Women with hyperthyroidism may experience menstrual disorders, reduced fertility, and even infertility treatment.
Thyroid function is linked to hormones involved in reproduction such as estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. Thyroid hormones are essential for the normal functioning of the female reproductive system because they regulate the growth and metabolism of placental, uterine, and ovarian tissues.
An overactive thyroid gland, called hyperthyroidism, can cause early miscarriage; decreased fertility; premature birth; preeclampsia; failure of the ovaries to release eggs during menstruation; intellectual disability in children... or irregular menstruation. Studies show that 65% of people with hyperthyroidism have problems with their menstrual cycle and 22% have menstrual disorders. This is because hyperthyroidism causes the liver to produce more sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) protein. Increased levels of SHBG lead to irregular menstruation and infertility. Hyperthyroidism also increases the production of the hormone prolactin, which prevents the ovaries from releasing eggs, hindering the fertilization process.
This disorder makes it difficult to conceive and reduces the chance of getting pregnant. Some women with hyperthyroidism experience primary infertility, meaning they are unable to conceive the first time around; a small number experience secondary infertility, meaning they are unable to conceive after having had at least one previous pregnancy.
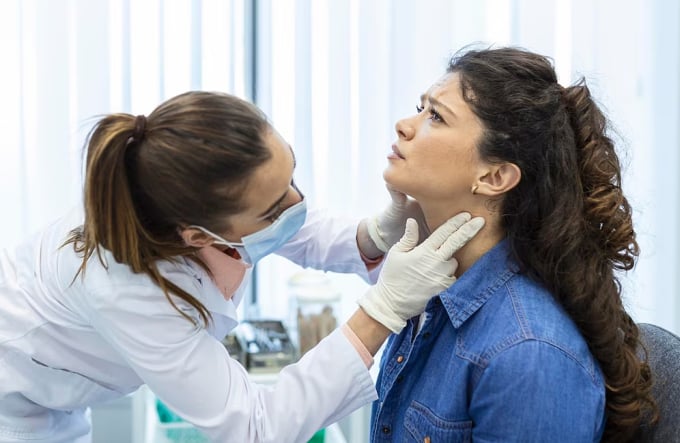
Hyperthyroidism not only affects health but also fertility. Photo: Freepik
Symptoms of hyperthyroidism include: irregular periods; diarrhea; rapid, irregular heartbeat; weight loss; muscle weakness; irritability or nervousness; difficulty sleeping, fatigue, or sweating. People with symptoms of hyperthyroidism should contact their doctor, as untreated hyperthyroidism can lead to serious complications.
To diagnose hyperthyroidism, the doctor may perform tests and thyroid ultrasound. To diagnose infertility in women with hyperthyroidism, the doctor needs to do a cervical smear; blood tests to measure hormone levels... To resolve infertility related to hyperthyroidism, the patient needs to treat this disease.
Surgery is a treatment option. The doctor will remove part of the thyroid gland, helping thyroid hormone levels return to normal. In addition, hyperthyroidism can also be treated with radioactive iodine. However, this therapy contributes to delayed pregnancy, irregular menstrual cycles and early menopause. Therefore, the doctor will advise the patient to avoid pregnancy for 6-12 months to avoid the risk of radiation affecting the eggs.
Most cases of infertility caused by hyperthyroidism can be successfully treated. To prevent hyperthyroidism, women should stop smoking; drink less alcohol; avoid iodine in certain foods (such as seaweed, supplements, and medications, including cough syrups, which can cause or worsen hyperthyroidism); exercise regularly, maintain a healthy lifestyle, and reduce stress.
Hai My ( According to Medical News Today )
Source link



![[Photo] General Secretary To Lam chairs the third meeting to review the implementation of Resolution No. 18-NQ/TW](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/10f646e55e8e4f3b8c9ae2e35705481d)
![[Photo] General Secretary and President of China Xi Jinping arrives in Hanoi, starting a State visit to Vietnam](https://vstatic.vietnam.vn/vietnam/resource/IMAGE/2025/4/14/9e05688222c3405cb096618cb152bfd1)
























































































Comment (0)