Lymphedema, infection, hematoma, keloid scarring… are complications that can occur when treating skin cancer.
Skin cancer is common and can be cured in its early stages. Complications often arise when the cancer is not diagnosed or treated early enough to prevent it from spreading. There are three common types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma (the most dangerous type of cancer).
DNA damage from exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet (UV) rays is a common cause of skin cancer. It can also be caused by genetics, exposure to radiation, chemicals, etc. Below are the complications of the disease.
Increased or decreased pigmentation
Hyperpigmentation is caused by an excess of melanin (the brown pigment that gives skin its normal color) causing darker patches on the skin. Hypopigmentation is a loss of pigment in the skin, causing areas of skin to appear lighter than the overall skin tone. Both can occur in areas of skin that have been treated for cancer and usually do not return to normal.
Changes in skin firmness and texture
Melanoma that grows around nerves and has grown quite deep and very large may require surgery and adjuvant radiation therapy. After surgery, radiation is focused on the tumor site and the lymph nodes that drain the area to prevent the cancer from returning. This can result in skin that is tighter and harder, changes in blood vessels, and changes in the texture of the skin. These changes are often permanent.
Lymphedema
Lymphedema is swelling caused by fluid buildup when the lymphatic system is blocked and cannot drain. This often occurs when lymph nodes are damaged or removed. Skin cancer that has spread to the lymph nodes, or cancer cells that have grown so deep that they cause skin ulcers (broken skin), requiring surgical removal, can lead to lymphedema.
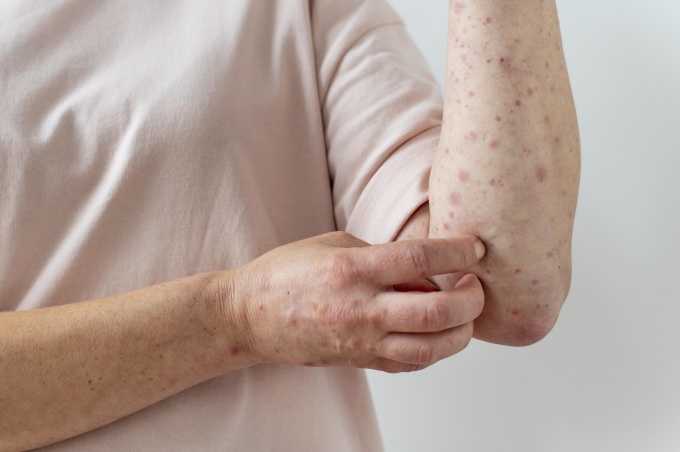
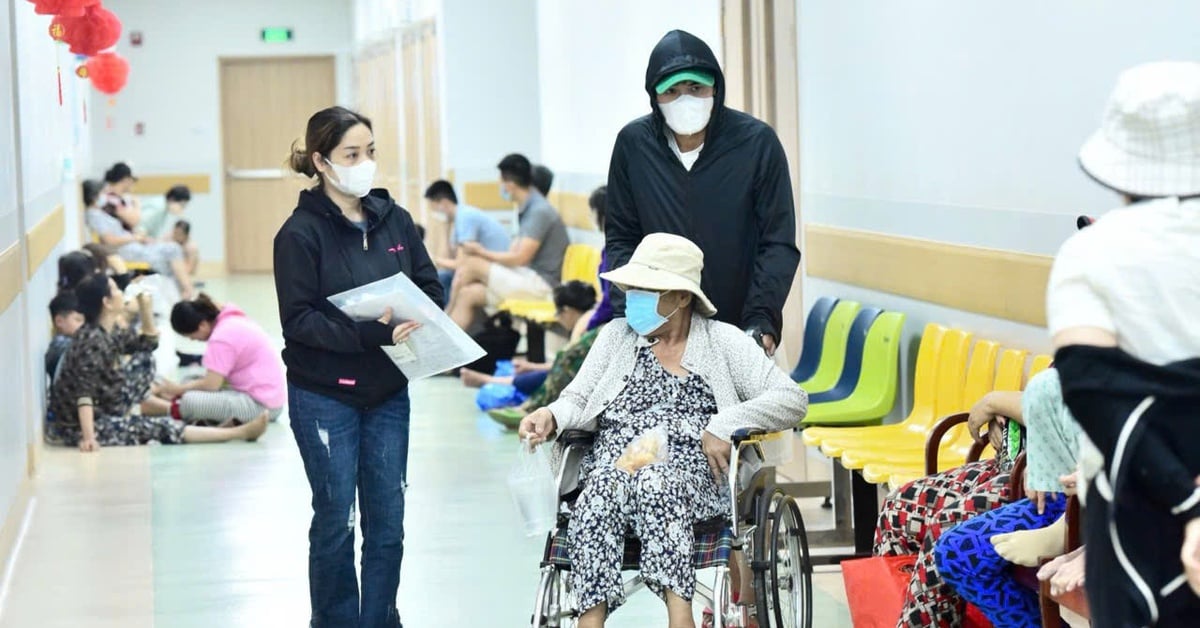
Too much exposure to sunlight or ultraviolet rays is a common cause of skin cancer. Photo: Freepik
Wound infection
Infection after skin cancer surgery can occur if the surgical wound is not properly cared for. Most surgical wound infections occur within 30 days of surgery. Symptoms of infection include pus draining from the wound, redness, pain, and warmth to the touch. Staph infections are the most common, usually in the nasal area.
Factors that increase the risk of infection after surgery include poorly controlled diabetes, immune disorders, being overweight or obese, smoking, using steroids, or having surgery that lasts longer than 2 hours. To reduce the risk of infection, you should wash your hands thoroughly before caring for the wound, avoid caring for the wound in the bathroom because many bacteria can live there, apply moisturizer after cleaning the surgical wound....
Congestion
A hematoma is bleeding under the skin that forms a mass and puts pressure on a wound. If the hematoma ruptures, it can cause infection and make healing difficult. Strenuous activities that cause too much impact on an unhealed wound can cause a hematoma. People who take blood thinners are at higher risk of this condition and should be especially careful.
Numbness and pain
Skin cancer patients may experience numbness, tingling, and pain due to nerve damage from surgery. These symptoms may improve over time.
