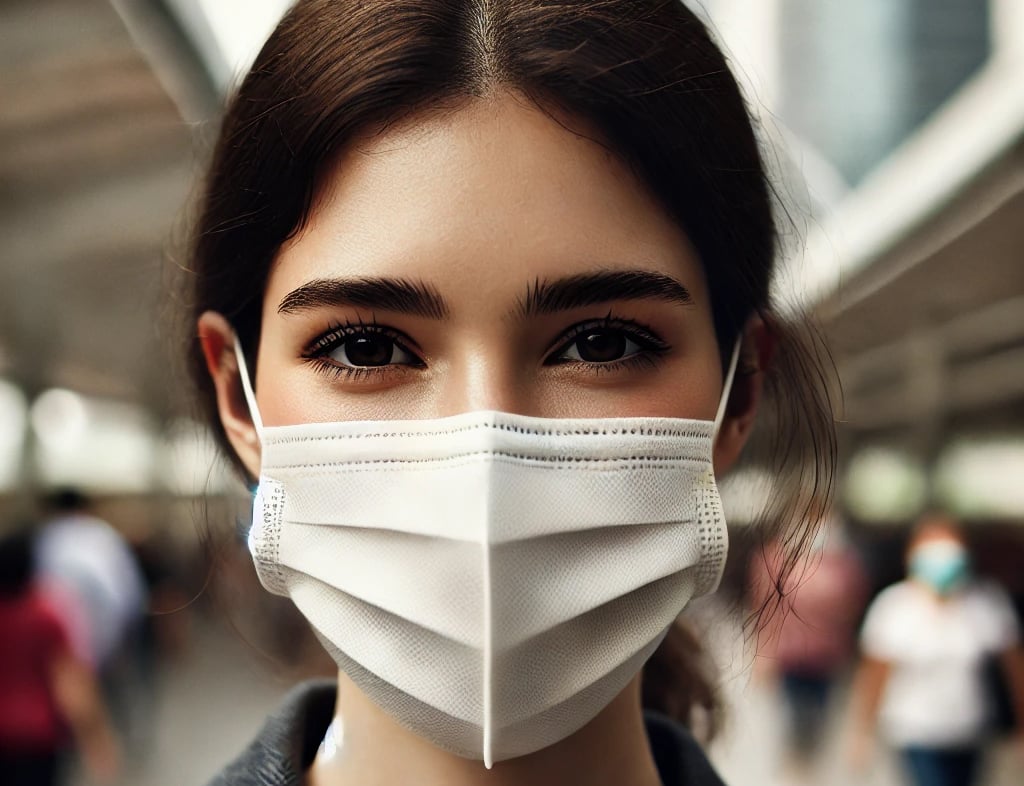

When going out, especially between 10am and 4pm - wear a mask, long pants, long-sleeved shirts, gloves, dark socks, wide-brimmed hats, sunglasses...
How to limit recurrence and prevent new freckles?
Brown spots related to UV exposure can be prevented by carefully protecting the skin from the sun.
According to Dr. Tri, physical protection with clothing, hats, sunglasses, etc. is more effective in preventing new age spots than sunscreen. You should limit sun exposure; when going out from 6am to 6pm - especially from 10am to 4pm - you should use a mask, long pants, long-sleeved shirts, gloves, dark socks, wide-brimmed hats, and sunglasses.
In addition, you should use sunscreen 30 minutes before going out in the sun, apply a broad spectrum type, physical sunscreen ingredients such as titanium dioxide, zinc oxide (less risk of skin irritation than chemical sunscreen). Choose a sunscreen with a sun protection factor (SPF) of 30 or higher, apply enough dose and reapply every 2 hours or more often if swimming or sweating a lot.
How to treat age spots?
According to Dr. Le Cao Tri, age spots usually do not affect health, but cause loss of aesthetics and lack of confidence when communicating. Treatment can fade or remove age spots; however, any treatment method has the risk of complications or side effects, patients need to be examined and treated by a dermatologist to limit the risk. Specific treatment methods include:
- Topical medications: Occasionally cause skin irritation at the site of application.
- Chemical peels: Risk of scarring or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation if performed incorrectly.
- Cryotherapy: Using liquid nitrogen.
- IPL: Uses intense pulsed light.
- Pigment laser: Most effective, using selective photothermal lysis technology to break down melanin pigment particles without damaging surrounding tissue.
“After treatment procedures, patients need to avoid the sun as much as possible and take gentle, proper care of their skin according to the instructions of their doctor,” Dr. Tri added.
Source: https://thanhnien.vn/doi-moi-tren-da-co-that-su-vo-hai-185250221233953774.htm


![[Photo] Opening of the Exhibition on Green Growth](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/253372a4bb6e4138b6f308bc5c63fd51)

![[Photo] The 9th Vietnam-China Border Defense Friendship Exchange](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/10e73e2e0b344c0888ad6df3909b8cca)
![[Photo] President Luong Cuong meets 100 typical examples of the Deeds of Kindness Program](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/ce8300edfa7e4afbb3d6da8f2172d580)
![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh receives Cambodian Deputy Prime Minister Neth Savoeun](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/e3dc78ec4b844a7385f6984f1df10e7b)
![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam gave a speech at the National Conference to disseminate the Resolution of the 11th Central Conference, 13th tenure.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/04e0587ea84b43588d2c96614d672a9c)

























































































Comment (0)