Muscle, nerve and bone damage
Untreated melanoma can grow deep enough to affect muscles and bones. In this case, the doctor may have to surgically remove some nerves to remove the cancer, causing the patient to have post-surgical changes (disabilities) in the bones and muscles in the surgical area. These changes cannot be reversed.
Metastasis
Melanoma is more likely to metastasize than squamous cell or basal cell skin cancer. Melanoma can spread to the lymph nodes, lungs, liver, bones, and brain, causing pain, bleeding, and paralysis, and can be life-threatening.
Melanoma has a recurrence rate of less than 5% after lumpectomy because cancer cells may have spread to lymph nodes and tissues before surgery. Recurrent melanoma looks like dark or pink spots at or around the surgical site.
Scar
Scars left after skin cancer treatment depend on the growth of the tumor, the associated features, the degree of malignancy as well as the organ it attacks. The face, the area around the eyes, nose, lips, hands and feet, genitals, front of the lower legs are areas with a high risk of scarring.
Basal cell and squamous cell carcinomas can be treated with lasers, cryotherapy, topical creams, or photodynamic therapy. These treatments leave little scarring. Melanoma is usually treated with surgery, which often leaves more scars because the tumor is deeper in the skin than other skin cancers. The surgeon usually removes the tumor and some surrounding healthy tissue to prevent the cancer from recurring, which can leave large, raised scars. Surgical scars are usually harmless but can be unsightly.
Anxiety and depression
You may be anxious, stressed and depressed about the treatment or the cancer itself. However, patients should be calm and mentally prepared for the treatment plan. Skin cancer can be cured, even melanoma if detected early, treatment can prolong the prognosis.
Mai Cat (According to Everyday Health )
Source link


![[Photo] Opening of the National Conference to disseminate and implement the Resolution of the 11th Central Conference](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/e19da044c71d4330b6a03f49adcdb4f7)












![[Video] Reorganizing medical facilities according to the 2-tier local government model](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/d4d9f1a2fef14905ace8f70d53acf7f9)












![[Photo] Prime Minister Pham Minh Chinh holds talks with Ethiopian Prime Minister Abiy Ahmed Ali](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/15/4f7ba52301694c32aac39eab11cf70a4)
![[Photo] The two Prime Ministers witnessed the signing ceremony of cooperation documents between Vietnam and Ethiopia.](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/15/16e350289aec4a6ea74b93ee396ada21)














































![[Update] - Thanh Hoa: 55 thousand delegates attended the conference to disseminate and implement the Resolution of the 11th Conference of the 13th Party Central Committee](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/f1c6083279f5439c9412180dda016c15)









![[Photo] The capital of Binh Phuoc province enters the political season](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/16/c91c1540a5744f1a80970655929f4596)








Comment (0)